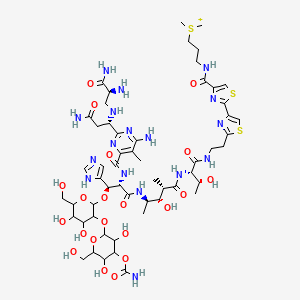
Bleomycin
"A complex of related glycopeptide antibiotics from Streptomyces verticillus consisting of bleomycin A2 and B2. It inhibits DNA metabolism and is used as an antineoplastic, especially for solid tumors." (MeSH 2013)
Found this page useful?
 Web Resources: Bleomycin
Web Resources: Bleomycin Latest Research Publications
Latest Research PublicationsWeb Resources: Bleomycin (6 links)
Cancer Research UK
Irish Cancer Society
Macmillan Cancer Support
MedlinePlus.gov
NHS Evidence
PubChem
Latest Research Publications
This list of publications is regularly updated (Source: PubMed).
Xu S, Yu Y, ElHakim H, et al.
The Therapeutic Effect of the Combination of Intratumor Injection of Bleomycin and Electroresection/Electrocautery on the Hemangiomas in Hypopharynx and Larynx Through Suspension Laryngoscopy.
Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2019; 128(6):575-580 [PubMed] Related Publications
The Therapeutic Effect of the Combination of Intratumor Injection of Bleomycin and Electroresection/Electrocautery on the Hemangiomas in Hypopharynx and Larynx Through Suspension Laryngoscopy.
Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2019; 128(6):575-580 [PubMed] Related Publications
OBJECTIVES: The treatment of hemangiomas in the hypopharynx and larynx can be challenging and stressful because of the high tumor recurrence rate. The objective of this study was to investigate the therapeutic effect of the combination of intratumor injection of bleomycin and electroresection/electrocautery on the hemangiomas in the hypopharynx and larynx through suspension laryngoscopy.
METHODS: With patients under general anesthesia, the hemangiomas were fully exposed through suspension laryngoscopy. After intratumor injection of bleomycin, in some patients, the hemangiomas were completely resected along the bottom of the tumor pedicle by polypus-forceps electroscalpel; for other patients, the hemangiomas were pinched and held, and then the whole-tumor tissues were cauterized and coagulated by the electroscalpel. Prior to commencing the study, all participants signed informed consents, and all procedures were approved by the hospital ethical committee.
RESULTS: There was almost no bleeding during the operations, no postoperative dyspnea, and no hemorrhage. The patients were followed up for 3 years; the 3-year cure rate was 97%.
CONCLUSION: The hemangioma in the hypopharynx and larynx can be cured by a single-session treatment, using the combination of intratumor injection of bleomycin and electroresection/electrocautery through suspension laryngoscopy. Our method is reliable, affordable, and effective, and it could be widely applied in other hospitals.
METHODS: With patients under general anesthesia, the hemangiomas were fully exposed through suspension laryngoscopy. After intratumor injection of bleomycin, in some patients, the hemangiomas were completely resected along the bottom of the tumor pedicle by polypus-forceps electroscalpel; for other patients, the hemangiomas were pinched and held, and then the whole-tumor tissues were cauterized and coagulated by the electroscalpel. Prior to commencing the study, all participants signed informed consents, and all procedures were approved by the hospital ethical committee.
RESULTS: There was almost no bleeding during the operations, no postoperative dyspnea, and no hemorrhage. The patients were followed up for 3 years; the 3-year cure rate was 97%.
CONCLUSION: The hemangioma in the hypopharynx and larynx can be cured by a single-session treatment, using the combination of intratumor injection of bleomycin and electroresection/electrocautery through suspension laryngoscopy. Our method is reliable, affordable, and effective, and it could be widely applied in other hospitals.
Kristiansson S, Reizenstein J, von Beckerath M, Landström F
Long-term follow-up in patients treated with electrochemotherapy for non-melanoma skin cancer in the head and neck area.
Acta Otolaryngol. 2019; 139(2):195-200 [PubMed] Related Publications
Long-term follow-up in patients treated with electrochemotherapy for non-melanoma skin cancer in the head and neck area.
Acta Otolaryngol. 2019; 139(2):195-200 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Electrochemotherapy (ECT) is a cancer treatment modality where the intracellular accumulation of chemotherapeutic agents is enhanced by an applied electrical field.
AIMS/OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the long-term efficacy, safety and functional outcome after ECT treatment in high-risk non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) with curative intent.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Seven patients with SCC or BCC in the head and neck area were treated with ECT with intratumoral bleomycin administration.
RESULTS: Five patients were cured by ECT as a mono-modality treatment after a median 10-year follow-up period. Two patients had recurrences and/or persisting tumors after treatment that required salvage surgery and radiotherapy. In two patients, the eye was spared with no visual impairment. In another patient, full facial nerve function was spared.
CONCLUSIONS: ECT can be a curative as well as an organ and function-sparing mono modality treatment in high-risk NMSC.
SIGNIFICANCE: Today ECT is mostly used as a palliative treatment. Its curative potential should be further investigated. Randomized studies comparing ECT with standard treatment is needed. Hopefully, this small study can encourage such studies.
AIMS/OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the long-term efficacy, safety and functional outcome after ECT treatment in high-risk non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) with curative intent.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Seven patients with SCC or BCC in the head and neck area were treated with ECT with intratumoral bleomycin administration.
RESULTS: Five patients were cured by ECT as a mono-modality treatment after a median 10-year follow-up period. Two patients had recurrences and/or persisting tumors after treatment that required salvage surgery and radiotherapy. In two patients, the eye was spared with no visual impairment. In another patient, full facial nerve function was spared.
CONCLUSIONS: ECT can be a curative as well as an organ and function-sparing mono modality treatment in high-risk NMSC.
SIGNIFICANCE: Today ECT is mostly used as a palliative treatment. Its curative potential should be further investigated. Randomized studies comparing ECT with standard treatment is needed. Hopefully, this small study can encourage such studies.
Yong F, Juan L, Jinhuan W, et al.
Urethral cavernous hemangioma: a highly misdiagnosed disease (a case report of two patients and literature review).
BMC Urol. 2019; 19(1):13 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Urethral cavernous hemangioma: a highly misdiagnosed disease (a case report of two patients and literature review).
BMC Urol. 2019; 19(1):13 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Diagnosis of urethral cavernous hemangioma (UCH) is very rare. It can be easy to misdiagnose and mistreat due to its atypical clinical manifestations and a lack of relevant knowledge. The study is to explore the diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and treatment of UCH.
CASE PRESENTATION: The first patient was a 15-year-old male, who was admitted to the hospital for more than 1 year with repeated hematuria. UCH was diagnosed by cystoscope biopsy, and cured with local injection of pingyangmycin. The second patient was a 49-year-old male, who was admitted for repeated painless gross hematuria and intermittent urethral bleeding after penile erection for more than 20 years. The case had been misdiagnosed as seminal vesiculitis, urethritis, or prostatitis, for over 20 years, until it was diagnosed as UCH by MR examination of the penis. It was treated by injection of pingyangmycin into the hemangioma's lumen and base. A small incision in the ventral penile area was separated from the location of the hemangioma, which was injected with pingyangmycin again. A biopsy of resected tissue further confirmed the diagnosis of UCH.
CONCLUSIONS: UCH is an easily misdiagnosed disease. Intermittent painless hematuria is important characteristic of UCH. Local injection of pingyangmycin is a good option for treatment of UCH.
CASE PRESENTATION: The first patient was a 15-year-old male, who was admitted to the hospital for more than 1 year with repeated hematuria. UCH was diagnosed by cystoscope biopsy, and cured with local injection of pingyangmycin. The second patient was a 49-year-old male, who was admitted for repeated painless gross hematuria and intermittent urethral bleeding after penile erection for more than 20 years. The case had been misdiagnosed as seminal vesiculitis, urethritis, or prostatitis, for over 20 years, until it was diagnosed as UCH by MR examination of the penis. It was treated by injection of pingyangmycin into the hemangioma's lumen and base. A small incision in the ventral penile area was separated from the location of the hemangioma, which was injected with pingyangmycin again. A biopsy of resected tissue further confirmed the diagnosis of UCH.
CONCLUSIONS: UCH is an easily misdiagnosed disease. Intermittent painless hematuria is important characteristic of UCH. Local injection of pingyangmycin is a good option for treatment of UCH.
Tetikkurt C, Ongel D, Tetikkurt S
A case of bleomycin-induced lung toxicity.
Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2018; 88(3):981 [PubMed] Related Publications
A case of bleomycin-induced lung toxicity.
Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2018; 88(3):981 [PubMed] Related Publications
A 64-year-old female was admitted for dry cough, dyspnea, fever, loss of appetite, and weight loss. Past medical history revealed scoliosis, cholecystectomy, and Hodgkin lymphoma. ABG values were: pH: 7.42, pCO2: 40.2 mm Hg, pO2: 61.4 mm Hg. Chest CT showed cystic lesions, emphysema, ground glass, and reticular opacities. ABG values worsened under 8L/min nasal oxygen. The patient underwent bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) and methylprednisolone 60 mg/day bid was commenced. The final diagnosis was respiratory insufficiency due to bleomycin toxicity. The patient deceased on the sixth day after transfer to the intensive care unit. Bleomycin is an effective chemotherapeutic agent used for Hodgkin lymphoma treatment. It causes significant lung toxicity in half of the patients. Clinicians should always remember that bleomycin toxicity may lead to fatal complications in patients with comorbid conditions. We present this case to remark the possible consequences of bleomycin toxicity and the precautions taken to preclude bleomycin-induced pulmonary complications are discussed.
Li Y, Disney MD
Precise Small Molecule Degradation of a Noncoding RNA Identifies Cellular Binding Sites and Modulates an Oncogenic Phenotype.
ACS Chem Biol. 2018; 13(11):3065-3071 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 16/11/2019 Related Publications
Precise Small Molecule Degradation of a Noncoding RNA Identifies Cellular Binding Sites and Modulates an Oncogenic Phenotype.
ACS Chem Biol. 2018; 13(11):3065-3071 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 16/11/2019 Related Publications
Herein, we describe the precise cellular destruction of an oncogenic noncoding RNA with a small molecule-bleomycin A5 conjugate, affording reversal of phenotype and a facile method to map the cellular binding sites of a small molecule. In particular, bleomycin A5 was coupled to a small molecule that selectively binds the microRNA-96 hairpin precursor (pri-miR-96). By coupling of bleomycin A5's free amine to the RNA binder, its affinity for binding to pri-miR-96 is >100-fold stronger than to DNA and the compound selectively cleaves pri-miR-96 in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. Indeed, selective cleavage of pri-miR-96 enhanced expression of FOXO1 protein, a pro-apoptotic transcription factor that miR-96 silences, and triggered apoptosis in TNBC cells. No effects were observed in healthy breast epithelial cells. Thus, conjugation of a small molecule to bleomycin A5's free amine may provide programmable control over its cellular targets. Few approaches are available to define the binding sites of small molecules within cellular RNAs. Our targeted cleavage method provides such an approach that is straightforward to implement. That is, we determined experimentally the site cleaved within pri-miR-96 in vitro and in cells; these studies revealed that the site of cleavage is the precise site for which the small molecule cleaver was designed and in agreement with modeling. These studies demonstrate the potential of sequence-based design to provide bioactive compounds that precisely recognize and cleave RNA in cells.
Watson RA, De La Peña H, Tsakok MT, et al.
Development of a best-practice clinical guideline for the use of bleomycin in the treatment of germ cell tumours in the UK.
Br J Cancer. 2018; 119(9):1044-1051 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
Development of a best-practice clinical guideline for the use of bleomycin in the treatment of germ cell tumours in the UK.
Br J Cancer. 2018; 119(9):1044-1051 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
Bleomycin, a cytotoxic chemotherapy agent, forms a key component of curative regimens for lymphoma and germ cell tumours. It can be associated with severe toxicity, long-term complications and even death in extreme cases. There is a lack of evidence or consensus on how to prevent and monitor bleomycin toxicity. We surveyed 63 germ cell cancer physicians from 32 cancer centres across the UK to understand their approach to using bleomycin. Subsequent guideline development was based upon current practice, best available published evidence and expert consensus. We observed heterogeneity in practice in the following areas: monitoring; route of administration; contraindications to use; baseline and follow-up investigations performed, and advice given to patients. A best-practice clinical guideline for the use of bleomycin in the treatment of germ cell tumours has been developed and includes recommendations regarding baseline investigations, the use of pulmonary function tests, route of administration, monitoring and patient advice. It is likely that existing heterogeneity in clinical practice of bleomycin prescribing has significant economic, safety and patient experience implications. The development of an evidence-based consensus guideline was supported by 93% of survey participants and aims to address these issues and homogenise practice across the UK.
Leon-Rodriguez E, Rivera-Franco MM, Lacayo-Leñero D, et al.
First - line, non - cryopreserved autologous stem cell transplant for poor - risk germ - cell tumors: Experience in a developing country.
Int Braz J Urol. 2019 Jan-Feb; 45(1):74-82 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
First - line, non - cryopreserved autologous stem cell transplant for poor - risk germ - cell tumors: Experience in a developing country.
Int Braz J Urol. 2019 Jan-Feb; 45(1):74-82 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
PURPOSE: The current first - line treatment for non - seminomatous germ cell tumor (NSGCT) consists of four cycles of cisplatin, etoposide, and bleomycin (BEP), which results in 5 - year overall survival < 60% in patients with poor - risk features. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (auto - HSCT) as a method for overcoming high toxicity after high dose chemotherapy (HDC) has been explored in different solid tumors, but has remained standard practice only for NSGCT. Our objective was to describe outcomes of patients with poor - risk NSGCT who underwent first - line autologous HSCT in a tertiary center in Mexico.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Twenty nine consecutive patients with NSGCT who received first - line, non - cryopreserved autologous HSCT at the National Institute of Medical Sciences and Nutrition Salvador Zubiran in Mexico City, Mexico, from November 1998 to June 2016, were retrospectively analyzed.
RESULTS: The median age at transplantation was 23 (15 - 39) years. Most patients (n = 18, 62%) had testicular primary tumor, and 23 had metastases (79%). Complete response after auto - HSCT was observed in 45%. Non - relapse mortality was 0. Five - year relapse / progression free and overall survival were 67% and 69%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS: This small single limited - resource institution study demonstrated that patients with poor - risk NSGCT are curable by first - line HDC plus autologous HSCT and that this procedure is feasible and affordable to perform using non - cryopreserved hematopoietic stem cells.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Twenty nine consecutive patients with NSGCT who received first - line, non - cryopreserved autologous HSCT at the National Institute of Medical Sciences and Nutrition Salvador Zubiran in Mexico City, Mexico, from November 1998 to June 2016, were retrospectively analyzed.
RESULTS: The median age at transplantation was 23 (15 - 39) years. Most patients (n = 18, 62%) had testicular primary tumor, and 23 had metastases (79%). Complete response after auto - HSCT was observed in 45%. Non - relapse mortality was 0. Five - year relapse / progression free and overall survival were 67% and 69%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS: This small single limited - resource institution study demonstrated that patients with poor - risk NSGCT are curable by first - line HDC plus autologous HSCT and that this procedure is feasible and affordable to perform using non - cryopreserved hematopoietic stem cells.
Niu Y, Yin R, Wang D, et al.
Clinical analysis of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced vulvar cancer: A STROBE-compliant article.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(34):e11786 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
Clinical analysis of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced vulvar cancer: A STROBE-compliant article.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(34):e11786 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
To investigate the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced vulvar cancer and to provide references for clinical treatment.Clinical and pathological data of 12 patients with advanced vulvar carcinoma were collected. The response and operability rates, adverse effects, and prognosis of neoadjuvant chemotherapy were retrospectively analyzed.The mean patient age was 45.8 (range 26-69) years. Among 12 patients, 9 underwent treatment with bleomycin and cisplatin with or without vincristine. The overall response rate was 67%. Five patients (56%) experienced grade 1 or 2 bone marrow suppression or gastrointestinal reactions. Seven patients (78%) underwent radical surgery. The mean overall survival time was 34.1 (range 3-69) months, the mean progression free survival time was 26 (range 3-69) months, and the 1-year survival rate was 83%. The other 3 patients received combined paclitaxel and cisplatin treatment. The overall response rate was 67%. All 3 patients (100%) experienced grade 2 hair loss or anemia and 2 of them (67%) underwent radical vulvectomy. The mean overall survival time was 11.7 (range 5-15) months, the mean progression free survival time was 7.7 (range 3-15) months and the 1-year survival rate was 100%. Time to overall survival and progression free survival were not significantly different between the 2 groups (P = .46 and P = .39).Owing to their high overall response rate and tolerable adverse effects, either bleomycin-cisplatin-based or paclitaxel-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen can be considered a therapeutic option for advanced vulvar cancer.
Merkle S, Tavernier SS
Cannabis Use and Bleomycin: An Overview and Case Study of Pulmonary Toxicity.
Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2018; 22(4):438-443 [PubMed] Related Publications
Cannabis Use and Bleomycin: An Overview and Case Study of Pulmonary Toxicity.
Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2018; 22(4):438-443 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Legalization efforts in many states have heightened awareness of the medicinal uses of cannabis, and oncology nurses are more frequently caring for patients who have used or are using cannabis. Significant epidemiologic data on the prevalence of cannabis use in patients with cancer are not yet available, and not much is known about the effects of cannabis on cancer treatment.
OBJECTIVES: This article describes the effects cannabis may have on the lungs, reviews indications for cannabis use in patients with cancer, and explores an atypical case of progressive pulmonary toxicity in a young patient with a history of Hodgkin lymphoma and cannabis use.
METHODS: A review of the literature on cannabis-associated lung injury was conducted, with 32 articles selected for full review.
FINDINGS: As cannabis use in cancer care continues to gain support, further research evaluating cannabis use in patients treated with bleomycin is warranted. In addition, the pros and cons of cannabis use must be fully evaluated and discussed with the patient with cancer prior to recommending its use.
OBJECTIVES: This article describes the effects cannabis may have on the lungs, reviews indications for cannabis use in patients with cancer, and explores an atypical case of progressive pulmonary toxicity in a young patient with a history of Hodgkin lymphoma and cannabis use.
METHODS: A review of the literature on cannabis-associated lung injury was conducted, with 32 articles selected for full review.
FINDINGS: As cannabis use in cancer care continues to gain support, further research evaluating cannabis use in patients treated with bleomycin is warranted. In addition, the pros and cons of cannabis use must be fully evaluated and discussed with the patient with cancer prior to recommending its use.
Mtonga W, Mujajati A, Munkombwe D, et al.
Therapeutic Outcomes in AIDS-Associated Kaposi's Sarcoma Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy Treated with Chemotherapy at Two Tertiary Hospitals in Lusaka, Zambia.
Curr HIV Res. 2018; 16(3):231-236 [PubMed] Related Publications
Therapeutic Outcomes in AIDS-Associated Kaposi's Sarcoma Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy Treated with Chemotherapy at Two Tertiary Hospitals in Lusaka, Zambia.
Curr HIV Res. 2018; 16(3):231-236 [PubMed] Related Publications
The incidence of HIV-associated Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) remains high in Zambia in the antiretroviral therapy era. The most efficacious treatment regimen for KS has yet to be established. In both developed and developing countries, treatment regimens have had limited efficacy. Late presentation in Africa affects therapeutic outcomes.
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to determine therapeutic outcomes of epidemic KS patients on combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) after completion of six cycles of Adriamycin, Bleomycin, and Vincristine (ABV) chemotherapy.
METHODS: This was a descriptive cross-sectional study. Study participants were drawn from a study database of confirmed incident KS patients seen at the Skin Clinic of the University Teaching Hospitals (UTH) during the period between August, 2015 and September, 2016.
RESULTS: Of the 38 successfully recruited study participants, a complete response was documented in 18 (47%) after 6 cycles of ABV whereas 20 (53%) experienced a partial response. KS recurrence was observed in 8 (44%) of the individuals that experienced an initial complete response. At the time of the study, clinical assessment revealed that KS lesions had completely regressed in 21 (55%) of all the patients.
CONCLUSION: ABV chemotherapy appears ineffective in long-term resolution of epidemic KS patients on ART. Recurrence rates are high after chemotherapy in patients that experience initially favorable responses to treatment. There is a need to diagnose KS earlier, and to develop more efficacious treatment options in order to reduce recurrence rates for epidemic KS.
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to determine therapeutic outcomes of epidemic KS patients on combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) after completion of six cycles of Adriamycin, Bleomycin, and Vincristine (ABV) chemotherapy.
METHODS: This was a descriptive cross-sectional study. Study participants were drawn from a study database of confirmed incident KS patients seen at the Skin Clinic of the University Teaching Hospitals (UTH) during the period between August, 2015 and September, 2016.
RESULTS: Of the 38 successfully recruited study participants, a complete response was documented in 18 (47%) after 6 cycles of ABV whereas 20 (53%) experienced a partial response. KS recurrence was observed in 8 (44%) of the individuals that experienced an initial complete response. At the time of the study, clinical assessment revealed that KS lesions had completely regressed in 21 (55%) of all the patients.
CONCLUSION: ABV chemotherapy appears ineffective in long-term resolution of epidemic KS patients on ART. Recurrence rates are high after chemotherapy in patients that experience initially favorable responses to treatment. There is a need to diagnose KS earlier, and to develop more efficacious treatment options in order to reduce recurrence rates for epidemic KS.
Sanie-Jahromi F, Saadat M
Effects of electromagnetic field, cisplatin and morphine on cytotoxicity and expression levels of DNA repair genes.
Mol Biol Rep. 2018; 45(5):807-814 [PubMed] Related Publications
Effects of electromagnetic field, cisplatin and morphine on cytotoxicity and expression levels of DNA repair genes.
Mol Biol Rep. 2018; 45(5):807-814 [PubMed] Related Publications
Morphine (Mor) is widely used as an analgesic drug in cancers and in combination with chemotherapy is known to have DNA damaging effects on non-targeted cell. This study surveyed the effect of Mor in combination with 50-Hz electromagnetic field (EMF) and co-treatment of cisplatin in combination with Mor and EMF on the expression of genes involved in DNA repair pathways. MCF-7 and SH-SY5Y cells were treated with 5.0 µM Mor and then exposed to 50-Hz 0.50 mT EMF in the intermittent pattern of 15 min field-on/15 min field-off. Gene expression, cisplatin and bleomycin cytotoxicity were measured using real-time PCR and MTT assay. Mor treated cells showed significant down-regulation of the examined genes, while in "Mor + EMF" treatments the genes were not significantly changed. IC
Akhlaghpoor S, Torkian P, Golzarian J
Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Embolization (B/LE) for Symptomatic Giant Hepatic Hemangioma.
Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018; 41(11):1674-1682 [PubMed] Related Publications
Transarterial Bleomycin-Lipiodol Embolization (B/LE) for Symptomatic Giant Hepatic Hemangioma.
Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018; 41(11):1674-1682 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Large hepatic hemangiomas can cause symptoms such as pain and bleeding. No consensus currently exists on the optimal management of large and symptomatic hemangiomas. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the role of transarterial bleomycin-lipiodol embolization (B/LE) in the treatment of symptomatic large hepatic hemangioma.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We retrospectively reviewed 23 patients (29 hemangiomas) treated between July 2011 and August 2017. Transarterial B/LE was performed using 7-15 cc of Lipiodol mixed with 30-45 IU of bleomycin by standard three-way stopcocks. All patients were followed clinically and by imaging for an average of 7.5 months. Patterns of bleomycin-lipiodol distribution in the periphery of hemangiomas were categorized into four different grades. Technical success was defined as proper delivery of bleomycin-lipiodol into the hemangioma confirmed by post-embolization computed tomography. Clinical success was defined as more than 50% reduction of hemangioma volume and symptom improvement during follow-ups.
RESULTS: Technical success and clinical success were 100 and 73.9% (17 patients), respectively. Six patients (26.08%) experienced transient post-embolization syndrome. Significant size reduction was seen in patients with grade 4 hemangioma border coverage (P = 0.042).
CONCLUSION: Transarterial B/LE is a safe and efficient alternative for controlling symptoms related to large hemangiomas.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We retrospectively reviewed 23 patients (29 hemangiomas) treated between July 2011 and August 2017. Transarterial B/LE was performed using 7-15 cc of Lipiodol mixed with 30-45 IU of bleomycin by standard three-way stopcocks. All patients were followed clinically and by imaging for an average of 7.5 months. Patterns of bleomycin-lipiodol distribution in the periphery of hemangiomas were categorized into four different grades. Technical success was defined as proper delivery of bleomycin-lipiodol into the hemangioma confirmed by post-embolization computed tomography. Clinical success was defined as more than 50% reduction of hemangioma volume and symptom improvement during follow-ups.
RESULTS: Technical success and clinical success were 100 and 73.9% (17 patients), respectively. Six patients (26.08%) experienced transient post-embolization syndrome. Significant size reduction was seen in patients with grade 4 hemangioma border coverage (P = 0.042).
CONCLUSION: Transarterial B/LE is a safe and efficient alternative for controlling symptoms related to large hemangiomas.
Prevc A, Niksic Zakelj M, Kranjc S, et al.
Electrochemotherapy with cisplatin or bleomycin in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Improved effectiveness of cisplatin in HPV-positive tumors.
Bioelectrochemistry. 2018; 123:248-254 [PubMed] Related Publications
Electrochemotherapy with cisplatin or bleomycin in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Improved effectiveness of cisplatin in HPV-positive tumors.
Bioelectrochemistry. 2018; 123:248-254 [PubMed] Related Publications
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is an important etiological factor in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs). Standard treatment of HPV-positive tumors with platinum-based radio(chemo)therapy results in a better outcome than in HPV-negative tumors. Electrochemotherapy is becoming an increasingly recognized mode of treatment in different cancers; thus, its use in the management of head and neck SCC is of considerable interest. However, response to electrochemotherapy according to HPV status of the tumors has not been evaluated yet. Thus, our aim was to compare the effect of electrochemotherapy with cisplatin or bleomycin between HPV-negative and HPV-positive human pharyngeal SCC derived cell lines and tumor models. HPV-positive cells and tumors were found to be more sensitive to electrochemotherapy with cisplatin than HPV-negative ones, whereas sensitivity to electrochemotherapy with bleomycin was similar irrespective of the HPV status. The higher sensitivity of HPV-positive cells and tumors to electrochemotherapy with cisplatin is likely due to the higher level and slower repair of DNA damage. In HPV-negative tumors, a higher number of complete responses was recorded after bleomycin-based rather than cisplatin-based electrochemotherapy, while in HPV-positive tumors electrochemotherapy with cisplatin was more effective.
Kong J, Yi L, Xiong Y, et al.
The discovery and development of microbial bleomycin analogues.
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018; 102(16):6791-6798 [PubMed] Related Publications
The discovery and development of microbial bleomycin analogues.
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018; 102(16):6791-6798 [PubMed] Related Publications
The bleomycins (BLMs) belong to a subfamily of glycopeptide antibiotics and are clinically applied in combination chemotherapy regimens to treat various malignancies. But the therapeutic applications of BLMs are restricted by the accompanied dose-dependent lung toxicity and potential incidence of lung fibrosis. Many efforts have been devoted to develop novel BLM analogues, for seeking of drug leads with improved antitumor activity and/or reduced lung toxicity. The progresses in the biosynthetic studies of BLMs have greatly expedited the process to achieve such goals. This review highlights the discovery and development of microbial BLM analogues in the past two decades, especially those derived from engineered biosynthesis. Moreover, the summarized structure-activity relationship, which is specifically focusing on the sugar moiety, shall shed new insights into the prospective development of BLM analogues.
Fondello C, Agnetti L, Glikin GC, Finocchiaro LME
Mechanisms Enhancing the Cytotoxic Effects of Bleomycin plus Suicide or Interferon-β Gene Lipofection in Metastatic Human Melanoma Cells.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018; 18(9):1338-1348 [PubMed] Related Publications
Mechanisms Enhancing the Cytotoxic Effects of Bleomycin plus Suicide or Interferon-β Gene Lipofection in Metastatic Human Melanoma Cells.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018; 18(9):1338-1348 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Three metastatic human melanoma cell lines generated from patient removed lymph nodes and spleen metastasis were established in our laboratory.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the mechanisms enhancing the cytotoxic effects of Bleomycin (BLM), herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase/ganciclovir Suicide Gene (SG) and human interferon-β gene (hIFNβ) lipofection in early passages of these melanoma cell lines.
METHODS: In these cell lines, we determined: cytotoxicity, bystander effect, lipofection efficiencies, apoptosis, necrosis, senescence, colony forming capacity and mitochondrial membrane depolarization after treatments.
RESULTS: The three assayed cell lines displayed sensitivity to single and combined BLM/gene treatments. BLM improved the antitumor and anti-clonogenic effects of SG and hIFNβ genes. Considering the low lipofection efficiencies (<10%), one of the main causes of the SG and hIFNβ gene effectiveness was their bystander effect. In one of these cell lines, this effect eradicated up to 60% of the cells although <1% expressed the transgene. In the three cell lines, BLM alone or combined with SG or hIFNβ gene significantly increased the percentage of cells exhibiting membrane compromise, DNA damage, and senescence. Interestingly, the strong BLM/hIFNβ gene combination was able to generate from 73% to 98% of non-viable cells. The high proportion of senescent cells induced by BLM alone or combined with genes strongly decreased the clonogenic capacity of surviving cells.
CONCLUSION: The presented results indicate that BLM improves the antitumor effects of SG and hIFNβ transgene expression. Altogether, these findings strongly support the clinical potential of these combined approaches.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the mechanisms enhancing the cytotoxic effects of Bleomycin (BLM), herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase/ganciclovir Suicide Gene (SG) and human interferon-β gene (hIFNβ) lipofection in early passages of these melanoma cell lines.
METHODS: In these cell lines, we determined: cytotoxicity, bystander effect, lipofection efficiencies, apoptosis, necrosis, senescence, colony forming capacity and mitochondrial membrane depolarization after treatments.
RESULTS: The three assayed cell lines displayed sensitivity to single and combined BLM/gene treatments. BLM improved the antitumor and anti-clonogenic effects of SG and hIFNβ genes. Considering the low lipofection efficiencies (<10%), one of the main causes of the SG and hIFNβ gene effectiveness was their bystander effect. In one of these cell lines, this effect eradicated up to 60% of the cells although <1% expressed the transgene. In the three cell lines, BLM alone or combined with SG or hIFNβ gene significantly increased the percentage of cells exhibiting membrane compromise, DNA damage, and senescence. Interestingly, the strong BLM/hIFNβ gene combination was able to generate from 73% to 98% of non-viable cells. The high proportion of senescent cells induced by BLM alone or combined with genes strongly decreased the clonogenic capacity of surviving cells.
CONCLUSION: The presented results indicate that BLM improves the antitumor effects of SG and hIFNβ transgene expression. Altogether, these findings strongly support the clinical potential of these combined approaches.
Bagheri R, Noori M, Rajayi M, et al.
The effect of iodopovidone versus bleomycin in chemical pleurodesis.
Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2018; 26(5):382-386 [PubMed] Related Publications
The effect of iodopovidone versus bleomycin in chemical pleurodesis.
Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2018; 26(5):382-386 [PubMed] Related Publications
Background Malignant pleural effusion continues to be a common problem in patients with metastatic disease. This study was conducted to compare the efficacy and safety of bleomycin pleurodesis with povidone-iodine pleurodesis through a chest drain as palliative treatment for recurrent malignant pleural effusion. Methods Sixty cancer patients (36 males and 24 females) with recurrent malignant pleural effusion were enrolled in a prospective randomized trial. Thirty patients received povidone-iodine pleurodesis and 30 received bleomycin pleurodesis. Age, sex, side of the primary pathology, treatment outcome (recurrence and relapse time), and complications were analyzed. Results The mean age was 59.63 ± 7.68 years in the povidone-iodine group and 57.97 ± 9.27 years in the bleomycin group ( p = 0.452). The complications were identical in both groups: 2 (6.7%) patients had chest pain, 2 (6.7%) had fever, and one (3.3%) had hypotension. There was a good response to therapy in 20 (66.7%) patients in the bleomycin group and 25 (83.3%) in the povidone-iodine group ( p = 0.136). Conclusion The results of this study indicate that povidone-iodine should be considered as a selective chemical agent to perform pleurodesis in patients with recurrent malignant pleural effusion because it has the same effect but costs less than bleomycin.
Murray V, Chen JK, Chung LH
The Interaction of the Metallo-Glycopeptide Anti-Tumour Drug Bleomycin with DNA.
Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(5) [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
The Interaction of the Metallo-Glycopeptide Anti-Tumour Drug Bleomycin with DNA.
Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(5) [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
The cancer chemotherapeutic drug, bleomycin, is clinically used to treat several neoplasms including testicular and ovarian cancers. Bleomycin is a metallo-glycopeptide antibiotic that requires a transition metal ion, usually Fe(II), for activity. In this review, the properties of bleomycin are examined, especially the interaction of bleomycin with DNA. A Fe(II)-bleomycin complex is capable of DNA cleavage and this process is thought to be the major determinant for the cytotoxicity of bleomycin. The DNA sequence specificity of bleomycin cleavage is found to at 5′-GT* and 5′-GC* dinucleotides (where * indicates the cleaved nucleotide). Using next-generation DNA sequencing, over 200 million double-strand breaks were analysed, and an expanded bleomycin sequence specificity was found to be 5′-RTGT*AY (where R is G or A and Y is T or C) in cellular DNA and 5′-TGT*AT in purified DNA. The different environment of cellular DNA compared to purified DNA was proposed to be responsible for the difference. A number of bleomycin analogues have been examined and their interaction with DNA is also discussed. In particular, the production of bleomycin analogues via genetic manipulation of the modular non-ribosomal peptide synthetases and polyketide synthases in the bleomycin gene cluster is reviewed. The prospects for the synthesis of bleomycin analogues with increased effectiveness as cancer chemotherapeutic agents is also explored.
Maruyama Y, Sadahira T, Mitsui Y, et al.
Prognostic impact of bleomycin pulmonary toxicity on the outcomes of patients with germ cell tumors.
Med Oncol. 2018; 35(6):80 [PubMed] Related Publications
Prognostic impact of bleomycin pulmonary toxicity on the outcomes of patients with germ cell tumors.
Med Oncol. 2018; 35(6):80 [PubMed] Related Publications
Bleomycin pulmonary toxicity (BPT) has been well described in patients with germ cell tumors treated with bleomycin etoposide and cisplatin chemotherapy (BEP). To assess the prognostic impact of BPT, we retrospectively identified 52 patients who underwent bleomycin etoposide and cisplatin chemotherapy from 2008 to 2017 in our institution, and evaluated the risk factors of BPT and its effect on prognosis. Patients who had received chemotherapy at another institution were excluded. BPT was defined as bleomycin discontinuation in response to pulmonary function test decline, pulmonary symptoms, or interstitial pneumonia on computed tomography without infection. We divided the patients into two groups according to this definition: BPT and non-BPT. Their median age was 34.2 years, and their median body mass index was 22.8 kg/m
Pandey V, Tiwari P, Sharma SP, et al.
Role of intralesional bleomycin and intralesional triamcinolone therapy in residual haemangioma following propranolol.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018; 47(7):908-912 [PubMed] Related Publications
Role of intralesional bleomycin and intralesional triamcinolone therapy in residual haemangioma following propranolol.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018; 47(7):908-912 [PubMed] Related Publications
With the emergence of propranolol as the first choice of treatment for problematic infantile haemangioma at many centres, the number of patients with a partial or non-response to propranolol has also been growing. This study investigated the role of intralesional bleomycin and triamcinolone in patients with residual disease following propranolol therapy for infantile haemangioma. Sixty-seven patients with residual haemangioma were assigned randomly to receive either intralesional bleomycin (group A, n=36) or intralesional triamcinolone (group B, n=31). The response to treatment and adverse effects were assessed in both groups. All patients received at least four doses and a maximum of six doses of the assigned drug. In group A (mean follow-up 9.38months), 47.2% had an excellent response and 44.4% a good response. In group B (mean follow-up 7.42months), 25.8% had an excellent response and 48.4% a good response. There was no difference in overall response between the groups (P=0.074). Among patients who were initially non-responders to propranolol, bleomycin showed a better response than triamcinolone (P=0.037). This may be due to an overlap in the mechanism of action of propranolol and triamcinolone. Thus, intralesional bleomycin should be preferred in patients with no initial response to propranolol therapy, while bleomycin or triamcinolone can be used in patients with a partial response to propranolol therapy, as they have equal efficacy.
Fiorentzis M, Kalirai H, Katopodis P, et al.
Electrochemotherapy with bleomycin and cisplatin enhances cytotoxicity in primary and metastatic uveal melanoma cell lines in vitro.
Neoplasma. 2018; 65(2):210-215 [PubMed] Related Publications
Electrochemotherapy with bleomycin and cisplatin enhances cytotoxicity in primary and metastatic uveal melanoma cell lines in vitro.
Neoplasma. 2018; 65(2):210-215 [PubMed] Related Publications
Electrochemotherapy (ECT) enhances responsiveness to cytotoxic drugs in numerous cell lines in vitro. Clinically ECT is widely applied for skin tumor ablation and has shown efficacy in treating non-resectable colorectal liver metastases. There is limited experience of ECT for ocular tumor therapy. We investigated the cytotoxic effect of bleomycin and cisplatin in combination with electroporation on chemoresistant human uveal melanoma (UM) cell lines in vitro. Four UM cell lines (Mel 270, 92-1, OMM-1, OMM-2.5) were treated with electroporation (pulse amplitude 300-1000 V/cm, 8-80 pulses, 100 μs, 5 Hz) and increasing concentrations of bleomycin and cisplatin (0-7.5 μg/ml). Cell survival was analyzed by MTT viability assay after 36 hours. UM cell lines were resistant to both bleomycin and cisplatin. In combination with electro- poration, the effects of bleomycin and cisplatin were increased 8-70 fold and 3-15 fold, respectively, in all UM cell lines. At the lowest concentration of bleomycin tested (1 μg/ml), viability was maximally reduced in all UM cell lines by ≥69% with electroporation conditions of 750 V/cm and 20 pulses. All UM cell lines were more resistant to cisplatin; however, electro- poration of 1000 V/cm and 8 pulses resulted in similar reductions in cell viability of 92-1, Mel270 with 2.5 μg/ml cisplatin, OMM2-5 cells with 5 μg/ml cisplatin and OMM1 cells with 1 μg/ml cisplatin. In vitro ECT with bleomycin or cisplatin is more effective than the highest concentration of the antineoplastic drug or electroporation alone, opening new perspectives in primary and metastatic UM treatment.
Djokic M, Cemazar M, Popovic P, et al.
Electrochemotherapy as treatment option for hepatocellular carcinoma, a prospective pilot study.
Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018; 44(5):651-657 [PubMed] Related Publications
Electrochemotherapy as treatment option for hepatocellular carcinoma, a prospective pilot study.
Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018; 44(5):651-657 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Electrochemotherapy provides non-thermal ablation of cutaneous as well as deep seated tumors. Based on positive results of the treatment of colorectal liver metastases, we conducted a prospective pilot study on hepatocellular carcinomas with the aim of testing the feasibility, safety and effectiveness of electrochemotherapy.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Electrochemotherapy with bleomycin was performed on 17 hepatocellular carcinomas in 10 patients using a previously established protocol. The procedure was performed during open surgery and the patients were followed for median 20.5 months.
RESULTS: Electrochemotherapy was feasible for all 17 lesions, and no treatment-related adverse events or major post-operative complications were observed. The median size of the treated lesions was 24 mm (range 8-41 mm), located either centrally, i.e., near the major hepatic vessels, or peripherally. The complete response rate at 3-6 months was 80% per patient and 88% per treated lesion.
CONCLUSIONS: Electrochemotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma proved to be a feasible and safe treatment in all 10 patients included in this study. To evaluate the effectiveness of this method, longer observation period is needed; however the results at medium observation time of 20.5 months after treatment are encouraging, in 15 out of 17 lesions complete response was obtained. Electrochemotherapy is predominantly applicable in patients with impaired liver function due to liver cirrhosis and/or with lesions where a high-risk operation is needed to achieve curative intent, given the intra/perioperative risk for high morbidity and mortality.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Electrochemotherapy with bleomycin was performed on 17 hepatocellular carcinomas in 10 patients using a previously established protocol. The procedure was performed during open surgery and the patients were followed for median 20.5 months.
RESULTS: Electrochemotherapy was feasible for all 17 lesions, and no treatment-related adverse events or major post-operative complications were observed. The median size of the treated lesions was 24 mm (range 8-41 mm), located either centrally, i.e., near the major hepatic vessels, or peripherally. The complete response rate at 3-6 months was 80% per patient and 88% per treated lesion.
CONCLUSIONS: Electrochemotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma proved to be a feasible and safe treatment in all 10 patients included in this study. To evaluate the effectiveness of this method, longer observation period is needed; however the results at medium observation time of 20.5 months after treatment are encouraging, in 15 out of 17 lesions complete response was obtained. Electrochemotherapy is predominantly applicable in patients with impaired liver function due to liver cirrhosis and/or with lesions where a high-risk operation is needed to achieve curative intent, given the intra/perioperative risk for high morbidity and mortality.
Chang L, Chen H, Yang X, et al.
Intralesional Bleomycin Injection for Propranolol-Resistant Hemangiomas.
J Craniofac Surg. 2018; 29(2):e128-e130 [PubMed] Related Publications
Intralesional Bleomycin Injection for Propranolol-Resistant Hemangiomas.
J Craniofac Surg. 2018; 29(2):e128-e130 [PubMed] Related Publications
Propranolol has been the first-line treatment for alarming hemangiomas. However, some hemangiomas are propranolol-resistant. The authors reported 1 propranolol-resistant hemangioma which was treated with intralesional bleomycin injections. Sixteen months after 3 injections, the lesion still remained stable. Its potential mechanism was clarified by ultrasonic monitoring. Intralesional bleomycin injection can be considered an ideal option in treating propranolol-resistant hemangiomas.
Bekolo CE, Soumah MM, Tiemtore OW, et al.
Assessing the outcomes of HIV-infected persons receiving treatment for Kaposi sarcoma in Conakry-Guinea.
BMC Cancer. 2017; 17(1):806 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
Assessing the outcomes of HIV-infected persons receiving treatment for Kaposi sarcoma in Conakry-Guinea.
BMC Cancer. 2017; 17(1):806 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Médecins Sans Frontières is supporting comprehensive HIV care and treatment for Kaposi Sarcoma (KS) in Guinea, where antiretroviral coverage is low and access to KS treatment is very limited. We aimed to evaluate treatment response and survival outcomes of epidemic KS in this setting.
METHODS: Retrospective survival analysis of routinely collected clinical data of HIV-infected patients with clinically diagnosed KS, receiving ART and chemotherapy consisting of a combination of bleomycin and vincristine at the Donka National Hospital in Conakry between 2012 and 2015.
RESULTS: A total of 225 patients were enrolled for KS treatment within the three-year period. Late presentation with stage T1 disease was common (82.7%). At the end of a median of 8 cycles of chemotherapy (IQR: 2-12), complete remission was observed in 65 (28.9%), partial remission in 53 (23.6%), stable disease in 15 (6.7%) and unknown response for all 92 (40.9%) patients who dropped out of care. The chances of achieving complete remission doubled after each additional cycle of chemotherapy (aOR = 2.09 95% CI: 1.44-3.01) but were reduced by about two-thirds for each additional month delay between treatment and onset of KS (aOR = 0.31, 95% CI: 0.11-0.86). Treatment response was seriously compromised in patients with woody skin oedema (aOR = 0.05, 95% CI: 0.01-0.38) and those with prior chemotherapy (aOR = 0.21, 95% CI: 0.05-0.80). The median survival time was 7.6 months (95% CI: 5.9-9.8). Attrition from care was reduced by 22% for every additional cycle of chemotherapy administered (aH0R = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.71-0.84) and was lower in those with complete remission compared with those with partial or no response (aHR = 0.05, 95% CI: 0.007-0.43).
CONCLUSION: There has been an increased access to KS treatment. The overall response rate is 52.4%, which is considered a satisfactory result. Poor outcomes were common and were largely due to late presentation and defaulting on treatment. Efforts towards early HIV/KS diagnosis and adherence to a full round of chemotherapy are needed for optimising outcomes. Newer drugs may be required for patients previously exposed to chemotherapy.
METHODS: Retrospective survival analysis of routinely collected clinical data of HIV-infected patients with clinically diagnosed KS, receiving ART and chemotherapy consisting of a combination of bleomycin and vincristine at the Donka National Hospital in Conakry between 2012 and 2015.
RESULTS: A total of 225 patients were enrolled for KS treatment within the three-year period. Late presentation with stage T1 disease was common (82.7%). At the end of a median of 8 cycles of chemotherapy (IQR: 2-12), complete remission was observed in 65 (28.9%), partial remission in 53 (23.6%), stable disease in 15 (6.7%) and unknown response for all 92 (40.9%) patients who dropped out of care. The chances of achieving complete remission doubled after each additional cycle of chemotherapy (aOR = 2.09 95% CI: 1.44-3.01) but were reduced by about two-thirds for each additional month delay between treatment and onset of KS (aOR = 0.31, 95% CI: 0.11-0.86). Treatment response was seriously compromised in patients with woody skin oedema (aOR = 0.05, 95% CI: 0.01-0.38) and those with prior chemotherapy (aOR = 0.21, 95% CI: 0.05-0.80). The median survival time was 7.6 months (95% CI: 5.9-9.8). Attrition from care was reduced by 22% for every additional cycle of chemotherapy administered (aH0R = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.71-0.84) and was lower in those with complete remission compared with those with partial or no response (aHR = 0.05, 95% CI: 0.007-0.43).
CONCLUSION: There has been an increased access to KS treatment. The overall response rate is 52.4%, which is considered a satisfactory result. Poor outcomes were common and were largely due to late presentation and defaulting on treatment. Efforts towards early HIV/KS diagnosis and adherence to a full round of chemotherapy are needed for optimising outcomes. Newer drugs may be required for patients previously exposed to chemotherapy.
Rotunno R, Campana LG, Quaglino P, et al.
Electrochemotherapy of unresectable cutaneous tumours with reduced dosages of intravenous bleomycin: analysis of 57 patients from the International Network for Sharing Practices of Electrochemotherapy registry.
J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018; 32(7):1147-1154 [PubMed] Related Publications
Electrochemotherapy of unresectable cutaneous tumours with reduced dosages of intravenous bleomycin: analysis of 57 patients from the International Network for Sharing Practices of Electrochemotherapy registry.
J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018; 32(7):1147-1154 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Electrochemotherapy (ECT) is currently used to treat unresectable superficial tumours of different histotypes through the combination of cytotoxic chemotherapy and local application of electric pulses. In 2006, a collaborative project defined the ESOPE (European Standard Operating Procedures of Electrochemotherapy) guidelines to standardize the procedure. The International Network for Sharing Practices of Electrochemotherapy (InspECT) aims to refine the ESOPE and improve clinical practice. Limiting patient exposure to systemic chemotherapy would be advisable to ameliorate ECT safety profile.
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of ECT with reduced chemotherapy dosages.
METHODS: In a retrospective analysis of a prospectively maintained database (InspECT registry), we evaluated the outcome of patients who received ECT with reduced dosages of bleomycin (7500, 10 000 or 13 500 IU/m
RESULTS: We identified 57 patients with 147 tumours (melanoma, 38.6%; squamous cell carcinoma, 22.8%; basal cell carcinoma, 17.5%; breast cancer 7%; Kaposi sarcoma 7%; other histotypes, 7.1%). Per-tumour complete response (CR) rate at 60 days was 70.1% (partial, 16.3%); per-patient CR was 57.9% (partial, 21.1%). Local pain was the most frequently reported side-effect (n = 22 patients [39%]), mostly mild; two patients experienced flu-like symptoms, one patient nausea. We observed the same CR rate (55%) in patients with melanoma treated by reduced or conventional bleomycin dosages (P = 1.00).
CONCLUSIONS: Electrochemotherapy performed with reduced bleomycin dosages could be as effective as with currently recommended dose. Patients with impaired renal function or candidate to multiple ECT cycles could benefit from a reduced dose protocol. Our findings need prospective confirmation before being adopted in clinical practice.
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of ECT with reduced chemotherapy dosages.
METHODS: In a retrospective analysis of a prospectively maintained database (InspECT registry), we evaluated the outcome of patients who received ECT with reduced dosages of bleomycin (7500, 10 000 or 13 500 IU/m
RESULTS: We identified 57 patients with 147 tumours (melanoma, 38.6%; squamous cell carcinoma, 22.8%; basal cell carcinoma, 17.5%; breast cancer 7%; Kaposi sarcoma 7%; other histotypes, 7.1%). Per-tumour complete response (CR) rate at 60 days was 70.1% (partial, 16.3%); per-patient CR was 57.9% (partial, 21.1%). Local pain was the most frequently reported side-effect (n = 22 patients [39%]), mostly mild; two patients experienced flu-like symptoms, one patient nausea. We observed the same CR rate (55%) in patients with melanoma treated by reduced or conventional bleomycin dosages (P = 1.00).
CONCLUSIONS: Electrochemotherapy performed with reduced bleomycin dosages could be as effective as with currently recommended dose. Patients with impaired renal function or candidate to multiple ECT cycles could benefit from a reduced dose protocol. Our findings need prospective confirmation before being adopted in clinical practice.
Plaschke CC, Bertino G, McCaul JA, et al.
European Research on Electrochemotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer (EURECA) project: Results from the treatment of mucosal cancers.
Eur J Cancer. 2017; 87:172-181 [PubMed] Related Publications
European Research on Electrochemotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer (EURECA) project: Results from the treatment of mucosal cancers.
Eur J Cancer. 2017; 87:172-181 [PubMed] Related Publications
AIM: Electrochemotherapy is an effective local treatment for cutaneous tumours and metastases. In this prospective trial, six European institutions investigated electrochemotherapy in recurrent, mucosal head and neck tumours.
PATIENT AND METHODS: Forty-three patients with recurrent mucosal head and neck tumours and no further curative or reasonably effective palliative treatment options were enrolled and treated with electrochemotherapy. Patients were treated in general anaesthesia using intravenous or local injection of bleomycin followed by delivery of electric pulses to the tumour area. Primary end-point was local tumour response. Secondary end-points were safety and toxicity, overall and progression free survival, and quality-of-life.
RESULTS: Thirty-seven patients were evaluable for tumour response, pain score, side-effects and quality of life questionnaires. Six patients were not evaluable due to lost follow-up, disease progression or death before evaluation. Intention to treat analysis revealed an objective response of 56% (complete response 8 (19%), partial response 16 (37%), stable disease 10 (23%), progressive disease 3 (7%), and not evaluable 6 (14%)). Three patients (7%) remained in complete response at 30, 34, and 84 months post-treatment. The treatment procedure was generally well tolerated. Swelling of the mucosa was observed in the first days after treatment. Pain and use of pain medication rose temporarily; fatigue and dysphagia were also noted in the quality of life assessment.
CONCLUSION: Electrochemotherapy can be applied to mucosal head and neck recurrent tumours accessible to the procedure with promising objective response, survival and toxicity profile. Attention should be paid to post-treatment swelling and planning of pain medication. These favourable results indicate that electrochemotherapy could play a role in patients with recurrent head and neck cancer.
PATIENT AND METHODS: Forty-three patients with recurrent mucosal head and neck tumours and no further curative or reasonably effective palliative treatment options were enrolled and treated with electrochemotherapy. Patients were treated in general anaesthesia using intravenous or local injection of bleomycin followed by delivery of electric pulses to the tumour area. Primary end-point was local tumour response. Secondary end-points were safety and toxicity, overall and progression free survival, and quality-of-life.
RESULTS: Thirty-seven patients were evaluable for tumour response, pain score, side-effects and quality of life questionnaires. Six patients were not evaluable due to lost follow-up, disease progression or death before evaluation. Intention to treat analysis revealed an objective response of 56% (complete response 8 (19%), partial response 16 (37%), stable disease 10 (23%), progressive disease 3 (7%), and not evaluable 6 (14%)). Three patients (7%) remained in complete response at 30, 34, and 84 months post-treatment. The treatment procedure was generally well tolerated. Swelling of the mucosa was observed in the first days after treatment. Pain and use of pain medication rose temporarily; fatigue and dysphagia were also noted in the quality of life assessment.
CONCLUSION: Electrochemotherapy can be applied to mucosal head and neck recurrent tumours accessible to the procedure with promising objective response, survival and toxicity profile. Attention should be paid to post-treatment swelling and planning of pain medication. These favourable results indicate that electrochemotherapy could play a role in patients with recurrent head and neck cancer.
Groselj A, Bosnjak M, Strojan P, et al.
Efficiency of electrochemotherapy with reduced bleomycin dose in the treatment of nonmelanoma head and neck skin cancer: Preliminary results.
Head Neck. 2018; 40(1):120-125 [PubMed] Related Publications
Efficiency of electrochemotherapy with reduced bleomycin dose in the treatment of nonmelanoma head and neck skin cancer: Preliminary results.
Head Neck. 2018; 40(1):120-125 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: In the present study, effectiveness of electrochemotherapy was compared in patients with nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC) of the head and neck using standard and reduced doses of bleomycin.
METHODS: Twenty-eight patients older than 65 years were prospectively treated with electrochemotherapy for nonmelanoma head and neck skin cancer. In the experimental group (n = 12 patients; 24 lesions), reduced bleomycin doses (10 000 IU/m
RESULTS: Complete tumor response at 2 months post-electrochemotherapy with the reduced bleomycin dose was 100% and with the standard bleomycin dose it was 96%. No statistically significant difference regarding skin toxicity was observed between the 2 groups (P = .20). Skin toxicity of grade 3 or less was recorded only in the control group (7% of treated lesions).
CONCLUSION: Presented results show the comparable antitumor effectiveness of electrochemotherapy when using standard or reduced bleomycin dose in elderly patients with nonmelanoma head and neck skin cancer.
METHODS: Twenty-eight patients older than 65 years were prospectively treated with electrochemotherapy for nonmelanoma head and neck skin cancer. In the experimental group (n = 12 patients; 24 lesions), reduced bleomycin doses (10 000 IU/m
RESULTS: Complete tumor response at 2 months post-electrochemotherapy with the reduced bleomycin dose was 100% and with the standard bleomycin dose it was 96%. No statistically significant difference regarding skin toxicity was observed between the 2 groups (P = .20). Skin toxicity of grade 3 or less was recorded only in the control group (7% of treated lesions).
CONCLUSION: Presented results show the comparable antitumor effectiveness of electrochemotherapy when using standard or reduced bleomycin dose in elderly patients with nonmelanoma head and neck skin cancer.
Cary C, Jacob JM, Albany C, et al.
Long-Term Survival of Good-Risk Germ Cell Tumor Patients After Postchemotherapy Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection: A Comparison of BEP × 3 vs. EP × 4 and Treating Institution.
Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018; 16(2):e307-e313 [PubMed] Related Publications
Long-Term Survival of Good-Risk Germ Cell Tumor Patients After Postchemotherapy Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection: A Comparison of BEP × 3 vs. EP × 4 and Treating Institution.
Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018; 16(2):e307-e313 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Patients with International Germ Cell Cancer Collaborative Group (IGCCCG) good-risk testicular cancer might receive either 4 cycles of etoposide and cisplatin (EP × 4) or 3 cycles of bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin (BEP × 3). We sought to examine differences in survival after retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (PC-RPLND) between patients who received EP × 4 compared with BEP × 3.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: The Indiana University Testis Cancer database was queried to identify IGCCCG good-risk PC-RPLND patients who received either EP × 4 or BEP × 3 induction chemotherapy. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS). Kaplan-Meier plots were generated for the EP × 4 and BEP × 3 groups and compared using the log rank test. Cox regression analysis was used to determine risk of mortality.
RESULTS: A total of 223 patients met inclusion criteria between 1985 and 2011. Induction chemotherapy consisted of EP × 4 in 45 (20%) patients and BEP × 3 in 178 (80%). Most patients (78%) received their chemotherapy at outside institutions and were subsequently referred for PC-RPLND. The location of treating institution did not influence outcomes significantly when similar chemotherapy regimens were compared in this good-risk cohort. The 10-year OS for the EP × 4 and BEP × 3 groups were 91% and 98%, respectively (log rank P < .01). The adjusted risk of death in the EP × 4 group showed a nonsignificant trend of 3 times greater compared with the BEP × 3 group (hazard ratio, 3.1; 95% confidence interval, 0.8-12.0; P = .10).
CONCLUSION: The regimen of BEP × 3 resulted in a trend toward improved survival, however, this did not reach statistical significance. The location of treating institution seems less important in this risk group of patients.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: The Indiana University Testis Cancer database was queried to identify IGCCCG good-risk PC-RPLND patients who received either EP × 4 or BEP × 3 induction chemotherapy. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS). Kaplan-Meier plots were generated for the EP × 4 and BEP × 3 groups and compared using the log rank test. Cox regression analysis was used to determine risk of mortality.
RESULTS: A total of 223 patients met inclusion criteria between 1985 and 2011. Induction chemotherapy consisted of EP × 4 in 45 (20%) patients and BEP × 3 in 178 (80%). Most patients (78%) received their chemotherapy at outside institutions and were subsequently referred for PC-RPLND. The location of treating institution did not influence outcomes significantly when similar chemotherapy regimens were compared in this good-risk cohort. The 10-year OS for the EP × 4 and BEP × 3 groups were 91% and 98%, respectively (log rank P < .01). The adjusted risk of death in the EP × 4 group showed a nonsignificant trend of 3 times greater compared with the BEP × 3 group (hazard ratio, 3.1; 95% confidence interval, 0.8-12.0; P = .10).
CONCLUSION: The regimen of BEP × 3 resulted in a trend toward improved survival, however, this did not reach statistical significance. The location of treating institution seems less important in this risk group of patients.
Kroupa M, Polivkova Z, Rachakonda S, et al.
Bleomycin-induced chromosomal damage and shortening of telomeres in peripheral blood lymphocytes of incident cancer patients.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2018; 57(2):61-69 [PubMed] Related Publications
Bleomycin-induced chromosomal damage and shortening of telomeres in peripheral blood lymphocytes of incident cancer patients.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2018; 57(2):61-69 [PubMed] Related Publications
Disruption of genomic integrity due to deficient DNA repair capacity and telomere shortening constitute hallmarks of malignant diseases. Incomplete or deficient repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) is manifested by chromosomal aberrations and their frequency reflects inter-individual differences of response to exposure to mutagenic compounds. In this study, we investigated chromosomal integrity in peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) from newly diagnosed cancer patients, including 47 breast (BC) and 44 colorectal cancer (CRC) patients and 90 matched healthy controls. Mutagen sensitivity was evaluated by measuring chromatid breaks (CTAs) induced by bleomycin and supplemented by the chemiluminescent measurement of γ-H2AX phosphorylation in 19 cancer patients (11 BC, 8 CRC). Relative telomere length (RTL) was determined in 22 BC, 32 CRC, and 64 controls. We observed statistically significant increased level of CTAs (P = .03) and increased percentage of aberrant cells (ACs) with CTAs (P = .05) in CRC patients compared with controls after bleomycin treatment. No differences were observed between BC cases and corresponding controls. CRC and BC patients with shorter RTL (below median) exhibited significantly higher amount of ACs (P = .02), CTAs (P = .02), and cells with high frequency of CTAs (≥12 CTAs/PBL; P = .03) after bleomycin treatment. No such associations were observed in healthy controls. γ-H2AX phosphorylation after bleomycin treatment in PBL did not differ between CRC and BC patients. Our results suggest that altered DSB repair measured by sensitivity towards mutagen in PBL occurs particularly in CRC carcinogenesis. Irrespective of cancer type, telomere shortening may be associated with a decreased capacity to repair DSB.
Hirabayashi F, Iwanaga K, Okinaga T, et al.
Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted sonoporation with microbubbles enhances therapeutic efficacy in a squamous cell carcinoma model.
PLoS One. 2017; 12(9):e0185293 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted sonoporation with microbubbles enhances therapeutic efficacy in a squamous cell carcinoma model.
PLoS One. 2017; 12(9):e0185293 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 30/10/2019 Related Publications
Sonoporation is a drug and gene delivery system using ultrasonication that allows the intracellular delivery of foreign molecules that cannot enter cells under normal conditions. We previously reported that sonoporation with microbubbles (MBs) could achieve effective intracellular drug delivery to human gingival squamous carcinoma Ca9-22 cells. In this study, we developed anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibody-conjugated MBs (EGFR-MBs) and evaluated their capacity to enhance anti-cancer drug toxicity in vitro and in vivo. We first assessed the effect of sonoporation with EGFR-MBs on Ca9-22 cells by the WST-8 assay, flow cytometry and Hoechst's staining in vitro. Sonoporation and EGFR-MB had a strong cytotoxic effect on Ca9-22 cells with low-dose bleomycin. Furthermore, bleomycin delivery using sonoporation with EGFR-MBs remarkably increased the number of apoptotic cells. We next examined the effect of EGFR-MBs in a murine squamous cell carcinoma model. Bleomycin delivery by sonoporation with EGFR-MBs exhibited remarkable antitumor activity. Together, our results show that EGFR-MBs and ultrasound treatment increases the efficacy and specificity of intracellular drug uptake, suggesting this could be a novel drug-targeting modality for oral squamous cell carcinoma chemotherapy treatment.
Madabhavi I, Modi G, Patel A, et al.
Pulmonary toxicity following bleomycin use: A single-center experience.
J Cancer Res Ther. 2017 Jul-Sep; 13(3):466-470 [PubMed] Related Publications
Pulmonary toxicity following bleomycin use: A single-center experience.
J Cancer Res Ther. 2017 Jul-Sep; 13(3):466-470 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Bleomycin-induced pulmonary (BIP) toxicity is a notorious entity and cropped up in roughly 10% of cases. The aim of the study is to evaluate BIP at our tertiary care cancer center.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: This is a retrospective, analytical study conducted at a tertiary care center from January 1998 to December 2012. Records of all the patients who were offered bleomycin chemotherapy as an integral part of adriamycin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine or bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin regimen in Hodgkin disease (HD) or germ cell tumor (GCT) were studied for the study inclusion criteria. Twenty-two patients treated with bleomycin who had respiratory symptoms and/or abnormal high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) findings, suggestive of bleomycin-induced lung injury were included in this study. Results and Statistical Analysis: A total of 22 patients met the inclusion criteria for the study cohort. Of 22 patients, 8 were of HD and 14 were of GCT (nonseminomatous GCT [NSGCT] = 10 and seminomatous GCT = 4). Of 22 patients, 14 had symptoms of nonproductive cough, dyspnea and showed HRCT findings of ground glass opacities, diffuse alveolar damage, extensive reticular markings, traction bronchiectasis, and/or nodular densities. Two patients had fever and pleuritic pain. Eight patients were asymptomatic. Symptomatic patients were treated with prednisone at the dose of 0.75-1 mg/kg 4-8 weeks then gradually tapered. Four patients required noninvasive ventilatory support and managed with oxygen, nebulization, and antibiotics. Two patients required mechanical ventilatory support (HD = 1 and NSGCT = 1) and developed multiorgan failure subsequently succumbed to death.
CONCLUSION: BIP is noteworthy lung toxicity as subsequent mortality ranges from 10% to 20% and shrinks survival rate in patients with highly curable malignant conditions. Physicians should be vigilant concerning this impending side effect.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: This is a retrospective, analytical study conducted at a tertiary care center from January 1998 to December 2012. Records of all the patients who were offered bleomycin chemotherapy as an integral part of adriamycin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine or bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin regimen in Hodgkin disease (HD) or germ cell tumor (GCT) were studied for the study inclusion criteria. Twenty-two patients treated with bleomycin who had respiratory symptoms and/or abnormal high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) findings, suggestive of bleomycin-induced lung injury were included in this study. Results and Statistical Analysis: A total of 22 patients met the inclusion criteria for the study cohort. Of 22 patients, 8 were of HD and 14 were of GCT (nonseminomatous GCT [NSGCT] = 10 and seminomatous GCT = 4). Of 22 patients, 14 had symptoms of nonproductive cough, dyspnea and showed HRCT findings of ground glass opacities, diffuse alveolar damage, extensive reticular markings, traction bronchiectasis, and/or nodular densities. Two patients had fever and pleuritic pain. Eight patients were asymptomatic. Symptomatic patients were treated with prednisone at the dose of 0.75-1 mg/kg 4-8 weeks then gradually tapered. Four patients required noninvasive ventilatory support and managed with oxygen, nebulization, and antibiotics. Two patients required mechanical ventilatory support (HD = 1 and NSGCT = 1) and developed multiorgan failure subsequently succumbed to death.
CONCLUSION: BIP is noteworthy lung toxicity as subsequent mortality ranges from 10% to 20% and shrinks survival rate in patients with highly curable malignant conditions. Physicians should be vigilant concerning this impending side effect.



 Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Hypopharyngeal Cancer