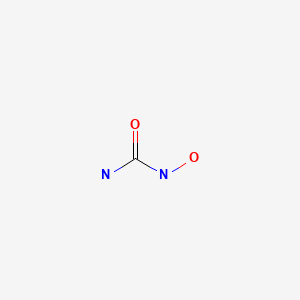
Hydroxycarbamide
"An antineoplastic agent that inhibits DNA synthesis through the inhibition of ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase." (MeSH 2013)
Found this page useful?
 Web Resources: Hydroxycarbamide
Web Resources: Hydroxycarbamide Recent Research Publications
Recent Research PublicationsWeb Resources: Hydroxycarbamide (6 links)
Cancer Research UK
Macmillan Cancer Support
NHS Evidence
MedlinePlus
 Hydroxyurea - Substance Summary
Hydroxyurea - Substance Summary
PubChem
 Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide, Hydrea)
Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide, Hydrea)
Irish Cancer Society
Recent Research Publications
Cuthbert D, Stein BL
Therapy-associated leukemic transformation in myeloproliferative neoplasms - What do we know?
Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2019; 32(1):65-73 [PubMed] Related Publications
Therapy-associated leukemic transformation in myeloproliferative neoplasms - What do we know?
Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2019; 32(1):65-73 [PubMed] Related Publications
Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNs) are a group of progressive diseases that share a common pathogenesis, clinical and laboratory features, as well as a spontaneous risk of secondary AML. Certain MPN therapies have been associated with an increased risk of leukemic conversion, with robust data highlighting the highest rates with
Demuynck T, Verhoef G, Delforge M, et al.
Polycythemia vera and hydroxyurea resistance/intolerance: a monocentric retrospective analysis.
Ann Hematol. 2019; 98(6):1421-1426 [PubMed] Related Publications
Polycythemia vera and hydroxyurea resistance/intolerance: a monocentric retrospective analysis.
Ann Hematol. 2019; 98(6):1421-1426 [PubMed] Related Publications
Hydroxyurea (HU) resistance or intolerance occurs in 15 to 24% of patients with polycythemia vera (PV). Resistance to HU is associated with a shortened life expectancy, intolerance has no prognostic value. We assessed the occurrence of HU resistance or intolerance comparing the original (ELNo) versus the modified European Leukemia Net (ELNm) criteria as applied in recent large clinical trials including PV patients. We retrospectively analyzed 106 patients with PV treated with HU at the University Hospitals of Leuven between 1990 and 2016 for occurrence of HU resistance/intolerance when using both ELNo as ELNm. After a mean duration of treatment of 5.1 years, when applying the ELNo 20.7% of patients had shown resistance or intolerance to HU in comparison to 39.6% when using the ELNm. When using the ELNo 4.7% of patients were resistant to HU versus 23.6% when applying the ELNm. In total, 16.0% of patients were HU intolerant. This rate was identical when using both ELNo and ELNm. 20.7% of PV patients were considered as HU-resistant or intolerant when using the original ELN criteria. However, when applying the modified ELN criteria 39.6% of PV patients were resistant or intolerant to HU. In our hands, no patient received a minimum dose of 2 g HU a day, as such the ELNm seem better adapted for daily clinical use. However, the prognostic value of HU-resistance in PV, when defined by the ELNm, still needs to be confirmed.
Melikyan AL, Subortseva IN, Gilyazitdinova EA, et al.
Cepeginterferon alfa-2b in the treatment of chronic myeloproliferative diseases.
Ter Arkh. 2018; 90(7):23-29 [PubMed] Related Publications
Cepeginterferon alfa-2b in the treatment of chronic myeloproliferative diseases.
Ter Arkh. 2018; 90(7):23-29 [PubMed] Related Publications
AIM: A comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of different therapeutic strategies in patients with polycythemia vera (PV) and essential thrombocythemia (ET).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Patients with PV or ET, diagnosed according to the criteria WHO 2016 were included in the study. The primary endpoint - 6 months of therapy (clinical-hematological and molecular responses). The secondary endpoint - 12 months of therapy (clinico-hematologic, molecular, histological responses). Sixty three patients were included in the analysis: the first group consisted of 33 patients who received the therapy with ce-pegiterferone alpha-2b (ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b), 10 of them received previous treatment; the second group - 23 patients btained hydroxycarbamide; the third group - 7 patients were treated with recombinant interferon alpha therapy (rINFα). In comparison groups, differences in age were revealed: patients receiving hydroxycarbamide therapy were older. Phlebotomy occurred in 36% of patients in the first group, 9% in the second group, and 14% in the third group.
RESULTS: By the 6th month of therapy, 43% of the patients receiving the ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b had complete clinical-hematologic response, 36% had partial clinical-hematologic remission and stabilization of the disease was established in 21% cases. No disease progression occured. By the 12th month of therapy, statistically significant differences in terms of efficacy between the different therapeutic groups (p = 0.2462, Fisher's exact test). In all three groups, the allelic load of JAK2V617F decreased: from 50 to 19%, from 22.3 to 15.8%, from 50 to 7.19%, respectively. The lower the allele load positively correlated with better response to therapy, which was observed in all analyzed groups. Hematologic adverse events (AEs) were more frequently observed in patients receiving ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b therapy. Local reactions developed on 3-7 days of therapy as a hyperemic macula at the injection site. Both these reactions and hair loss did not influence on patient's condition. In the second group (patients with hydroxycarbamide therapy) there were changes in the skin and mucous membranes: dry skin, stomatitis, and in older patients new keratomas appeared. The flu-like syndrome was the most common adverse event associated with the therapy of ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b, which fully relived during the first month of therapy. There was only one case with the flu-like syndrome we observed at the 11th month of therapy. As a rule, the biochemical blood test changes did not influence on patient's condition, were mostly associated with dietary violations, had a tendency to self-resolution and did not require medical interventions. Serious AEs were reported in one case - pulmonary embolism in a patient treated with rINFα. The reasons for the therapy discontinue in group 1: toxic hepatitis, intolerance, by the request of the patient, inadequate efficacy of therapy; in group 2: skin toxicity, in group 3: thromboses.
CONCLUSION: Treatment of ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b in patients with PV and ET is highly effective - the most patients pbtained clinical and hematological responses. There were no statistically significant differences in these parameters in comparison with hydroxycarbamide and rINFα. The use of the ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b had an acceptable safety profile. The estimated therapeutic dose should be calculated according to body weight. To reduce the frequency of hematologic AE, titration of the drug dose is required.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Patients with PV or ET, diagnosed according to the criteria WHO 2016 were included in the study. The primary endpoint - 6 months of therapy (clinical-hematological and molecular responses). The secondary endpoint - 12 months of therapy (clinico-hematologic, molecular, histological responses). Sixty three patients were included in the analysis: the first group consisted of 33 patients who received the therapy with ce-pegiterferone alpha-2b (ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b), 10 of them received previous treatment; the second group - 23 patients btained hydroxycarbamide; the third group - 7 patients were treated with recombinant interferon alpha therapy (rINFα). In comparison groups, differences in age were revealed: patients receiving hydroxycarbamide therapy were older. Phlebotomy occurred in 36% of patients in the first group, 9% in the second group, and 14% in the third group.
RESULTS: By the 6th month of therapy, 43% of the patients receiving the ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b had complete clinical-hematologic response, 36% had partial clinical-hematologic remission and stabilization of the disease was established in 21% cases. No disease progression occured. By the 12th month of therapy, statistically significant differences in terms of efficacy between the different therapeutic groups (p = 0.2462, Fisher's exact test). In all three groups, the allelic load of JAK2V617F decreased: from 50 to 19%, from 22.3 to 15.8%, from 50 to 7.19%, respectively. The lower the allele load positively correlated with better response to therapy, which was observed in all analyzed groups. Hematologic adverse events (AEs) were more frequently observed in patients receiving ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b therapy. Local reactions developed on 3-7 days of therapy as a hyperemic macula at the injection site. Both these reactions and hair loss did not influence on patient's condition. In the second group (patients with hydroxycarbamide therapy) there were changes in the skin and mucous membranes: dry skin, stomatitis, and in older patients new keratomas appeared. The flu-like syndrome was the most common adverse event associated with the therapy of ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b, which fully relived during the first month of therapy. There was only one case with the flu-like syndrome we observed at the 11th month of therapy. As a rule, the biochemical blood test changes did not influence on patient's condition, were mostly associated with dietary violations, had a tendency to self-resolution and did not require medical interventions. Serious AEs were reported in one case - pulmonary embolism in a patient treated with rINFα. The reasons for the therapy discontinue in group 1: toxic hepatitis, intolerance, by the request of the patient, inadequate efficacy of therapy; in group 2: skin toxicity, in group 3: thromboses.
CONCLUSION: Treatment of ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b in patients with PV and ET is highly effective - the most patients pbtained clinical and hematological responses. There were no statistically significant differences in these parameters in comparison with hydroxycarbamide and rINFα. The use of the ce-pegalpha-INF-α-2b had an acceptable safety profile. The estimated therapeutic dose should be calculated according to body weight. To reduce the frequency of hematologic AE, titration of the drug dose is required.
Dulíček P
Treatment of polycythemia vera.
Vnitr Lek. Fall 2018; 64(10):955-960 [PubMed] Related Publications
Treatment of polycythemia vera.
Vnitr Lek. Fall 2018; 64(10):955-960 [PubMed] Related Publications
Polycythemia vera is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by hematopoietic stem cell-derived clonal myeloproliferation resulting in erythrocytosis, leukocytosis and thrombocytosis. Survival is reduced compared with general population. Main reasons of death include thrombohemorrhagic complications, fibrotic progression and leuk-aemic transformation. Presence of Janus kinase (JAK2) gene mutations is a diagnostic marker and standard dia-gnostic criterion. World Health Organization 2016 diagnostic criteria focusing on hemoglobin levels, hematocrit, red cell mass and bone marrow morphology are mandatory. Therapeutic approach depends on stratification of patients according age and personal risk of thrombosis. Low-risk patients are treated first line with low-dose aspirin and phlebo-tomy. Cytoreduction is indicated in high-risk patients. Interferon-α has demonstrated efficacy in many clinical trials. Its pegylated form is well tolerated, enabling less frequent administration than standard interferon. Therefore it is therapy of choice based on Central European Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Organisation recommendation. Ropeginterferon α-2b has been shown to be more efficacious than hydroxyurea. Hydroxyurea is suspected of leukemogenic potential. JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor ruxolitinib is approved for hydroxyurea resistant/intolerant patients. Key words: diagnosis - polycythemia vera - therapy.
Pathak PK, Kumar A, Prasad BB
Functionalized nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots and bimetallic Au/Ag core-shell decorated imprinted polymer for electrochemical sensing of anticancerous hydroxyurea.
Biosens Bioelectron. 2019; 127:10-18 [PubMed] Related Publications
Functionalized nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots and bimetallic Au/Ag core-shell decorated imprinted polymer for electrochemical sensing of anticancerous hydroxyurea.
Biosens Bioelectron. 2019; 127:10-18 [PubMed] Related Publications
A novel molecularly imprinted polymer-capped acrylated nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots and bimetallic Au/Ag core-shell was synthesized to serve as a sensing nano-hybrid film for the detection of an anticancerous drug, hydroxyurea. This exploited the use of a functionalized nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots iniferter. This initiated the polymerization, following "surface grafting-from" approach, over the surface of a screen-printed carbon electrode to obtain requisite stability and selectivity of the measurement. Herein, nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots were prepared utilizing the degree of dehydration/carbonization of citric acid (carbon skeleton) and urea (nitrogen dopant) as source materials. This provided an efficient sensor platform anchoring bimetallic Au/Ag core-shell on its surface. The nano-assembly of acrylated nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots and bimetallic Au/Ag core-shell@imprinted polymer actually amplified the electrode kinetics by improving the diffusion coefficient (~20-fold) and electron-transfer kinetics (~5-fold), in comparison to the simple bimetallic Au/Ag core-shell decorated imprinted sensor. Under optimized conditions of differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetric transduction, a linear relationship between the current and the concentration was obtained in the range of 0.62-102.33 ng mL
Birgegård G, Folkvaljon F, Garmo H, et al.
Leukemic transformation and second cancers in 3649 patients with high-risk essential thrombocythemia in the EXELS study.
Leuk Res. 2018; 74:105-109 [PubMed] Related Publications
Leukemic transformation and second cancers in 3649 patients with high-risk essential thrombocythemia in the EXELS study.
Leuk Res. 2018; 74:105-109 [PubMed] Related Publications
EXELS, a post-marketing observational study, is the largest prospective study of high-risk essential thrombocythemia (ET) patients, with an observation time of 5 years. EXELS found higher event rates of acute leukemia transformation in patients treated with hydroxycarbamide (HC). In the current analysis, we report age-adjusted rates of malignant transformation from 3460 EXELS patients exposed to HC, anagrelide (ANA), or both. At registration, 481 patients had ANA treatment without HC exposure, 2305 had HC without ANA exposure, and 674 had been exposed to both. Standard incidence ratios (SIRs) were calculated using data from the Cancer Incidence in Five Continents database to account for differences in age-, gender-, and country-specific background rates. SIRs for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) were high in ET patients. SIRs for AML were high in HC-treated patients, but AML was rare in ANA-treated patients; no cases of AML were found in patients only treated with ANA. No statistically significant difference was seen between SIRs for ANA and HC treatment for AML or skin cancer. SIRs for other cancers were similar in the HC and ANA groups and close to 1, indicating little difference in risk. Although statistically inconclusive, this study strengthens concerns regarding possible leukemogenic risk with HC treatment. (NCT00202644).
Brusson M, De Grandis M, Cochet S, et al.
Impact of hydroxycarbamide and interferon-α on red cell adhesion and membrane protein expression in polycythemia vera.
Haematologica. 2018; 103(6):972-981 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Impact of hydroxycarbamide and interferon-α on red cell adhesion and membrane protein expression in polycythemia vera.
Haematologica. 2018; 103(6):972-981 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Polycythemia vera is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by the JAK2V617F mutation, elevated blood cell counts and a high risk of thrombosis. Although the red cell lineage is primarily affected by JAK2V617F, the impact of mutated JAK2 on circulating red blood cells is poorly documented. Recently, we showed that in polycythemia vera, erythrocytes had abnormal expression of several proteins including Lu/BCAM adhesion molecule and proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, mainly calreticulin and calnexin. Here we investigated the effects of hydroxycarbamide and interferon-α treatments on the expression of erythroid membrane proteins in a cohort of 53 patients. Surprisingly, while both drugs tended to normalize calreticulin expression, proteomics analysis showed that hydroxycarbamide deregulated the expression of 53 proteins in red cell ghosts, with overexpression and downregulation of 37 and 16 proteins, respectively. Within over-expressed proteins, hydroxycarbamide was found to enhance the expression of adhesion molecules such as Lu/BCAM and CD147, while interferon-α did not. In addition, we found that hydroxycarbamide increased Lu/BCAM phosphorylation and exacerbated red cell adhesion to its ligand laminin. Our study reveals unexpected adverse effects of hydroxycarbamide on red cell physiology in polycythemia vera and provides new insights into the effects of this molecule on gene regulation and protein recycling or maturation during erythroid differentiation. Furthermore, our study shows deregulation of Lu/BCAM and CD147 that are two ubiquitously expressed proteins linked to progression of solid tumors, paving the way for future studies to address the role of hydroxycarbamide in tissues other than blood cells in myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Korkmaz S
The management of hyperleukocytosis in 2017: Do we still need leukapheresis?
Transfus Apher Sci. 2018; 57(1):4-7 [PubMed] Related Publications
The management of hyperleukocytosis in 2017: Do we still need leukapheresis?
Transfus Apher Sci. 2018; 57(1):4-7 [PubMed] Related Publications
Hyperleukocytosis is defined as a white blood cell count greater than 100.000/μL in patients affected by acute or chronic leukemias. Hyperleukocytosis is more common in acute leukemias than in chronic leukemias. Risk factors include younger age, acute myeloid leukemia, the microgranular variant of acute promyelocytic leukemia, acute lymphoblastic leukemia and some cytogenetic abnormalities. Although it can affect any organ system, symptoms usually arise from involvement of the cerebral, pulmonary and renal microvasculature. The term "leukostasis" refers to 'symptomatic hyperleukocytosis' which is a medical emergency that needs prompt recognition and initiation of therapy to prevent renal and respiratory failure or intracranial haemorrhage. The underlying mechanisms of hyperleukocytosis and leukostasis are poorly understood. The management of hyperleukocytosis and leukostasis involves supportive measures and reducing the number of circulating leukemic blast cells by induction chemotherapy, hydroxyurea, low-dose chemotherapy, and leukapheresis. The measures such as hydroxyurea, low-dose chemotherapy, and leukapheresis shouldn't be considered to correct the laboratory abnormalities in patients with hyperleukocytosis who have no signs or symptoms. Also, neither hydroxyurea nore leukapheresis is able to show benefit on short and long term outcomes in patients with symptomatic hyperleukocytosis. The optimal management of symptomatic hyperleukocytosis is still uncertain, and there are no randomized studies demonstrating one is superior to each other. Therefore, it is recommended that intensive chemotherapy should be implemented as quickly as possible in treatment-eligible patients, in parallel with supportive measures for DIC and TLS.
Trepte ML, Auten JJ, Clark SM, van Deventer HW
Dose-related mucositis with hydroxyurea for cytoreduction in acute myeloid leukemia.
J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2019; 25(4):801-805 [PubMed] Related Publications
Dose-related mucositis with hydroxyurea for cytoreduction in acute myeloid leukemia.
J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2019; 25(4):801-805 [PubMed] Related Publications
Hyperleukocytosis occurs in 15-20% of all newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia patients and requires emergent treatment with leukapheresis or hydroxyurea when accompanied by signs or symptoms of leukostasis. Currently, there is no standardized hydroxyurea dosing strategy, although usual dosing ranges from 50 to 150 mg/kg/day, and prescribing patterns vary significantly among oncologists and institutions. In addition to other hematologic and dermatologic toxicities, the use of hydroxyurea may be associated with significant mucositis and mucositis-related pain. The purpose of this study was to compare mucositis-related pain between two different hydroxyurea dosing strategies in patients who received hydroxyurea for cytoreduction during induction. A retrospective chart review of adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia treated with chemotherapy at UNC Medical Center from April 2014 to April 2016 who received at least one dose of hydroxyurea for cytoreduction was conducted. This study compared the safety and toxicity profiles of hydroxyurea in patients who received high-dose hydroxyurea (≥75 mg/kg/day) versus low-dose hydroxyurea (<75 mg/kg/day). Safety and toxicity were evaluated based on indicators of mucositis and cumulative intravenous narcotic requirements following induction chemotherapy. Data collection included baseline demographics, mucositis risk factors, baseline laboratory values, hydroxyurea dosing, mucositis indicators, and pain indicators. A total of 55 patients were included in the study, 21 patients (38.2%) received the high-dose hydroxyurea dosing strategy. The high-dose hydroxyurea dosing strategy had a significantly higher white blood cell count at diagnosis, increased duration of hydroxyurea, and received a higher cumulative dose of hydroxyurea. Additionally, the high-dose hydroxyurea dosing strategy patients were associated with significantly more grade 3 or 4 mucositis requiring a formulation change (0% versus 28.6%, p = 0.002) and significantly higher cumulative intravenous narcotic requirements during induction (p = 0.019). No significant differences in baseline demographics or mucositis risk factors between dosing strategies were identified. The high-dose hydroxyurea dosing strategy patients had a significant increase in cumulative intravenous narcotic requirements and formulation changes, both common interventions made for the treatment of mucositis. Additional studies are needed to further elucidate the safety and toxicity profiles of hydroxyurea dosing strategies and to explore the correlation between total cumulative hydroxyurea dose and total cumulative narcotic requirements.
Neill B, Ryser T, Neill J, et al.
A patient case highlighting the myriad of cutaneous adverse effects of prolonged use of hydroxyurea.
Dermatol Online J. 2017; 23(11) [PubMed] Related Publications
A patient case highlighting the myriad of cutaneous adverse effects of prolonged use of hydroxyurea.
Dermatol Online J. 2017; 23(11) [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Hydroxyurea is an antimetabolite primarily used to treat myeloproliferative disorders, and chronic treatment is associated with many cutaneous adverse effects ranging in severity from ichthyosis to aggressive nonmelanoma skin cancer.
CASE PRESENTATION: We report a 67-year-oldman with a history of polycythemia vera who was referred for management of progressively worsening dorsal hand lesions. The patient presented withhyperpigmentation, ichthyosis, plantar keratoderma, dermatomyositis-like eruptions, two squamous cell carcinomas, and actinic keratoses. The adversereactions observed were acknowledged to be related to chronic hydroxyurea use. The patient underwent Mohs excision of the squamous cell carcinomas and thehydroxyurea was promptly discontinued; subsequent cutaneous improvement of the dermatomyositislike lesions ensued. Another clinically suspicious aggressive squamous cell carcinoma was suspected and the patient was referred to the plastic surgery department for complete excision because of the size of the lesion. The patient remains on periodic dermatology follow up.
CONCLUSIONS: We report a case that exemplifies the cutaneous adverse effects of chronic hydroxyurea therapy. Although many cases improve after drug discontinuation, strict photoprotection and ongoing surveillance are indicated given the recently proposed premalignant potential of dermatomyositis-like eruptions and the aggressive nature of hydroxyurea-induced nonmelanoma skin cancer.
CASE PRESENTATION: We report a 67-year-oldman with a history of polycythemia vera who was referred for management of progressively worsening dorsal hand lesions. The patient presented withhyperpigmentation, ichthyosis, plantar keratoderma, dermatomyositis-like eruptions, two squamous cell carcinomas, and actinic keratoses. The adversereactions observed were acknowledged to be related to chronic hydroxyurea use. The patient underwent Mohs excision of the squamous cell carcinomas and thehydroxyurea was promptly discontinued; subsequent cutaneous improvement of the dermatomyositislike lesions ensued. Another clinically suspicious aggressive squamous cell carcinoma was suspected and the patient was referred to the plastic surgery department for complete excision because of the size of the lesion. The patient remains on periodic dermatology follow up.
CONCLUSIONS: We report a case that exemplifies the cutaneous adverse effects of chronic hydroxyurea therapy. Although many cases improve after drug discontinuation, strict photoprotection and ongoing surveillance are indicated given the recently proposed premalignant potential of dermatomyositis-like eruptions and the aggressive nature of hydroxyurea-induced nonmelanoma skin cancer.
Parasuraman SV, Shi N, Paranagama DC, Bonafede M
Health Care Costs and Thromboembolic Events in Hydroxyurea-Treated Patients with Polycythemia Vera.
J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018; 24(1):47-55 [PubMed] Related Publications
Health Care Costs and Thromboembolic Events in Hydroxyurea-Treated Patients with Polycythemia Vera.
J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018; 24(1):47-55 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Patients with polycythemia vera (PV) are at increased risk of thromboembolic events (TEs), which are key contributors to reduced overall survival compared with the age- and sex-matched general population. In addition to aspirin and phlebotomy to maintain hematocrit level < 45%, many patients receive cytoreduction with hydroxyurea (HU), which is associated with improved survival and may reduce the risk of cardiovascular events and TEs. However, 1 in 4 patients become resistant to or intolerant of HU. In the general population, prophylaxis and treatment following arterial and venous thromboses are associated with increased health care resource utilization and costs.
OBJECTIVE: To describe the health care resource utilization and costs associated with TEs in patients with PV treated with HU in the United States.
METHODS: This retrospective cross-sectional analysis of the Truven Health Analytics MarketScan Research Databases included adult patients with a PV diagnosis who were newly treated with HU and continuously enrolled in medical and pharmacy benefit plans for ≥ 12 months pre- and post-index. HU treatment administration, persistence, adherence, and related adverse events, as well as TEs, were reported during the 12-month follow-up period. HU treatment patterns were further analyzed in a subgroup analysis comparing patients with and without a ≥ 45-day gap in HU treatment. Health care resource utilization and costs were analyzed in a subgroup analysis comparing patients who had TEs in the 12-month follow-up period with those who did not. Tests for statistically significant differences across the comparison groups were conducted, including chi-square tests for categorical variables and t-tests for continuous variables.
RESULTS: The records of 1,322 patients with PV were included in this study. Mean age was 66.0 years; 51.3% were men; and 14.0% had a history of TEs. During the first year of HU treatment, 764 (57.8%) patients had a treatment gap of ≥ 45 days; however, treatment adherence was similar between those with and those without a gap (85.2% vs. 90.7%, respectively). TEs occurred in 216 (16.3%) patients within 12 months of HU initiation. Health care resource utilization was higher for patients with TEs versus those without, including the proportion of patients requiring inpatient services (50.9% vs. 18.4%; P < 0.001) and emergency room visits (48.1% vs. 26.3%; P < 0.001) and the mean number of inpatient admissions (1.7 vs. 1.3; P = 0.004); office visits (18.9 vs. 14.1; P < 0.001); and prescriptions (45.8 vs. 36.2; P<0.001). In addition, total mean health care costs ($45,040 vs. $16,438; P < 0.001); inpatient costs ($18,952 vs. $4,794; P < 0.001); outpatient costs ($20,844 vs. $8,046; P < 0.001); and outpatient pharmacy costs ($5,244 vs. $3,598; P = 0.002) were higher among patients with TEs than those without.
CONCLUSIONS: Patients with PV receiving treatment with HU remain at risk for TEs. The occurrence of TEs during the 12-month follow-up in this patient population was associated with higher health care resource utilization and costs.
DISCLOSURES: This study was funded by Incyte Corporation. Parasuraman and Paranagama are employees and stockholders of Incyte Corporation. Shi and Bonafede are employees of Truven Health Analytics, which was awarded a research contract to conduct this study with and on behalf of Incyte Corporation. Study concept and design were contributed by all of the authors, who also interpreted the data and wrote and revised the manuscript. Bonafede and Shi collected the data. This study was presented as an abstract at the Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy NEXUS Annual Meeting on October 26-29, 2015, in Orlando, Florida.
OBJECTIVE: To describe the health care resource utilization and costs associated with TEs in patients with PV treated with HU in the United States.
METHODS: This retrospective cross-sectional analysis of the Truven Health Analytics MarketScan Research Databases included adult patients with a PV diagnosis who were newly treated with HU and continuously enrolled in medical and pharmacy benefit plans for ≥ 12 months pre- and post-index. HU treatment administration, persistence, adherence, and related adverse events, as well as TEs, were reported during the 12-month follow-up period. HU treatment patterns were further analyzed in a subgroup analysis comparing patients with and without a ≥ 45-day gap in HU treatment. Health care resource utilization and costs were analyzed in a subgroup analysis comparing patients who had TEs in the 12-month follow-up period with those who did not. Tests for statistically significant differences across the comparison groups were conducted, including chi-square tests for categorical variables and t-tests for continuous variables.
RESULTS: The records of 1,322 patients with PV were included in this study. Mean age was 66.0 years; 51.3% were men; and 14.0% had a history of TEs. During the first year of HU treatment, 764 (57.8%) patients had a treatment gap of ≥ 45 days; however, treatment adherence was similar between those with and those without a gap (85.2% vs. 90.7%, respectively). TEs occurred in 216 (16.3%) patients within 12 months of HU initiation. Health care resource utilization was higher for patients with TEs versus those without, including the proportion of patients requiring inpatient services (50.9% vs. 18.4%; P < 0.001) and emergency room visits (48.1% vs. 26.3%; P < 0.001) and the mean number of inpatient admissions (1.7 vs. 1.3; P = 0.004); office visits (18.9 vs. 14.1; P < 0.001); and prescriptions (45.8 vs. 36.2; P<0.001). In addition, total mean health care costs ($45,040 vs. $16,438; P < 0.001); inpatient costs ($18,952 vs. $4,794; P < 0.001); outpatient costs ($20,844 vs. $8,046; P < 0.001); and outpatient pharmacy costs ($5,244 vs. $3,598; P = 0.002) were higher among patients with TEs than those without.
CONCLUSIONS: Patients with PV receiving treatment with HU remain at risk for TEs. The occurrence of TEs during the 12-month follow-up in this patient population was associated with higher health care resource utilization and costs.
DISCLOSURES: This study was funded by Incyte Corporation. Parasuraman and Paranagama are employees and stockholders of Incyte Corporation. Shi and Bonafede are employees of Truven Health Analytics, which was awarded a research contract to conduct this study with and on behalf of Incyte Corporation. Study concept and design were contributed by all of the authors, who also interpreted the data and wrote and revised the manuscript. Bonafede and Shi collected the data. This study was presented as an abstract at the Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy NEXUS Annual Meeting on October 26-29, 2015, in Orlando, Florida.
Kouzuki K, Umeda K, Saida S, et al.
Sudden Intracranial Hemorrhage in a Patient With Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase.
J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2018; 40(8):e553-e556 [PubMed] Related Publications
Sudden Intracranial Hemorrhage in a Patient With Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase.
J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2018; 40(8):e553-e556 [PubMed] Related Publications
A 16-year-old boy was incidentally found to have hyperleukocytosis during a school physical examination. He was diagnosed with atypical chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase. Although treatment with hydoxyurea was started, his white blood cell count increased and he eventually developed lethal intracranial hemorrhage. Although very rare, intracranial hemorrhage should be considered as a possible complication in patients with atypical chronic myeloid leukemia, even in chronic phase, if they have hyperleukocytosis and thrombocytopenia.
Bargagli E, Palazzi M, Perri F, et al.
Fibrotic Lung Toxicity Induced by Hydroxycarbamide.
In Vivo. 2017 Nov-Dec; 31(6):1221-1223 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Fibrotic Lung Toxicity Induced by Hydroxycarbamide.
In Vivo. 2017 Nov-Dec; 31(6):1221-1223 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
A patient treated for 4 months with hydroxycarbamide (hydroxyurea) for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia was admitted to hospital for recently developed severe dyspnea and acute respiratory failure. The computed tomographic scan of the chest showed diffuse ground glass opacities, some centrilobular low-density nodules (resembling hypersensitivity pneumonitis-like pattern), and minimal interstitial reticulation of the subpleural region. The analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid excluded infection, as did serological examinations. The patient was started on oxygen therapy and with relief of thrombocytopenia and suspected hemolytic anemia, hydroxyurea treatment was discontinued. The patient underwent steroid therapy, with a rapid progressive improvement of clinical and radiological features. As hydroxyurea is increasingly used for a number of systemic disorders, physicians must be aware of its potential lung toxicity, requiring immediate cessation of the treatment and empiric corticosteroid therapy.
Teng J, Hejazi S, Hiddingh L, et al.
Recycling drug screen repurposes hydroxyurea as a sensitizer of glioblastomas to temozolomide targeting de novo DNA synthesis, irrespective of molecular subtype.
Neuro Oncol. 2018; 20(5):642-654 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Recycling drug screen repurposes hydroxyurea as a sensitizer of glioblastomas to temozolomide targeting de novo DNA synthesis, irrespective of molecular subtype.
Neuro Oncol. 2018; 20(5):642-654 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Background: Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and most aggressive primary malignant brain tumor. Standard-of-care treatment involves maximal surgical resection of the tumor followed by radiation and chemotherapy (temozolomide [TMZ]). The 5-year survival rate of patients with GBM is <10%, a colossal failure that has been partially attributed to intrinsic and/or acquired resistance to TMZ through O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation status in the tumor.
Methods: A drug screening aimed at evaluating the potential recycling and repurposing of known drugs was conducted in TMZ-resistant GBM cell lines and primary cultures of newly diagnosed GBM with different MGMT promoter methylation status, phenotypic/genotypic background and subtype, and validated with sphere formation, cell migration assays, and quantitative invasive orthotopic in vivo models.
Results: We identified hydroxyurea (HU) to synergize with TMZ in GBM cells in culture and in vivo, irrespective of MGMT promoter methylation status, subtype, and/or stemness. HU acts specifically on the S-phase of the cell cycle by inhibiting the M2 unit of enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. Knockdown of this enzyme using RNA interference and other known chemical inhibitors exerted a similar effect to HU in combination with TMZ both in culture and in vivo.
Conclusions: We demonstrate preclinical efficacy of repurposing hydroxyurea in combination with TMZ for adjuvant GBM therapy. This combination benefit is of direct clinical interest given the extensive use of TMZ and the associated problems with TMZ-related resistance and treatment failure.
Methods: A drug screening aimed at evaluating the potential recycling and repurposing of known drugs was conducted in TMZ-resistant GBM cell lines and primary cultures of newly diagnosed GBM with different MGMT promoter methylation status, phenotypic/genotypic background and subtype, and validated with sphere formation, cell migration assays, and quantitative invasive orthotopic in vivo models.
Results: We identified hydroxyurea (HU) to synergize with TMZ in GBM cells in culture and in vivo, irrespective of MGMT promoter methylation status, subtype, and/or stemness. HU acts specifically on the S-phase of the cell cycle by inhibiting the M2 unit of enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. Knockdown of this enzyme using RNA interference and other known chemical inhibitors exerted a similar effect to HU in combination with TMZ both in culture and in vivo.
Conclusions: We demonstrate preclinical efficacy of repurposing hydroxyurea in combination with TMZ for adjuvant GBM therapy. This combination benefit is of direct clinical interest given the extensive use of TMZ and the associated problems with TMZ-related resistance and treatment failure.
Moyo TK, Savona MR
Therapy for Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia in a New Era.
Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2017; 12(5):468-477 [PubMed] Related Publications
Therapy for Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia in a New Era.
Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2017; 12(5):468-477 [PubMed] Related Publications
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is a myeloid malignancy which shares clinical and morphologic features of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) and is classified by the WHO as an MDS/MPN. The defining feature of CMML is clonal hematopoiesis that results in peripheral monocytosis. The benefit of early treatment is currently unclear, and treatment may be held until the disease exhibits accelerated blast counts or the patient becomes symptomatic. Optimal treatments for CMML are not well defined. Conventional treatments include hydroxyurea, cytarabine, and hypomethylating agents. However, all treatment options are limited and, with the exception of allogeneic stem cell transplantation, are considered palliative. As we continue to learn about the genomics of CMML and about arising therapeutic targets and those under active clinical investigation, the future therapy of CMML will likely improve considerably. Here, we review the data available for conventional therapies and highlight emerging therapeutic strategies.
Kirito K, Suzuki K, Miyamura K, et al.
Ruxolitinib is effective and safe in Japanese patients with hydroxyurea-resistant or hydroxyurea-intolerant polycythemia vera with splenomegaly.
Int J Hematol. 2018; 107(2):173-184 [PubMed] Related Publications
Ruxolitinib is effective and safe in Japanese patients with hydroxyurea-resistant or hydroxyurea-intolerant polycythemia vera with splenomegaly.
Int J Hematol. 2018; 107(2):173-184 [PubMed] Related Publications
Ruxolitinib, a potent JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, was found to be superior to the best available therapy (BAT) in controlling hematocrit, reducing splenomegaly, and improving symptoms in the phase 3 RESPONSE study of patients with polycythemia vera with splenomegaly who experienced an inadequate response to or adverse effects from hydroxyurea. We report findings from a subgroup analysis of Japanese patients in RESPONSE (n = 18). The composite response rate (hematocrit control and spleen response) was higher in patients receiving ruxolitinib (50.0%) than in those receiving BAT (8.3%). A total of 50.0% of patients randomized to ruxolitinib achieved a spleen response vs 8.3% of those receiving BAT; 100 and 33.3% of patients in the respective groups achieved hematocrit control, with mean hematocrit in ruxolitinib-treated patients remaining stable at < 45% throughout the study. Similarly, a higher proportion of ruxolitinib-treated patients achieved complete hematologic remission (33.3 vs 16.7%). Ruxolitinib also led to rapid improvements in pruritus. All responses with ruxolitinib were durable to week 80, and its safety profile was consistent with that in the overall study. These findings suggest that ruxolitinib is an effective and well-tolerated treatment option for Japanese patients with polycythemia vera with an inadequate response to or adverse effects from hydroxyurea.
Maffioli M, Mora B, Passamonti F
Polycythemia vera: from new, modified diagnostic criteria to new therapeutic approaches.
Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2017; 15(9):700-707 [PubMed] Related Publications
Polycythemia vera: from new, modified diagnostic criteria to new therapeutic approaches.
Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2017; 15(9):700-707 [PubMed] Related Publications
Polycythemia vera (PV) is a Philadelphia chromosome-negative chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm that is associated with a Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) mutation in most cases. The most recent update to the World Health Organization diagnostic criteria for PV was published in 2016. These were the modifications with the greatest effect: (1) lowering the hemoglobin threshold, allowing a diagnosis of PV at 16.5 g/dL in males and at 16.0 g/dL in females and (2) introducing a hematocrit cutoff (49% in males and 48% in females). Patients with PV who are older than 60 years or have had a previous thrombotic event are considered at high risk for thrombosis. Leukocytosis and a high allele burden are additional risk factors for thrombosis and myelofibrosis, respectively. After disease has progressed to post-polycythemia vera myelofibrosis (PPV-MF), survival must be assessed according to the recently developed Myelofibrosis Secondary to PV and ET-Prognostic Model (MYSEC-PM). This model is based on age at diagnosis, a hemoglobin level below 11 g/dL, a platelet count lower than 150 × 109/L, a percentage of circulating blasts of 3% or higher, a CALR-unmutated genotype, and the presence of constitutional symptoms. Therapy is based on phlebotomy to maintain the hematocrit below 45% and (if not contraindicated) aspirin. When a cytoreductive drug is necessary, hydroxyurea or interferon can be used as first-line therapy, although the demonstration of an advantage of interferon over hydroxyurea is still pending. In patients whose disease fails to respond to hydroxyurea, ruxolitinib is a safe and effective choice.
Tian Y, Liu G, Wang H, et al.
Valproic acid sensitizes breast cancer cells to hydroxyurea through inhibiting RPA2 hyperphosphorylation-mediated DNA repair pathway.
DNA Repair (Amst). 2017; 58:1-12 [PubMed] Related Publications
Valproic acid sensitizes breast cancer cells to hydroxyurea through inhibiting RPA2 hyperphosphorylation-mediated DNA repair pathway.
DNA Repair (Amst). 2017; 58:1-12 [PubMed] Related Publications
It was reported that valproic acid (VPA, a histone deacetylase inhibitor) can sensitize cancer cells to hydroxyurea (HU, a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor) for chemotherapy, although the mechanism of VPA-induced HU sensitization is unclear. In this study, we systematically characterized VPA-induced HU sensitization of breast cancer cells. Multiple breast cancer cell models were employed to investigate whether the safe concentration of 0.5mM VPA and 2mM HU can result in DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and impact cell survival. Furthermore, the underlying mechanism was explored through cell biology assays, including clonogenic survival, homologous recombination (HR) activity, immunoblot and immunofluorescence. We found that VPA and HU cooperatively suppressed cancer cell survival. VPA resulted in the accumulation of more DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in response to HU-induced replication arrest and was able to block HU-stimulated homologous recombination (HR) through inhibiting the activity of two key HR repair proteins by hyperphosphorylation of replication protein A2 (RPA2-p) and recombinase Rad51. However, apoptosis was not detected under this condition. In addition, the results from the survival fraction in the cells expressing defective RPA2-p showed that VPA disrupted the HU-induced RPA2-p-Rad51-mediated HR pathway. Importantly, these findings were further supported by analyzing primary-culture cells from the tissue of chemical carcinogen (DMBA)-induced breast cancer in rats. Thus, our data demonstrated that VPA and HU synergistically suppressed tumor cells via disturbing RPA2-p-mediated DNA repair pathway, which provides a new way for combining chemotherapeutic drugs to sensitize breast cancer cells.
Barbui T, Vannucchi AM, Finazzi G, et al.
A reappraisal of the benefit-risk profile of hydroxyurea in polycythemia vera: A propensity-matched study.
Am J Hematol. 2017; 92(11):1131-1136 [PubMed] Related Publications
A reappraisal of the benefit-risk profile of hydroxyurea in polycythemia vera: A propensity-matched study.
Am J Hematol. 2017; 92(11):1131-1136 [PubMed] Related Publications
The use of hydroxyurea (HU) as first line therapy in polycythemia vera (PV) has been criticized because no solid demonstration that this drug prevents thrombosis or prolongs survival has been so far produced. Here we present the outcomes of a large cohort of patients with PV included in the European Collaborative Low-dose Aspirin (ECLAP) study. We selected 1,042 patients who, during the follow-up, had received only phlebotomy (PHL) or HU to maintain the hematocrit level < 45%. To assure comparability, we conducted a propensity score matching analysis. The two groups (PHL n = 342 and HU n = 681) were well balanced for the parameters included in the propensity score (overall balance: χ
Saqlain N, Ahmed N
Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia, BCR-ABL1 Negative, in a 5-Month Baby - ARare Presentation.
J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2016; 26(11):103-105 [PubMed] Related Publications
Atypical Chronic Myeloid Leukemia, BCR-ABL1 Negative, in a 5-Month Baby - ARare Presentation.
J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2016; 26(11):103-105 [PubMed] Related Publications
Atypical chronic myeloid leukemia (aCML) is a neoplasm with poor prognosis, characterized by myeloid hyperplasia, dysmyelopoiesis and absence of BCR-ABL1 gene. Clinically, the disease course may be similar to chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), BCR-ABL1 positive. It presents in seventh to eighth decade of life with few cases of paediatric aCML being reported. Here, we report a case of aCMLin a 5-month baby who presented with massive splenomegaly. The diagnosis was in accordance with the WHO criteria established in 2008.
Hai X, Guo M, Gao C, Zhou J
Quantification of hydroxyurea in human plasma by HPLC-MS/MS and its application to pharmacokinetics in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia.
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017; 137:213-219 [PubMed] Related Publications
Quantification of hydroxyurea in human plasma by HPLC-MS/MS and its application to pharmacokinetics in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia.
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017; 137:213-219 [PubMed] Related Publications
Hydroxyurea (HU) has been used in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) and other myeloproliferative malignancies. Considering patient's wide variation in clinical response to HU, a new and simple liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method was developed and validated to monitor patients' compliance to treatment and investigate the pharmacokinetics of HU in patients with CML. Stable isotope labeled HU-
Gerds AT, Dao KH
Polycythemia Vera Management and Challenges in the Community Health Setting.
Oncology. 2017; 92(4):179-189 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Polycythemia Vera Management and Challenges in the Community Health Setting.
Oncology. 2017; 92(4):179-189 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Patients with polycythemia vera (PV) experience shortened survival, increased risk of thromboembolic and hemorrhagic events, and burdensome symptoms. For all patients with PV, treatment with aspirin and hematocrit control with phlebotomy are recommended. In addition, patients with high-risk status or poor hematocrit control benefit from cytoreductive therapy with hydroxyurea, although approximately 1 in 4 patients develops resistance or intolerance. For patients who are resistant to or intolerant of hydroxyurea, studies have shown that ruxolitinib, a Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor, provides hematocrit control, reduces spleen size, normalizes blood counts, and improves PV-related symptoms. For many patients, PV is managed in a community health setting, and it is important that community hematologists, oncologists, and internists are familiar with the contemporary management of PV to improve patient outcomes, including management for patients who present with unique health-care needs. This review provides an overview of current treatment options for patients with PV and discusses challenging circumstances encountered by community providers in the management of PV, including symptom assessment, identification of hydroxyurea resistance/intolerance, pregnancy, elective surgeries, concomitant immunosuppressants, and managing patients in areas with limited access to specialized hematologic care.
Mesa R, Vannucchi AM, Yacoub A, et al.
The efficacy and safety of continued hydroxycarbamide therapy versus switching to ruxolitinib in patients with polycythaemia vera: a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, symptom study (RELIEF).
Br J Haematol. 2017; 176(1):76-85 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
The efficacy and safety of continued hydroxycarbamide therapy versus switching to ruxolitinib in patients with polycythaemia vera: a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, symptom study (RELIEF).
Br J Haematol. 2017; 176(1):76-85 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
The randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, phase 3b RELIEF trial evaluated polycythaemia vera (PV)-related symptoms in patients who were well controlled with a stable dose of hydroxycarbamide (also termed hydroxyurea) but reported PV-related symptoms. Patients were randomized 1:1 to ruxolitinib 10 mg BID (n = 54) or hydroxycarbamide (prerandomization dose/schedule; n = 56); crossover to ruxolitinib was permitted after Week 16. The primary endpoint, ≥50% improvement from baseline in myeloproliferative neoplasm -symptom assessment form total symptom score cytokine symptom cluster (TSS-C; sum of tiredness, itching, muscle aches, night sweats, and sweats while awake) at Week 16, was achieved by 43·4% vs. 29·6% of ruxolitinib- and hydroxycarbamide-treated patients, respectively (odds ratio, 1·82; 95% confidence interval, 0·82-4·04; P = 0·139). The primary endpoint was achieved by 34% of a subgroup who maintained their hydroxycarbamide dose from baseline to Weeks 13-16. In a post hoc analysis, the primary endpoint was achieved by more patients with stable screening-to-baseline TSS-C scores (ratio ≤ 2) receiving ruxolitinib than hydroxycarbamide (47·4% vs. 25·0%; P = 0·0346). Ruxolitinib treatment after unblinding was associated with continued symptom score improvements. Adverse events were primarily grades 1/2 with no unexpected safety signals. Ruxolitinib was associated with a nonsignificant trend towards improved PV-related symptoms versus hydroxycarbamide, although an unexpectedly large proportion of patients who maintained their hydroxycarbamide dose reported symptom improvement.
Huang J, Wang L, Chen L, et al.
Changing Treatment May Affect the Predictive Ability of European Treatment Outcome Study Scoring for the Prognosis of Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.
Turk J Haematol. 2017; 34(1):10-15 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Changing Treatment May Affect the Predictive Ability of European Treatment Outcome Study Scoring for the Prognosis of Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.
Turk J Haematol. 2017; 34(1):10-15 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
OBJECTIVE: Previous studies compared the predictive ability of the European Treatment Outcome Study (EUTOS), Sokal, and Hasford scoring systems and demonstrated inconsistent findings with unknown reasons. This study was conducted to determine a useful scoring system to predict the prognosis of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and identify the probable factors that affect the scoring.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This is a retrospective cohort study. The predictive ability of EUTOS and the factors that affect scoring were analyzed in 234 Chinese chronic-phase CML patients treated with frontline imatinib, including a few patients temporarily administered hydroxyurea for cytoreduction before imatinib. Patients were stratified into different risk groups according to each scoring system to assess the treatment outcomes and the predictive ability of EUTOS scores between patients who received imatinib during the entire follow-up period and patients who received altered treatment because of intolerance, progression, and treatment failure.
RESULTS: Sixty-one (26.0%) patients received altered treatments during the follow-up. In the EUTOS low- and high-risk groups, the 5-year overall survival was 94.6% and 84.7% (p=0.011), 5-year event-free survival was 92.6% and 77.6% (p=0.001), and 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 95.3% and 82.4% (p=0.001), respectively. The predictive ability of EUTOS was better than that of the Sokal and Hasford scores (p=0.256, p=0.062, p=0.073) without statistical significance. All three scoring systems were valid in predicting early optimal response. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a high association between overall PFS and the EUTOS scores in the standard-dose imatinib group (p<0.001).
CONCLUSION: This study suggests that the EUTOS scoring system could predict the outcome of chronic-phase CML patients treated with standard-dose imatinib. Altered treatment is a crucial factor that affects the prognostic impact of EUTOS scoring. Achieving complete cytogenetic response at 18 months is an essential factor in predicting the prognosis of patients with CML.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This is a retrospective cohort study. The predictive ability of EUTOS and the factors that affect scoring were analyzed in 234 Chinese chronic-phase CML patients treated with frontline imatinib, including a few patients temporarily administered hydroxyurea for cytoreduction before imatinib. Patients were stratified into different risk groups according to each scoring system to assess the treatment outcomes and the predictive ability of EUTOS scores between patients who received imatinib during the entire follow-up period and patients who received altered treatment because of intolerance, progression, and treatment failure.
RESULTS: Sixty-one (26.0%) patients received altered treatments during the follow-up. In the EUTOS low- and high-risk groups, the 5-year overall survival was 94.6% and 84.7% (p=0.011), 5-year event-free survival was 92.6% and 77.6% (p=0.001), and 5-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 95.3% and 82.4% (p=0.001), respectively. The predictive ability of EUTOS was better than that of the Sokal and Hasford scores (p=0.256, p=0.062, p=0.073) without statistical significance. All three scoring systems were valid in predicting early optimal response. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a high association between overall PFS and the EUTOS scores in the standard-dose imatinib group (p<0.001).
CONCLUSION: This study suggests that the EUTOS scoring system could predict the outcome of chronic-phase CML patients treated with standard-dose imatinib. Altered treatment is a crucial factor that affects the prognostic impact of EUTOS scoring. Achieving complete cytogenetic response at 18 months is an essential factor in predicting the prognosis of patients with CML.
Alvarez-Larrán A, Pérez-Encinas M, Ferrer-Marín F, et al.
Risk of thrombosis according to need of phlebotomies in patients with polycythemia vera treated with hydroxyurea.
Haematologica. 2017; 102(1):103-109 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Risk of thrombosis according to need of phlebotomies in patients with polycythemia vera treated with hydroxyurea.
Haematologica. 2017; 102(1):103-109 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Hematocrit control below 45% is associated with a lower rate of thrombosis in polycythemia vera. In patients receiving hydroxyurea, this target can be achieved with hydroxyurea alone or with the combination of hydroxyurea plus phlebotomies. However, the clinical implications of phlebotomy requirement under hydroxyurea therapy are unknown. The aim of this study was to evaluate the need for additional phlebotomies during the first five years of hydroxyurea therapy in 533 patients with polycythemia vera. Patients requiring 3 or more phlebotomies per year (n=85, 16%) showed a worse hematocrit control than those requiring 2 or less phlebotomies per year (n=448, 84%). There were no significant differences between the two study groups regarding leukocyte and platelet counts. Patients requiring 3 or more phlebotomies per year received significantly higher doses of hydroxyurea than the remaining patients. A significant higher rate of thrombosis was found in patients treated with hydroxyurea plus 3 or more phlebotomies per year compared to hydroxyurea with 0-2 phlebotomies per year (20.5% vs. 5.3% at 3 years; P<0.0001). In multivariate analysis, independent risk factors for thrombosis were phlebotomy dependency (HR: 3.3, 95%CI: 1.5-6.9; P=0.002) and thrombosis at diagnosis (HR: 4.7, 95%CI: 2.3-9.8; P<0.0001). The proportion of patients fulfilling the European LeukemiaNet criteria of resistance/intolerance to hydroxyurea was significantly higher in the group requiring 3 or more phlebotomies per year (18.7% vs. 7.1%; P=0.001) mainly due to extrahematologic toxicity. In conclusion, phlebotomy requirement under hydroxyurea therapy identifies a subset of patients with increased proliferation of polycythemia vera and higher risk of thrombosis.
Iman M, Khansefid Z, Davood A
Modeling and Proposed Molecular Mechanism of Hydroxyurea Through Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulation to Curtail the Action of Ribonucleotide Reductase.
Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2016; 11(4):461-468 [PubMed] Related Publications
Modeling and Proposed Molecular Mechanism of Hydroxyurea Through Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulation to Curtail the Action of Ribonucleotide Reductase.
Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2016; 11(4):461-468 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Ribonucleotide Reductase (RNR) is an important anticancer chemotherapy target. It has main key role in DNA synthesis and cell growth. Therefore several RNR inhibitors, such as hydroxyurea, have entered the clinical trials. Based on our proposed mechanism, radical site of RNR protein reacts with hydroxyurea in which hydroxyurea is converted into its oxidized form compound III, and whereby the tyrosyl radical is converted into a normal tyrosine residue.
OBJECTIVE: In this study, docking and molecular dynamics simulations were used for proposed molecular mechanism of hydroxyurea in RNR inhibition as anticancer agent.
METHOD: The binding affinity of hydroxyurea and compound III to RNR was studied by docking method. The docking study was performed for the crystal structure of human RNR with the radical scavenger Hydroxyurea and its oxidized form to inhibit the human RNR. hydroxyurea and compound III bind at the active site with Tyr-176, which are essential for free radical formation. This helps to understand the functional aspects and also aids in the development of novel inhibitors for the human RNR2. To confirm the binding mode of inhibitors, the molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed using GROMACS 4.5.5, based upon the docked conformation of inhibitors.
RESULTS: Both of the studied compounds stayed in the active site. The results of MD simulations confirmed the binding mode of ligands, accuracy of docking and the reliability of active conformations which were obtained by AutoDock.
CONCLUSION: MD studies confirm our proposed mechanism in which compound III reacts with the active site residues specially Tyr-176, and inhibits the radical generation and subsequently inhibits the RNR enzyme.
OBJECTIVE: In this study, docking and molecular dynamics simulations were used for proposed molecular mechanism of hydroxyurea in RNR inhibition as anticancer agent.
METHOD: The binding affinity of hydroxyurea and compound III to RNR was studied by docking method. The docking study was performed for the crystal structure of human RNR with the radical scavenger Hydroxyurea and its oxidized form to inhibit the human RNR. hydroxyurea and compound III bind at the active site with Tyr-176, which are essential for free radical formation. This helps to understand the functional aspects and also aids in the development of novel inhibitors for the human RNR2. To confirm the binding mode of inhibitors, the molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed using GROMACS 4.5.5, based upon the docked conformation of inhibitors.
RESULTS: Both of the studied compounds stayed in the active site. The results of MD simulations confirmed the binding mode of ligands, accuracy of docking and the reliability of active conformations which were obtained by AutoDock.
CONCLUSION: MD studies confirm our proposed mechanism in which compound III reacts with the active site residues specially Tyr-176, and inhibits the radical generation and subsequently inhibits the RNR enzyme.
Hansen IO, Sørensen AL, Hasselbalch HC
Second malignancies in hydroxyurea and interferon-treated Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Eur J Haematol. 2017; 98(1):75-84 [PubMed] Related Publications
Second malignancies in hydroxyurea and interferon-treated Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Eur J Haematol. 2017; 98(1):75-84 [PubMed] Related Publications
OBJECTIVE: In an era of controversy in regard to 'hydroxyurea-leukaemogenicity' and when interferon-alfa2 (IFN) is being revived in the treatment of Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), we aim in this single-centre observational study to describe the frequencies of second malignancies in a cohort of MPN patients treated with hydroxyurea (HU) or IFN monotherapy or the combination of these agents.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Records of a MPN cohort of 196 patients were reviewed, and a retrospective analysis was performed on 90 patients treated with HU, 38 patients treated with IFN and 68 patients treated with both IFN and HU. Logistic regression was used to compare frequencies in second malignancies.
RESULTS: Patients treated with HU had a significantly higher risk of developing all second malignancies compared with patients treated with IFN [HU vs. IFN: OR of 4.01 (95%CI: 1.12-14.27, P-value: 0.023) and HU-IFN vs. IFN: OR 5.58 (95%CI: 1.55-20.15, P-value: 0.004)].
CONCLUSION: We have found an increased risk of second malignancies in MPN patients treated with HU compared with patients treated with IFN.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Records of a MPN cohort of 196 patients were reviewed, and a retrospective analysis was performed on 90 patients treated with HU, 38 patients treated with IFN and 68 patients treated with both IFN and HU. Logistic regression was used to compare frequencies in second malignancies.
RESULTS: Patients treated with HU had a significantly higher risk of developing all second malignancies compared with patients treated with IFN [HU vs. IFN: OR of 4.01 (95%CI: 1.12-14.27, P-value: 0.023) and HU-IFN vs. IFN: OR 5.58 (95%CI: 1.55-20.15, P-value: 0.004)].
CONCLUSION: We have found an increased risk of second malignancies in MPN patients treated with HU compared with patients treated with IFN.
Hundemer GL, Rosales IA, Chen YB, et al.
Hydroxyurea for Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome Associated With Polycythemia Vera.
Am J Kidney Dis. 2016; 68(3):465-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Hydroxyurea for Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome Associated With Polycythemia Vera.
Am J Kidney Dis. 2016; 68(3):465-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Myeloproliferative disorders are a rare cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), although the mechanism is unclear. Hydroxyurea is commonly used in these disorders for its cytoreductive properties; however, the effect of this treatment on proteinuria or kidney function remains unclear in cases of myeloproliferative disorder-associated FSGS. We describe the clinical course of a patient with polycythemia vera and nephrotic-range proteinuria, demonstrated to have FSGS on biopsy. The patient had a distant history of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's), for which he routinely had his kidney function and proteinuria measured, allowing for early detection of nephrotic syndrome soon after being diagnosed with polycythemia vera. Treatment with hydroxyurea resulted in rapid improvement in proteinuria that correlated with a decrease in hematocrit. This response was replicated 2 additional times when the patient was taken off and then restarted on hydroxyurea therapy. He now maintains a steady dose of hydroxyurea with favorable kidney measures (proteinuria with <1g/d of protein excretion and serum creatinine of 1.27mg/dL [corresponding to estimated glomerular filtration rate of 56mL/min/1.73 m(2)]). This case suggests that early screening and treatment for myeloproliferative disorder-associated FSGS may lead to improved long-standing kidney function.
Nazha A, Gerds AT
Where to Turn for Second-Line Cytoreduction After Hydroxyurea in Polycythemia Vera?
Oncologist. 2016; 21(4):475-80 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Where to Turn for Second-Line Cytoreduction After Hydroxyurea in Polycythemia Vera?
Oncologist. 2016; 21(4):475-80 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
UNLABELLED: The goals of therapy in patients with polycythemia vera (PV) are to improve disease-related symptoms, prevent the incidence or recurrence of thrombosis, and possibly delay or prevent the transformation into myelofibrosis or acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Cytoreductive therapies have been used in older patients and those with a history of thrombosis to achieve these goals. Hydroxyurea (HU) remains the first-line cytoreductive choice; however, up to one in four patients treated with HU over time will develop resistance or intolerance to HU. More importantly, patients who fail HU have a 5.6-fold increase in mortality and a 6.8-fold increase risk of transformation to myelofibrosis or AML; therefore, alternative therapies are needed for these patients. Interferon-α has been used in PV and has shown significant activity in achieving hematologic responses and decreasing JAK2 V617F mutation allele burden. JAK inhibition has also been investigated and recently garnered regulatory approval for this indication. In this review, we will discuss the current treatment options that are available for patients after HU and the novel therapies that are currently under investigation.
IMPLICATIONS FOR PRACTICE: The outcomes of PV patients who fail or who are intolerant of hydroxyurea are poor. Although pegylated interferon can be considered in younger patients, currently, ruxolitinib is the only U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved agent in this setting, representing a viable option, leading to hematocrit control and a reduction in spleen size and constitutional symptoms. Although a small number of patients will achieve a molecular response with continuous treatment, the implications of such response on the clinical outcomes are still unknown. Patients whose disease is not adequately controlled with ruxolitinib, or who lose their response, can be treated with low-dose busulfan or pipobroman; however, they should be encouraged to participate in trials with novel therapies.
IMPLICATIONS FOR PRACTICE: The outcomes of PV patients who fail or who are intolerant of hydroxyurea are poor. Although pegylated interferon can be considered in younger patients, currently, ruxolitinib is the only U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved agent in this setting, representing a viable option, leading to hematocrit control and a reduction in spleen size and constitutional symptoms. Although a small number of patients will achieve a molecular response with continuous treatment, the implications of such response on the clinical outcomes are still unknown. Patients whose disease is not adequately controlled with ruxolitinib, or who lose their response, can be treated with low-dose busulfan or pipobroman; however, they should be encouraged to participate in trials with novel therapies.
Staake MD, Kashinatham A, McMorris TC, et al.
Hydroxyurea derivatives of irofulven with improved antitumor efficacy.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016; 26(7):1836-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Hydroxyurea derivatives of irofulven with improved antitumor efficacy.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016; 26(7):1836-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Irofulven is a semi-synthetic derivative of Illudin S, a toxic sesquiterpene isolated from the mushroom Omphalotus illudens. Irofulven has displayed significant antitumor activity in various clinical trials but displayed a limited therapeutic index. A new derivative of irofulven was prepared by reacting hydroxyurea with irofulven under acidic conditions. Acetylation of this new compound with acetic anhydride produced a second derivative. Both of these new derivatives displayed significant antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo comparable to or exceeding that of irofulven.

 Haematological Malignancies & Realted Disorders
Haematological Malignancies & Realted Disorders