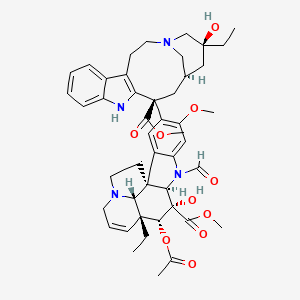
Vincristine
"Antitumor alkaloid isolated from Vinca Rosea. (Merck, 11th ed.)" (MeSH 2013)
Found this page useful?
 Web Resources: Vincristine
Web Resources: Vincristine Latest Research Publications
Latest Research PublicationsWeb Resources: Vincristine (6 links)
Cancer Research UK
Macmillan Cancer Support
NHS Evidence
 Vincristine - Substance Summary
Vincristine - Substance Summary
PubChem
Irish Cancer Society
MedlinePlus.gov
Latest Research Publications
This list of publications is regularly updated (Source: PubMed).
Kim JY, Park YJ, Lee BM, Yoon S
Co-treatment With HIV Protease Inhibitor Nelfinavir Greatly Increases Late-phase Apoptosis of Drug-resistant KBV20C Cancer Cells Independently of P-Glycoprotein Inhibition.
Anticancer Res. 2019; 39(7):3757-3765 [PubMed] Related Publications
Co-treatment With HIV Protease Inhibitor Nelfinavir Greatly Increases Late-phase Apoptosis of Drug-resistant KBV20C Cancer Cells Independently of P-Glycoprotein Inhibition.
Anticancer Res. 2019; 39(7):3757-3765 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND/AIM: The study focused on identifying the mechanisms or drugs that might sensitize resistant KBV20C human oral squamous carcinoma cells overexpressing P-glycoprotein (P-gp) to antimitotic drug treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Five HIV protease inhibitors (atazanavir, nelfinavir, darunavir, lopinavir, and ritonavir) were tested to identify drugs that could be used at a relatively low dose for sensitizing antimitotic drug-resistant KBV20C cells. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting, annexin V analyses, and rhodamine uptake tests were performed to further investigate the mechanism of action.
RESULTS: Co-treatment with nelfinavir or lopinavir had a high sensitizing effect on vincristine-treated KBV20C cells. Nelfinavir and lopinavir reduced cell viability, increased G
CONCLUSION: Highly antimitotic drug-resistant KBV20C cells can be sensitized by co-treatment with the repositioned HIV protease inhibitors nelfinavir and lopinavir. In particular, the sensitizing effect of co-treatment with nelfinavir on antimitotic drug-resistant cancer cells was found to be strong and independent of P-gp-inhibitory activity. As P-gp inhibition can be toxic to normal cells, selecting nelfinavir may be safer for normal cells in patients with drug-resistant cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Five HIV protease inhibitors (atazanavir, nelfinavir, darunavir, lopinavir, and ritonavir) were tested to identify drugs that could be used at a relatively low dose for sensitizing antimitotic drug-resistant KBV20C cells. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting, annexin V analyses, and rhodamine uptake tests were performed to further investigate the mechanism of action.
RESULTS: Co-treatment with nelfinavir or lopinavir had a high sensitizing effect on vincristine-treated KBV20C cells. Nelfinavir and lopinavir reduced cell viability, increased G
CONCLUSION: Highly antimitotic drug-resistant KBV20C cells can be sensitized by co-treatment with the repositioned HIV protease inhibitors nelfinavir and lopinavir. In particular, the sensitizing effect of co-treatment with nelfinavir on antimitotic drug-resistant cancer cells was found to be strong and independent of P-gp-inhibitory activity. As P-gp inhibition can be toxic to normal cells, selecting nelfinavir may be safer for normal cells in patients with drug-resistant cancer.
Wawro ME, Sobierajska K, Ciszewski WM, Niewiarowska J
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Prevent Vincristine-Dependent Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Formation.
Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(8) [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Prevent Vincristine-Dependent Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Formation.
Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(8) [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Vincristine is used in the clinical treatment of colon cancer, especially in patients diagnosed in the advanced phase of cancer development. Unfortunately, similar to other agents used during antitumor therapy, vincristine might induce chemoresistance. Studies of this process focus mainly on the analysis of the molecular mechanisms within cancer, usually ignoring the role of stromal cells. Our present findings confirm that vincristine stimulates the secretion of tumor growth factors class beta and interleukin-6 from cancer-associated fibroblasts as a result of paracrine stimulation by cancer cells. Based on alterations in morphology, modulation of capillary formation, and changes in endothelial and mesenchymal marker profile, our findings demonstrate that higher levels of tumor growth factor-βs and interleukin-6 enhance cancer-associated fibroblast-like cell formation through endothelial-mesenchymal transition and that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug treatment (aspirin and ibuprofen) is able to inhibit this phenomenon. The process appears to be regulated by the rate of microtubule polymerization, depending on β-tubulin composition. While higher levels of tubulin-β2 and tubulin-β4 caused slowed polymerization and reduced the level of factors secreted to the extracellular matrix, tubulin-β3 induced the opposite effect. We conclude that nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be considered for use during vincristine monotherapy in the treatment of patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer.
Patil S, Sankpal UT, Hurtado M, et al.
Combination of clotam and vincristine enhances anti-proliferative effect in medulloblastoma cells.
Gene. 2019; 705:67-76 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
Combination of clotam and vincristine enhances anti-proliferative effect in medulloblastoma cells.
Gene. 2019; 705:67-76 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
Medulloblastoma (MB) is characterized by highly invasive embryonal neuro-epithelial tumors that metastasize via cerebrospinal fluid. MB is difficult to treat and the chemotherapy is associated with significant toxicities and potential long-term disabilities. Previously, we showed that small molecule, clotam (tolfenamic acid: TA) inhibited MB cell proliferation and tumor growth in mice by targeting, survivin. Overexpression of survivin is associated with aggressiveness and poor prognosis in several cancers, including MB. The aim of this study was to test combination treatment involving Vincristine® (VCR), a standard chemotherapeutic drug for MB and TA against MB cells. DAOY and D283 MB cells were treated with 10 μg/mL TA or VCR (DAOY: 2 ng/mL; D283: 1 ng/mL) or combination (TA + VCR). These optimized doses were lower than individual IC
Taghizadehghalehjoughi A, Sezen S, Hacimuftuoglu A, Güllüce M
Vincristine combination with Ca
Mol Biol Rep. 2019; 46(2):2523-2528 [PubMed] Related Publications
Vincristine combination with Ca
Mol Biol Rep. 2019; 46(2):2523-2528 [PubMed] Related Publications
In this study, it was aimed to determine the effects of Amlodipine, a calcium channel blocker and vincristine (VCR) an antineoplastic, on human neuroblastomas using different doses. The cytotoxicity assays of the study were performed using the MTT method depending on time and concentration. After obtaining the mixture (up to 85% for SH-SY5Y) and sufficient branches (cortex neurons), the cells were treated with amlodipine (10 µM) and vincristine (0.5, 1 and 2 µg) at different concentrations for 24 h. MTT assay was performed by the commercially available kit (Sigma Aldrich, USA). Cells were harvested, washed and stained with PI and Annexin V, respectively, according to the manufacturer's protocol (Biovision, USA). Than analyzes were carried out. The results were quite impressive. When amlodipine (10 µM) was administered alone there was little change compared to the control. However, all doses of amlodipine (10 µM) and vincristine (0.5, 1 and 2 µg) were greater than the deaths in the doses alone (0.5, 1 and 2 µg) of vincristine alone. (P < 0.05). As a result, the combination of vincristine and amlodipine is more effective than vincristine alone in reducing the viability of cancer cells.
Timin AS, Peltek OO, Zyuzin MV, et al.
Safe and Effective Delivery of Antitumor Drug Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells Impregnated with Submicron Carriers.
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019; 11(14):13091-13104 [PubMed] Related Publications
Safe and Effective Delivery of Antitumor Drug Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells Impregnated with Submicron Carriers.
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019; 11(14):13091-13104 [PubMed] Related Publications
An important area in modern malignant tumor therapy is the optimization of antitumor drugs pharmacokinetics. The use of some antitumor drugs is limited in clinical practice due to their high toxicity. Therefore, the strategy for optimizing the drug pharmacokinetics focuses on the generation of high local concentrations of these drugs in the tumor area with minimal systemic and tissue-specific toxicity. This can be achieved by encapsulation of highly toxic antitumor drug (vincristine (VCR) that is 20-50 times more toxic than widely used the antitumor drug doxorubicin) into nano- and microcarriers with their further association into therapeutically relevant cells that possess the ability to migrate to sites of tumor. Here, we fundamentally examine the effect of drug carrier size on the behavior of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs), including internalization efficiency, cytotoxicity, cell movement, to optimize the conditions for the development of carrier-hMSCs drug delivery platform. Using the malignant tumors derived from patients, we evaluated the capability of hMSCs associated with VCR-loaded carriers to target tumors using a three-dimensional spheroid model in collagen gel. Compared to free VCR, the developed hMSC-based drug delivery platform showed enhanced antitumor activity regarding those tumors that express CXCL12 (stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)) gene, inducing directed migration of hMSCs via CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway. These results show that the combination of encapsulated antitumor drugs and hMSCs, which possess the properties of active migration into tumors, is therapeutically beneficial and demonstrated high efficiency and low systematic toxicity, revealing novel strategies for chemotherapy in the future.
Han Z, Huang H, Zhang T
Downregulation of
J Cancer Res Ther. 2019 Jan-Mar; 15(1):38-41 [PubMed] Related Publications
Downregulation of
J Cancer Res Ther. 2019 Jan-Mar; 15(1):38-41 [PubMed] Related Publications
Objective: This study was aimed to investigate the relationship between the expression of drebrin (DBN1) gene and resistance in colon cancer to reveal the mechanism of tumor drug resistance and provide a basis for the reversal of this drug resistance in tumor cells.
Materials and Methods: The human colon carcinoma cell line HCT-8 was used, and vincristine (VCR)-resistant colon cancer cell line HCT-8/V was established by gradually increasing the concentration of VCR. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers were designed for DBN1 gene. The DBN1 differential expression in colon cancer sensitive and resistant cell lines was detected by fluorescence quantitative PCR. Western blot analysis was used to study DBN1 expression in the resistant cells further.
Results: VCR resistance of HCT-8/V cell line was established. Quantitative PCR and Western blot results showed that DBN1 expression in the resistant cell line was significantly lower, the difference being statistically significant (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Low DBN1 gene expression may be associated with colon cancer cell resistance to VCR.
Materials and Methods: The human colon carcinoma cell line HCT-8 was used, and vincristine (VCR)-resistant colon cancer cell line HCT-8/V was established by gradually increasing the concentration of VCR. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers were designed for DBN1 gene. The DBN1 differential expression in colon cancer sensitive and resistant cell lines was detected by fluorescence quantitative PCR. Western blot analysis was used to study DBN1 expression in the resistant cells further.
Results: VCR resistance of HCT-8/V cell line was established. Quantitative PCR and Western blot results showed that DBN1 expression in the resistant cell line was significantly lower, the difference being statistically significant (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Low DBN1 gene expression may be associated with colon cancer cell resistance to VCR.
Ambar NBD, de Seixas Alves MT, Lederman HM, et al.
Irinotecan and vincristine for the treatment of refractory desmoplastic small round cell tumor in a developing country: a case report.
J Med Case Rep. 2019; 13(1):77 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
Irinotecan and vincristine for the treatment of refractory desmoplastic small round cell tumor in a developing country: a case report.
J Med Case Rep. 2019; 13(1):77 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
INTRODUCTION: Desmoplastic small round cell tumor is an extremely rare and aggressive cancer that affects mainly adolescents and young adults. Despite multiple therapeutic strategies, most patients have resistant disease with very poor survival rates.
CASE PRESENTATION: We present a case of a 10-year-old Caucasian boy with a desmoplastic small round cell tumor refractory to conventional treatment who exhibited a good response to alternative treatment. With use of irinotecan and vincristine in association with radiation therapy, a reduction of 96.9% of the dimensions of the target lesions compared with the initial image was observed.
CONCLUSION: This chemotherapy regimen, in association with radiation therapy, demonstrated efficacy for refractory desmoplastic small round cell tumor in our patient, and it is cost-effective.
CASE PRESENTATION: We present a case of a 10-year-old Caucasian boy with a desmoplastic small round cell tumor refractory to conventional treatment who exhibited a good response to alternative treatment. With use of irinotecan and vincristine in association with radiation therapy, a reduction of 96.9% of the dimensions of the target lesions compared with the initial image was observed.
CONCLUSION: This chemotherapy regimen, in association with radiation therapy, demonstrated efficacy for refractory desmoplastic small round cell tumor in our patient, and it is cost-effective.
Reynolds SB, Hashmi H, Ngo P, Kloecker G
Rescue therapy for acute idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura unresponsive to conventional treatment.
BMJ Case Rep. 2019; 12(1) [PubMed] Related Publications
Rescue therapy for acute idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura unresponsive to conventional treatment.
BMJ Case Rep. 2019; 12(1) [PubMed] Related Publications
A 61-year-old woman with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, with Richter's transformation to a diffuse, large, B-cell lymphoma, treated with six cycles of rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone and in complete remission, presented to the hospital after her platelets were found to be 2×10³/µL in outpatient laboratory studies. She initially underwent a platelet transfusion without improvement. This was followed by 4 days of high-dose dexamethasone and intravenous immunoglobulin, which again yielded no meaningful effect. Even a single-dose rituximab failed to achieve a platelet increase after 5 days of monitoring. The patient was then given 2 mg of intravenous vincristine along with a high-dose of dexamethasone and IVIG and demonstrated substantial recovery in platelets to >50×10³/µL within 48 hours. This case study provides an overview of the current management strategies for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura that is unresponsive to conventional medical therapy and particularly sheds light on their therapeutic benefits and potential adverse effects.
Tu HJ, Lin YJ, Chao MW, et al.
The anticancer effects of MPT0G211, a novel HDAC6 inhibitor, combined with chemotherapeutic agents in human acute leukemia cells.
Clin Epigenetics. 2018; 10(1):162 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
The anticancer effects of MPT0G211, a novel HDAC6 inhibitor, combined with chemotherapeutic agents in human acute leukemia cells.
Clin Epigenetics. 2018; 10(1):162 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
BACKGROUND: There are some limitations of standard chemotherapy for acute leukemia. Vincristine and doxorubicin are commonly used for acute leukemia, but they may induce serious side effects such as cardiomyopathy and neurotoxicity. Furthermore, chemotherapy resistance occurs more and more frequently. Therefore, effective treatment strategies are needed. Histone deacetylase 6 inhibition is considered as a potential therapeutic strategy for acute leukemia, since it is observed that HDAC6 is overexpressed in acute leukemia and regulates tumor survival. Combination therapy for cancer is used to minimize adverse drug effects, reduce drug dosage, enhance efficacy, and prevent drug resistance. In order to improve efficacy of chemotherapy agents of acute leukemia, this study will investigate the effects of combination MPT0G211, a novel histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor, with doxorubicin or vincristine on human acute leukemia cells.
RESULTS: MPT0G211 combined with doxorubicin induces DNA damage response on human acute myeloid leukemia cells. MPT0G211 can additionally increase Ku70 acetylation and release BAX to mitochondria. Ectopic expression of HDAC6 successively reversed the apoptosis triggered by the combined treatment. Moreover, co-treatment of MPT0G211 and vincristine may alter microtubule dynamics, triggering acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells arrest in mitotic phase followed by induction of the apoptotic pathway. Finally, MPT0G211 plus doxorubicin or vincristine can significantly improve the tumor growth delay in a tumor xenograft model.
CONCLUSIONS: Collectively, our data highlighted that MPT0G211 in combination with chemotherapy drugs has significant anticancer activity, suggesting a novel strategy for the treatment of acute leukemia.
RESULTS: MPT0G211 combined with doxorubicin induces DNA damage response on human acute myeloid leukemia cells. MPT0G211 can additionally increase Ku70 acetylation and release BAX to mitochondria. Ectopic expression of HDAC6 successively reversed the apoptosis triggered by the combined treatment. Moreover, co-treatment of MPT0G211 and vincristine may alter microtubule dynamics, triggering acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells arrest in mitotic phase followed by induction of the apoptotic pathway. Finally, MPT0G211 plus doxorubicin or vincristine can significantly improve the tumor growth delay in a tumor xenograft model.
CONCLUSIONS: Collectively, our data highlighted that MPT0G211 in combination with chemotherapy drugs has significant anticancer activity, suggesting a novel strategy for the treatment of acute leukemia.
Nazzaro G, Genovese G, Tourlaki A, et al.
Ultrasonographic intraoperative monitoring and follow-up of Kaposi's sarcoma nodules under treatment with intralesional vincristine.
Skin Res Technol. 2019; 25(2):200-203 [PubMed] Related Publications
Ultrasonographic intraoperative monitoring and follow-up of Kaposi's sarcoma nodules under treatment with intralesional vincristine.
Skin Res Technol. 2019; 25(2):200-203 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Intralesional vincristine is an effective treatment for Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) nodules on the skin, but there is little evidence of its action through imaging techniques. Ultrasonography can be an adjunctive tool in the diagnosis and management of KS skin lesions, but data in the literature are few.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Five patients with classic KS nodules were treated with intralesional vincristine. Ultrasonographic and color Doppler assessment were performed during vincristine injection and monitoring was repeated 1 and 3 months after the procedure. Partial response was defined as a reduction of more than 50% lesion volume and reduction of the vascular signal; complete response as a resolution of lesion associated with the absence of vascular signal.
RESULTS: Six KS nodules were included in the study. On ultrasonography examination, KS nodules appeared as oval or round, hypoechoic, homogeneous structures, with intralesional vascularization, more prominent in the deepest pole of the nodule. At month 1, 4 nodules achieved a complete response, while two nodules showed a partial response and were retreated with intralesional vincristine. At month 3, all lesions achieved a complete response.
CONCLUSION: Ultrasonography may be a valuable tool in assessing clinical response to intralesional vincristine therapy of cutaneous KS nodules.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Five patients with classic KS nodules were treated with intralesional vincristine. Ultrasonographic and color Doppler assessment were performed during vincristine injection and monitoring was repeated 1 and 3 months after the procedure. Partial response was defined as a reduction of more than 50% lesion volume and reduction of the vascular signal; complete response as a resolution of lesion associated with the absence of vascular signal.
RESULTS: Six KS nodules were included in the study. On ultrasonography examination, KS nodules appeared as oval or round, hypoechoic, homogeneous structures, with intralesional vascularization, more prominent in the deepest pole of the nodule. At month 1, 4 nodules achieved a complete response, while two nodules showed a partial response and were retreated with intralesional vincristine. At month 3, all lesions achieved a complete response.
CONCLUSION: Ultrasonography may be a valuable tool in assessing clinical response to intralesional vincristine therapy of cutaneous KS nodules.
Cheng C, Xie Z, Li Y, et al.
PTBP1 knockdown overcomes the resistance to vincristine and oxaliplatin in drug-resistant colon cancer cells through regulation of glycolysis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 108:194-200 [PubMed] Related Publications
PTBP1 knockdown overcomes the resistance to vincristine and oxaliplatin in drug-resistant colon cancer cells through regulation of glycolysis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 108:194-200 [PubMed] Related Publications
Drug-resistant cancer cells exhibit increased glycolysis, and targeting glycolysis is considered as a novel strategy to overcome drug resistance. Polypyrimidine tract-binding protein (PTBP1) has been found to be a regulator of glycolysis, however, the role of PTBP1 in drug resistance remains to be elucidated. Herein, we found that PTBP1 was highly expressed in two drug-resistant colon cancer cell lines, vincristine-resistant HCT-8 cell line (HCT-8/V) and oxaliplatin-resistant HCT116 cell line (HCT116/L-OHP). The levels of glucose consumption and lactate production as well as expression of pyruvate kinase M2 isoform (PKM2) and hexokinase II (HK2) were elevated, while PKM1 level was reduced in HCT-8/V and HCT116/L-OHP cells when compared with the HCT-8 and HCT116 cells. PTBP1 knockdown enhanced the sensitivity of HCT-8/V and HCT116/L-OHP cells to vincristine and oxaliplatin, and caused reduction in glucose consumption and lactate production. PKM2 expression, but not HK2, was decreased and PKM1 expression level was increased in cells transfected with si-PTBP1. In addition, PTBP1 overexpression significantly induced glycolysis and reduced drug sensitivity, whereas the effects were attenuated by si-PKM2. Treatment with 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) also attenuated the effect of PTBP1 overexpression on drug sensitivity. In conclusion, PTBP1 knockdown enhanced the sensitivity of drug-resistant colon cancer cells to vincristine and oxaliplatin through repression of glycolysis. Our study provided a promising therapeutic strategy to overcome drug resistance in colon cancer cells.
Torres Á, Arriagada V, Erices JI, et al.
FK506 Attenuates the MRP1-Mediated Chemoresistant Phenotype in Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells.
Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(9) [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
FK506 Attenuates the MRP1-Mediated Chemoresistant Phenotype in Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells.
Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(9) [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
Poor response to current treatments for glioblastoma has been attributed to the presence of glioblastoma stem-like cells (GSCs). GSCs are able to expel antitumor drugs to the extracellular medium using the multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1) transporter. Tacrolimus (FK506) has been identified as an MRP1 regulator in differentiated glioblastoma (GBM) cells (non-GSCs); however, the effect of FK506 on GSCs is currently unknown. The objective of the following research is to evaluate the effect of FK506 on the MRP1-related chemo-resistant phenotype of GSCs. For this, U87MG and C6 glioma cell lines were used to generate non-GSCs and GSCs. mRNA and MRP1-positive cells were evaluated by RT-qPCR and flow cytometry, respectively. A Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate (CFDA)-retention assay was performed to evaluate the MRP1 activity. Apoptosis and MTT assays were employed to evaluate the cytotoxic effects of FK506 plus Vincristine (MRP1 substrate). GSC-derived subcutaneous tumors were generated to evaluate the in vivo effect of FK506/Vincristine treatment. No differences in transcript levels and positive cells for MRP1 were observed in FK506-treated cells. Lesser cell viability, increased apoptosis, and CFDA-retention in the FK506/Vincristine-treated cells were observed. In vivo, the FK506/Vincristine treatment decreased the tumor size as well as ki67, Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP), and nestin expression. We conclude that FK506 confers a chemo-sensitive phenotype to MRP1-drug substrate in GSCs.
Das K, Singh S, Kalra B, Agrawal N
Oesophageal narrowing during combination chemotherapy in Ewing's sarcoma: Is vincristine a culprit?
BMJ Case Rep. 2018; 2018 [PubMed] Related Publications
Oesophageal narrowing during combination chemotherapy in Ewing's sarcoma: Is vincristine a culprit?
BMJ Case Rep. 2018; 2018 [PubMed] Related Publications
Vincristine is a widely used chemotherapeutic agent in paediatric oncology. A 7-year-old boy was diagnosed with non-metastatic Ewing's sarcoma of the pelvis. He was started on chemotherapy with vincristine-cyclophosphamide-adriamycin alternate with ifosfamide-etoposide. He developed recurrent vomiting after three cycles of chemotherapy. Evaluation showed oesophageal stricture involving the middle and lower third part. Biopsy was non-conclusive. His symptoms improved with dilatation. A chemotherapy-induced neuropathic dysmotility was suspected, and his chemotherapy was continued with serial dilatation. Vincristine, being neurotoxic, was suspected to be the reason of this morbidity. His need of dilatation decreased, and symptoms improved remarkably after completion of chemotherapy.Vincristine-induced oesophageal dysmotility is a rare side effect. There is no consensus on management. Omission of this effective agent in such situation is debatable.
Niu Y, Yin R, Wang D, et al.
Clinical analysis of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced vulvar cancer: A STROBE-compliant article.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(34):e11786 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
Clinical analysis of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced vulvar cancer: A STROBE-compliant article.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(34):e11786 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
To investigate the effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with advanced vulvar cancer and to provide references for clinical treatment.Clinical and pathological data of 12 patients with advanced vulvar carcinoma were collected. The response and operability rates, adverse effects, and prognosis of neoadjuvant chemotherapy were retrospectively analyzed.The mean patient age was 45.8 (range 26-69) years. Among 12 patients, 9 underwent treatment with bleomycin and cisplatin with or without vincristine. The overall response rate was 67%. Five patients (56%) experienced grade 1 or 2 bone marrow suppression or gastrointestinal reactions. Seven patients (78%) underwent radical surgery. The mean overall survival time was 34.1 (range 3-69) months, the mean progression free survival time was 26 (range 3-69) months, and the 1-year survival rate was 83%. The other 3 patients received combined paclitaxel and cisplatin treatment. The overall response rate was 67%. All 3 patients (100%) experienced grade 2 hair loss or anemia and 2 of them (67%) underwent radical vulvectomy. The mean overall survival time was 11.7 (range 5-15) months, the mean progression free survival time was 7.7 (range 3-15) months and the 1-year survival rate was 100%. Time to overall survival and progression free survival were not significantly different between the 2 groups (P = .46 and P = .39).Owing to their high overall response rate and tolerable adverse effects, either bleomycin-cisplatin-based or paclitaxel-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen can be considered a therapeutic option for advanced vulvar cancer.
Mörth C, Valachis A, Sabaa AA, et al.
Does the omission of vincristine in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma affect treatment outcome?
Ann Hematol. 2018; 97(11):2129-2135 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
Does the omission of vincristine in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma affect treatment outcome?
Ann Hematol. 2018; 97(11):2129-2135 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 15/10/2019 Related Publications
The standard treatment for diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is rituximab with CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine (VCR), and prednisone). Maintaining high dose intensity of cytotoxic treatment has been associated with better outcome but little is known about the role of maintaining VCR. This study aimed to answer whether the omission of vincristine due to neurotoxicity affects patient outcome. A Swedish cohort of patients primarily treated with curative intent for DLBCL or high-grade malignant B cell lymphoma was retrospectively analyzed. In total, 541 patients treated between 2000 and 2013 were included. Omission of VCR was decided in 95 (17.6%) patients and was more often decided during the last three cycles (n = 86, 90.5%). The omission of VCR did not affect disease-free or overall survival neither in the whole cohort nor in elderly patients. On the contrary, the relative dose intensity of doxorubicin was associated with overall survival (p = 0.014). Kidney or adrenal involvement (p = 0.014) as well as bulky disease (p = 0.037) was found to be associated with worse overall survival. According to our results, clinicians can safely decide to omit VCR in case of severe neurotoxicity due to VCR but should be aware of the importance of giving adequate doses of doxorubicin during treatment given the growing body of evidence on the role of dose intensity on survival. Considering the association of bulky disease and kidney/adrenal manifestation of lymphoma on survival, further studies should focus on whether the treatment options for these subgroups need to be individualized.
Zeki J, Taylor JS, Yavuz B, et al.
Disseminated injection of vincristine-loaded silk gel improves the suppression of neuroblastoma tumor growth.
Surgery. 2018; 164(4):909-915 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 01/10/2019 Related Publications
Disseminated injection of vincristine-loaded silk gel improves the suppression of neuroblastoma tumor growth.
Surgery. 2018; 164(4):909-915 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 01/10/2019 Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Advanced-stage neuroblastoma patients require multiagent chemotherapy. Intratumoral implantation of vincristine-loaded silk gel uses local diffusion to decrease orthotopic neuroblastoma tumor growth in mice. We hypothesize that injecting vincristine-loaded silk gel into 8 locations within the tumor, instead of only centrally, decreases the diffusion distance and improves tumor growth suppression.
METHODS: Human neuroblastoma cells, KELLY, were injected into mouse adrenal glands to create orthotopic tumors. After the tumors reached 100 mm
RESULTS: Vincristine-loaded silk gels suppressed tumor growth up to an inflection point (458.7 ± 234.4 mm
CONCLUSION: Injecting vincristine-loaded sustained release silk gel at 8 separate locations halved the diffusion distance and doubled the time for the tumor to reach the growth inflexion point.
METHODS: Human neuroblastoma cells, KELLY, were injected into mouse adrenal glands to create orthotopic tumors. After the tumors reached 100 mm
RESULTS: Vincristine-loaded silk gels suppressed tumor growth up to an inflection point (458.7 ± 234.4 mm
CONCLUSION: Injecting vincristine-loaded sustained release silk gel at 8 separate locations halved the diffusion distance and doubled the time for the tumor to reach the growth inflexion point.
Mtonga W, Mujajati A, Munkombwe D, et al.
Therapeutic Outcomes in AIDS-Associated Kaposi's Sarcoma Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy Treated with Chemotherapy at Two Tertiary Hospitals in Lusaka, Zambia.
Curr HIV Res. 2018; 16(3):231-236 [PubMed] Related Publications
Therapeutic Outcomes in AIDS-Associated Kaposi's Sarcoma Patients on Antiretroviral Therapy Treated with Chemotherapy at Two Tertiary Hospitals in Lusaka, Zambia.
Curr HIV Res. 2018; 16(3):231-236 [PubMed] Related Publications
The incidence of HIV-associated Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) remains high in Zambia in the antiretroviral therapy era. The most efficacious treatment regimen for KS has yet to be established. In both developed and developing countries, treatment regimens have had limited efficacy. Late presentation in Africa affects therapeutic outcomes.
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to determine therapeutic outcomes of epidemic KS patients on combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) after completion of six cycles of Adriamycin, Bleomycin, and Vincristine (ABV) chemotherapy.
METHODS: This was a descriptive cross-sectional study. Study participants were drawn from a study database of confirmed incident KS patients seen at the Skin Clinic of the University Teaching Hospitals (UTH) during the period between August, 2015 and September, 2016.
RESULTS: Of the 38 successfully recruited study participants, a complete response was documented in 18 (47%) after 6 cycles of ABV whereas 20 (53%) experienced a partial response. KS recurrence was observed in 8 (44%) of the individuals that experienced an initial complete response. At the time of the study, clinical assessment revealed that KS lesions had completely regressed in 21 (55%) of all the patients.
CONCLUSION: ABV chemotherapy appears ineffective in long-term resolution of epidemic KS patients on ART. Recurrence rates are high after chemotherapy in patients that experience initially favorable responses to treatment. There is a need to diagnose KS earlier, and to develop more efficacious treatment options in order to reduce recurrence rates for epidemic KS.
OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to determine therapeutic outcomes of epidemic KS patients on combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) after completion of six cycles of Adriamycin, Bleomycin, and Vincristine (ABV) chemotherapy.
METHODS: This was a descriptive cross-sectional study. Study participants were drawn from a study database of confirmed incident KS patients seen at the Skin Clinic of the University Teaching Hospitals (UTH) during the period between August, 2015 and September, 2016.
RESULTS: Of the 38 successfully recruited study participants, a complete response was documented in 18 (47%) after 6 cycles of ABV whereas 20 (53%) experienced a partial response. KS recurrence was observed in 8 (44%) of the individuals that experienced an initial complete response. At the time of the study, clinical assessment revealed that KS lesions had completely regressed in 21 (55%) of all the patients.
CONCLUSION: ABV chemotherapy appears ineffective in long-term resolution of epidemic KS patients on ART. Recurrence rates are high after chemotherapy in patients that experience initially favorable responses to treatment. There is a need to diagnose KS earlier, and to develop more efficacious treatment options in order to reduce recurrence rates for epidemic KS.
Fernandes E Silva E, Figueira FS, Cañedo AD, et al.
C-phycocyanin to overcome the multidrug resistance phenotype in human erythroleukemias with or without interaction with ABC transporters.
Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 106:532-542 [PubMed] Related Publications
C-phycocyanin to overcome the multidrug resistance phenotype in human erythroleukemias with or without interaction with ABC transporters.
Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 106:532-542 [PubMed] Related Publications
The phenotype of multidrug resistance (MDR) is one of the main causes of chemotherapy failure. Our study investigated the effect of C-phycocyanin (C-PC) in three human erythroleukemia cell lines with or without the MDR phenotype: K562 (non-MDR; no overexpression of drug efflux proteins), K562-Lucena (MDR; overexpression of ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B/ABCB1), and FEPS (MDR; overexpression of ABCB1 and ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C/ABCC1). Using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, we showed that 20 and 200 μg/mL C-PC decreased K562 viable cells after 24 h and 200 μg/mL C-PC decreased K562-Lucena cell proliferation after 48 h. C-PC did not decrease viable cells of FEPS cells. On the other hand, the MTT assay showed that exposure of 2, 20, and 200 μg/mL C-PC for 24 or 48 h was not cytotoxic to peritoneal macrophages. At 72 h, the trypan blue exclusion assay showed that 20 μg/mL C-PC decreased K562 and K562-Lucena cell proliferation and in FEPS cells, only 200 μg/mL C-PC decreased proliferation. In addition, protein-protein docking showed differences in energy and binding sites of ABCB1 and ABCC1 for C-PC, and these results were confirmed by the efflux protein activity assay. Only ABCC1 activity was altered in the presence of C-PC and FEPS cells showed lower C-PC accumulation, suggesting C-PC extrusion by ABCC1, conferring C-PC resistance. In combination with chemotherapy (vincristine [VCR] and daunorubicin [DNR]), the sensitivity of K562-Lucena cells for C-PC + VCR did not increase, whereas FEPS cell sensitivity for C-PC + DNR was increased. In molecular docking experiments, the estimated free energies of binding for C-PC associated with chemotherapy were similar (VCR: -6.9 kcal/mol and DNR: -7.2 kcal/mol) and these drugs were located within the C-PC cavity. However, C-PC exhibited specificity for tumor cells and K562 cells were more sensitive than K562-Lucena cells, followed by FEPS cells. Thus, C-PC is a possible chemotherapeutic agent for cells with the MDR phenotype, both alone in K562-Lucena cells (resistance due to ABCB1), or in combination with other drugs for cells similar to FEPS (resistance due to ABCC1). Moreover, C-PC did not damage healthy cells (peritoneal macrophages of Mus musculus).
Sirachainan N, Pakakasama S, Anurathapan U, et al.
Outcome of newly diagnosed high risk medulloblastoma treated with carboplatin, vincristine, cyclophosphamide and etoposide.
J Clin Neurosci. 2018; 56:139-142 [PubMed] Related Publications
Outcome of newly diagnosed high risk medulloblastoma treated with carboplatin, vincristine, cyclophosphamide and etoposide.
J Clin Neurosci. 2018; 56:139-142 [PubMed] Related Publications
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor among children. Although molecular study has been included in the new classification, in developing countries with limited resources the previous Chang staging system is still used. Therefore, treatment with postoperative radiation and chemotherapy remains the standard treatment. One common complication after treatment is ototoxicity, mainly due to radiation and cisplatinum. We report a revised chemotherapy protocol, replacing cisplatinum with carboplatin in newly diagnosed medulloblastoma cases. All 23 patients in this study had high risk medulloblastoma. Mean (SD) age was 9.5 ± 3.1 years. The 5-year progression free survival (PFS), 5-year overall survival (OS), and 10-year OS were 41.8 ± 12.2%, 60.0 ± 11.2%, and 48.0 ± 14.0 respectively. Most patients had grade 3-4 hematologic toxicity. Twelve patients had hearing tests, with 11 patients having grade 0 and 1 patient having grade 1 according to the Brock criteria.
Sy A, Cheng J, Cooper R, Mueller L
Heterozygosity for CMT Type 4 Predicts a Severe Vincristine-induced Polyneuropathy Phenotype: A Case Report and Review of Literature.
J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019; 41(1):e41-e43 [PubMed] Related Publications
Heterozygosity for CMT Type 4 Predicts a Severe Vincristine-induced Polyneuropathy Phenotype: A Case Report and Review of Literature.
J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019; 41(1):e41-e43 [PubMed] Related Publications
Vincristine (VCR) is a common chemotherapeutic agent used in the treatment of multiple types of pediatric tumors. VCR's adverse effects are well documented and commonly involve peripheral neuropathy via axonal degeneration. Neuropathic severity is dose-dependent, with sensory deficits occurring with as little as 4 mg cumulative dose. Severe peripheral neuropathy is generally rare, but its effects become additive when given to patients with undiagnosed hereditary peripheral neuropathy such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth. We report a case of an effect of VCR administration given to a patient who developed grade 4 neuropathy and was found to be a carrier of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 4.
Nikanjam M, Sun A, Albers M, et al.
Vincristine-associated Neuropathy With Antifungal Usage: A Kaiser Northern California Experience.
J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2018; 40(5):e273-e277 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 01/10/2019 Related Publications
Vincristine-associated Neuropathy With Antifungal Usage: A Kaiser Northern California Experience.
J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2018; 40(5):e273-e277 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 01/10/2019 Related Publications
The dose-limiting toxicity for vincristine is peripheral neuropathy which can be potentiated with concurrent usage of azole antifungals. The current retrospective study assessed the incidence of concurrent vincristine and azole antifungal usage to determine if it led to increased neurotoxicity for the Kaiser Northern California pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and Hodgkin lymphoma patient population. Data were obtained from the electronic medical record (2007 to 2014). In total, 130 subjects received at least one dose of vincristine for ALL or Hodgkin lymphoma (median age 9, 88% ALL, 58% male, 47% Caucasian). Thirty one percent of patients received concurrent antifungal usage (fluconazole, 78%; voriconazole, 10%; fluconazole/voriconazole, 12%); however, concurrent antifungal usage accounted for <15% of vincristine doses. Grade 2 or greater neuropathy occurred in 51% of patients; grade 3 neuropathy was present in 8% of patients. No difference in the incidence of grade 2 or greater neuropathy was observed with the concurrent use of antifungal therapy (P=0.35), sex (P=0.59), type of cancer (P=0.41), ethnicity (P=0.29), or age (P=0.39), but was higher with increasing amount of vincristine doses (P=0.004). These results suggest that concurrent azole antifungal usage with vincristine for patients with ALL and Hodgkin lymphoma was low in the Kaiser Northern California population and limited usage as needed may be reasonable and safe.
Qiu L, Dong C, Kan X
Lymphoma-targeted treatment using a folic acid-decorated vincristine-loaded drug delivery system.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018; 12:863-872 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 01/10/2019 Related Publications
Lymphoma-targeted treatment using a folic acid-decorated vincristine-loaded drug delivery system.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018; 12:863-872 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 01/10/2019 Related Publications
Purpose: B-cell lymphoma is the most frequently diagnosed lymphoid tumor. Folic acid (FA)-decorated systems were found to be preferentially internalized on the B-cell lymphoma cell line which is reported to express the folate receptor. This study was designed to develop an FA-decorated vincristine (VCR)-loaded system for targeted lymphoma treatment.
Methods: FA-decorated lipid was synthesized. VCR-loaded lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles (LPNs) were fabricated. In vitro cell lines and an in vivo lymphoma animal model was used to evaluate the anti B-cell lymphoma effect.
Results: FA-decorated, VCR-loaded LPNs (FA-VCR/LPNs) have shown a targeted effect in delivery to B-cell lymphoma cells. FA-VCR/LPNs also showed the highest anti-tumor effect in murine-bearing lymphoma xenografts.
Conclusion: FA-VCR/LPNs can achieve targeted delivery of VCR, bring about an outstanding therapeutic effect to treat lymphoma, and also reduce the systemic toxicity. FA-VCR/LPNs could be an excellent system for lymphoma therapy.
Methods: FA-decorated lipid was synthesized. VCR-loaded lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles (LPNs) were fabricated. In vitro cell lines and an in vivo lymphoma animal model was used to evaluate the anti B-cell lymphoma effect.
Results: FA-decorated, VCR-loaded LPNs (FA-VCR/LPNs) have shown a targeted effect in delivery to B-cell lymphoma cells. FA-VCR/LPNs also showed the highest anti-tumor effect in murine-bearing lymphoma xenografts.
Conclusion: FA-VCR/LPNs can achieve targeted delivery of VCR, bring about an outstanding therapeutic effect to treat lymphoma, and also reduce the systemic toxicity. FA-VCR/LPNs could be an excellent system for lymphoma therapy.
Bahmani F, Esmaeili S, Bashash D, et al.
Centaurea albonitens extract enhances the therapeutic effects of Vincristine in leukemic cells by inducing apoptosis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 99:598-607 [PubMed] Related Publications
Centaurea albonitens extract enhances the therapeutic effects of Vincristine in leukemic cells by inducing apoptosis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 99:598-607 [PubMed] Related Publications
Drug-induced toxicities and dose-related side effects are the major challenges in the conventional cancer therapy by the chemo drugs. On the other hand, herbal derivatives have obtained a great research interest in the field of therapeutic applications because of their more favorable specifications including less toxicity, cost-effective and more physiologically compatible than the chemical drugs. For this purpose, we evaluated methanolic extract prepared from Centaurea albonitens Turrill alone and in combination with Vincristine (VCR) for its potential cytotoxic effects in NALM-6, REH, NB4 and KMM-1 cell lines by using the various approaches. Centaurea genus is one of the current medicinal plants, which has used in traditional medicine, However, there are rare studies to examine its anticancer properties against hematologic malignant cells. In this study, we demonstrated Centaurea albonitens extract (CAE) induces cytotoxicity through G0/G1 phase arrest followed by apoptosis in a dose- and time- dependent manner, although with varying efficiency. Interestingly, normal cells didn't exhibit significant cytotoxicity after CAE treatment. Moreover, we found that low dose of CAE enhances anti-cancer effects of VCR in pre-B ALL cell lines (NALM-6 and REH). Further investigations validated synergistic anticancer activities of VCR and CAE through inducing apoptosis without significant cell cycle arrest. Taken together, our results demonstrated for the first time that the methanolic extract of Centaurea albonitens can be considered as a potential anticancer agent and/or an enhancer of chemotherapeutic sensitivity of VCR.
Zhuang Y, Zhao J, Xu X, Bi L
Downregulation of GLUT3 Promotes Apoptosis and Chemosensitivity of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells via EGFR Signaling.
Arch Iran Med. 2018; 21(2):73-78 [PubMed] Related Publications
Downregulation of GLUT3 Promotes Apoptosis and Chemosensitivity of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells via EGFR Signaling.
Arch Iran Med. 2018; 21(2):73-78 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Glucose transporter 3 (GLUT3) plays an important role in tumor progression and drug resistance in numerous malignancies, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, the effect of GLUT3 silencing on treatment of AML remains poorly understood. The purpose of this study was to investigate role of GLUT3 in proliferation and chemosensitivity of AML and its underlying mechanisms.
METHODS: The siRNA transfection was conducted using LipofectamineTM 2000. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot analyses were employed to measure the expression levels of mRNA and protein for GLUT3, respectively. The cytotoxic effects of siRNA and vincristine were determined using the MTT assay. Flow cytometry was performed to analyze apoptosis.
RESULTS: GLUT3 siRNA transfection significantly reduced expression levels of GLUT3 mRNA and protein, leading to a strong growth inhibition and enhanced apoptosis (P = 0.017) in AML cells. Moreover, treatment with GLUT3 siRNA, synergistically enhanced the cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of vincristine (P = 0.025). We further investigated the possible mechanism involved in regulation of GLUT3 in AML cell proliferation and apoptosis. We found that GLUT3 negatively regulates EGFR activity, as well as the expression of its downstream proteins.
CONCLUSION: Our results demonstrated that GLUT3 plays a fundamental role in the survival and resistance of AML cells to vincristine. Therefore, GLUT3 can be considered as an attractive target for gene therapy of AML patients and siRNA-mediated silencing of this gene may be a novel strategy in AML treatment.
METHODS: The siRNA transfection was conducted using LipofectamineTM 2000. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) and Western blot analyses were employed to measure the expression levels of mRNA and protein for GLUT3, respectively. The cytotoxic effects of siRNA and vincristine were determined using the MTT assay. Flow cytometry was performed to analyze apoptosis.
RESULTS: GLUT3 siRNA transfection significantly reduced expression levels of GLUT3 mRNA and protein, leading to a strong growth inhibition and enhanced apoptosis (P = 0.017) in AML cells. Moreover, treatment with GLUT3 siRNA, synergistically enhanced the cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of vincristine (P = 0.025). We further investigated the possible mechanism involved in regulation of GLUT3 in AML cell proliferation and apoptosis. We found that GLUT3 negatively regulates EGFR activity, as well as the expression of its downstream proteins.
CONCLUSION: Our results demonstrated that GLUT3 plays a fundamental role in the survival and resistance of AML cells to vincristine. Therefore, GLUT3 can be considered as an attractive target for gene therapy of AML patients and siRNA-mediated silencing of this gene may be a novel strategy in AML treatment.
Takayoshi K, Doi G, Tsuruta N, et al.
Successful chemotherapeutic treatment for metastatic littoral cell angioma: A case report.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(15):e0378 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 01/10/2019 Related Publications
Successful chemotherapeutic treatment for metastatic littoral cell angioma: A case report.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(15):e0378 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 01/10/2019 Related Publications
RATIONALE: Metastatic littoral cell angioma (LCA) is extremely rare. No standard therapeutic strategy has been established, and the impact of chemotherapy has not yet been evaluated.
PATIENT CONCERNS: A 61-year-old woman was admitted because of bicytopenia. She had a splenectomy for LCA of the spleen 10 years earlier. Bone marrow aspiration was normal, and a computed tomography (CT) scan showed hepatomegaly with multiple liver tumors.
DIAGNOSES: Liver biopsy samples showed macrophage-like cell infiltration in the hepatic sinusoids. Metastatic LCA was diagnosed based on immunohistochemistry, imaging tests, and the clinical course.
INTERVENTIONS: Immunosuppressive agents, such as prednisolone and cyclosporine, were ineffective. Next, cytotoxic agents, such as etoposide, paclitaxel, and vincristine, were administered.
OUTCOMES: Cytotoxic agents showed a prominent effect against LCA. CT showed improvement of the hepatomegaly, and fluoro-deoxyglucose (FDG) uptake decreased markedly at a follow-up FDG- positron emission tomography (PET) scan.
LESSONS: Chemotherapeutic treatment based on hemophagocytic syndrome or angiosarcoma might have anti-tumor activity against metastatic LCA. Analysis of the molecular characteristics of this tumor is needed to develop better treatment options.
PATIENT CONCERNS: A 61-year-old woman was admitted because of bicytopenia. She had a splenectomy for LCA of the spleen 10 years earlier. Bone marrow aspiration was normal, and a computed tomography (CT) scan showed hepatomegaly with multiple liver tumors.
DIAGNOSES: Liver biopsy samples showed macrophage-like cell infiltration in the hepatic sinusoids. Metastatic LCA was diagnosed based on immunohistochemistry, imaging tests, and the clinical course.
INTERVENTIONS: Immunosuppressive agents, such as prednisolone and cyclosporine, were ineffective. Next, cytotoxic agents, such as etoposide, paclitaxel, and vincristine, were administered.
OUTCOMES: Cytotoxic agents showed a prominent effect against LCA. CT showed improvement of the hepatomegaly, and fluoro-deoxyglucose (FDG) uptake decreased markedly at a follow-up FDG- positron emission tomography (PET) scan.
LESSONS: Chemotherapeutic treatment based on hemophagocytic syndrome or angiosarcoma might have anti-tumor activity against metastatic LCA. Analysis of the molecular characteristics of this tumor is needed to develop better treatment options.
Frommann K, Appl B, Hundsdoerfer P, et al.
Vincristine resistance in relapsed neuroblastoma can be efficiently overcome by Smac mimetic LCL161 treatment.
J Pediatr Surg. 2018; 53(10):2059-2064 [PubMed] Related Publications
Vincristine resistance in relapsed neuroblastoma can be efficiently overcome by Smac mimetic LCL161 treatment.
J Pediatr Surg. 2018; 53(10):2059-2064 [PubMed] Related Publications
PURPOSE: In spite of good initial therapy response neuroblastomas often spread to distant organs or relapse after periods of remission. Dysregulation of apoptosis, a hallmark of cancer, is often effected by elevated levels of antiapoptotic signals leading to resistance against chemotherapeutic drugs. Inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) are crucial cellular apoptosis regulators. Targeting IAPs with Smac mimetics has been demonstrated as a promising strategy for treatment of neuroblastoma and other tumors.
METHODS: In paired neuroblastoma cell lines, obtained from the same patient at time of diagnosis (CHLA-15) and postchemotherapy during progressive disease (CHLA-20), expression of crucial IAPs was determined. Furthermore, effects of vincristine on viability, cytotoxicity, apoptosis induction and caspase-3/7 activation were determined.
RESULTS: Cellular IAP-1 (cIAP-1) and X-linked IAP (XIAP) expression was increased in cell line CHLA-20. Moreover, biological effects of vincristine were significantly lower in these cells. Treatment of cells with Smac mimetic LCL161 increased the effects of vincristine in CHLA-15 cells and more importantly was able to overcome vincristine resistance in CHLA-20 cells.
CONCLUSIONS: These findings demonstrate the potential of Smac mimetics for the development of novel therapeutic approaches for the treatment of relapsed/resistant neuroblastoma.
METHODS: In paired neuroblastoma cell lines, obtained from the same patient at time of diagnosis (CHLA-15) and postchemotherapy during progressive disease (CHLA-20), expression of crucial IAPs was determined. Furthermore, effects of vincristine on viability, cytotoxicity, apoptosis induction and caspase-3/7 activation were determined.
RESULTS: Cellular IAP-1 (cIAP-1) and X-linked IAP (XIAP) expression was increased in cell line CHLA-20. Moreover, biological effects of vincristine were significantly lower in these cells. Treatment of cells with Smac mimetic LCL161 increased the effects of vincristine in CHLA-15 cells and more importantly was able to overcome vincristine resistance in CHLA-20 cells.
CONCLUSIONS: These findings demonstrate the potential of Smac mimetics for the development of novel therapeutic approaches for the treatment of relapsed/resistant neuroblastoma.
Ramos JC, Sparano JA, Rudek MA, et al.
Safety and Preliminary Efficacy of Vorinostat With R-EPOCH in High-risk HIV-associated Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (AMC-075).
Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018; 18(3):180-190.e2 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 01/10/2019 Related Publications
Safety and Preliminary Efficacy of Vorinostat With R-EPOCH in High-risk HIV-associated Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma (AMC-075).
Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018; 18(3):180-190.e2 [PubMed] Article available free on PMC after 01/10/2019 Related Publications
INTRODUCTION: Vorinostat (VOR), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances the anti-tumor effects of rituximab (R) and cytotoxic chemotherapy, induces viral lytic expression and cell killing in Epstein-Barr virus-positive (EBV
PATIENTS AND METHODS: We performed a phase I trial of VOR given with R-based infusional EPOCH (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin hydrochloride) (n = 12) and cART in aggressive HIV-associated B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in order to identify safe dosing and schedule. VOR (300 or 400 mg) was given orally on days 1 to 5 with each cycle of R-EPOCH for 10 high-risk patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (1 EBV
RESULTS: The recommended phase II dose of VOR was 300 mg, with dose-limiting toxicity in 2 of 6 patients at 400 mg (grade 4 thrombocytopenia, grade 4 neutropenia), and 1 of 6 treated at 300 mg (grade 4 sepsis from tooth abscess). Neither VOR, nor cART regimen, significantly altered chemotherapy steady-state concentrations. VOR chemotherapy did not negatively impact CD4+ cell counts or HIV viral loads, which decreased or remained undetectable in most patients during treatment. The response rate in high-risk patients with NHL treated with VOR(R)-EPOCH was 100% (complete 83% and partial 17%) with a 1-year event-free survival of 83% (95% confidence interval, 51.6%-97.9%).
CONCLUSION: VOR combined with R-EPOCH was tolerable and seemingly efficacious in patients with aggressive HIV-NHL.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: We performed a phase I trial of VOR given with R-based infusional EPOCH (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin hydrochloride) (n = 12) and cART in aggressive HIV-associated B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in order to identify safe dosing and schedule. VOR (300 or 400 mg) was given orally on days 1 to 5 with each cycle of R-EPOCH for 10 high-risk patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (1 EBV
RESULTS: The recommended phase II dose of VOR was 300 mg, with dose-limiting toxicity in 2 of 6 patients at 400 mg (grade 4 thrombocytopenia, grade 4 neutropenia), and 1 of 6 treated at 300 mg (grade 4 sepsis from tooth abscess). Neither VOR, nor cART regimen, significantly altered chemotherapy steady-state concentrations. VOR chemotherapy did not negatively impact CD4+ cell counts or HIV viral loads, which decreased or remained undetectable in most patients during treatment. The response rate in high-risk patients with NHL treated with VOR(R)-EPOCH was 100% (complete 83% and partial 17%) with a 1-year event-free survival of 83% (95% confidence interval, 51.6%-97.9%).
CONCLUSION: VOR combined with R-EPOCH was tolerable and seemingly efficacious in patients with aggressive HIV-NHL.
Vallacha A, Haider G, Raja W, Kumar D
Remission Rate of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) in Adolescents and Young Adults (AYA).
J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2018; 28(2):118-121 [PubMed] Related Publications
Remission Rate of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) in Adolescents and Young Adults (AYA).
J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2018; 28(2):118-121 [PubMed] Related Publications
OBJECTIVE: To determine the remission rate in adolescent and young adult (AYA) patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
STUDY DESIGN: Descriptive study.
PLACE AND DURATION OF STUDY: Department of Oncology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre (JPMC), Karachi from January, 2016 to March, 2017.
METHODOLOGY: Adolescent and young adult (AYA) patients aged 15-39 years, newly diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia from January, 2016 to March, 2017. Diagnosis was confirmed by bone marrow trephine biopsy and immunophenotyping. All the patients were treated with daunorubicin, vincristine, prednisone, and L-asparaginase in the induction phase. The response evaluation was done on day 35 of the induction phase and the remission rate was assessed by the bone marrow examination.
RESULTS: Of the total 50 AYA patients diagnosed with ALL, 41 patients could complete induction phase and 9 patients died during the first week of induction, therefore excluded from the study. Forty (97.8%) patients were <35years of age, 28 (68.3%) were male, of female 10 (24.4%) were housewives, 33 (80.5%) patients belonged to Sindh, 28 (68.3%) presented with fever and body ache, 17 (41.5%) patients had precursor B cell type ALL, with 7 (17.1%) patients had hemoglobin of <7 g/dL,11 (26.8%) patients had white cell count of >30x109/L, platelet count of <20x103/µL in 6 (14.6%) patients and complete morphological remission was reported in 29 (70.7%) patients.
CONCLUSION: The remission induction rate was 70.7% in the adolescents and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia at the study centre.
STUDY DESIGN: Descriptive study.
PLACE AND DURATION OF STUDY: Department of Oncology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre (JPMC), Karachi from January, 2016 to March, 2017.
METHODOLOGY: Adolescent and young adult (AYA) patients aged 15-39 years, newly diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia from January, 2016 to March, 2017. Diagnosis was confirmed by bone marrow trephine biopsy and immunophenotyping. All the patients were treated with daunorubicin, vincristine, prednisone, and L-asparaginase in the induction phase. The response evaluation was done on day 35 of the induction phase and the remission rate was assessed by the bone marrow examination.
RESULTS: Of the total 50 AYA patients diagnosed with ALL, 41 patients could complete induction phase and 9 patients died during the first week of induction, therefore excluded from the study. Forty (97.8%) patients were <35years of age, 28 (68.3%) were male, of female 10 (24.4%) were housewives, 33 (80.5%) patients belonged to Sindh, 28 (68.3%) presented with fever and body ache, 17 (41.5%) patients had precursor B cell type ALL, with 7 (17.1%) patients had hemoglobin of <7 g/dL,11 (26.8%) patients had white cell count of >30x109/L, platelet count of <20x103/µL in 6 (14.6%) patients and complete morphological remission was reported in 29 (70.7%) patients.
CONCLUSION: The remission induction rate was 70.7% in the adolescents and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia at the study centre.
Guzmán-Ortiz AL, Aparicio-Ozores G, Valle-Rios R, et al.
Proteomic changes in a childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line during the adaptation to vincristine.
Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2017 May - Jun; 74(3):181-192 [PubMed] Related Publications
Proteomic changes in a childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line during the adaptation to vincristine.
Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2017 May - Jun; 74(3):181-192 [PubMed] Related Publications
INTRODUCTION: Relapse occurs in approximately 20% of Mexican patients with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). In this group, chemoresistance may be one of the biggest challenges. An overview of complex cellular processes like drug tolerance can be achieved with proteomic studies.
METHODS: The B-lineage pediatric ALL cell line CCRF-SB was gradually exposed to the chemotherapeutic vincristine until proliferation was observed at 6nM, control cells were cultured in the absence of vincristine. The proteome from each group was analyzed by nanoHPLC coupled to an ESI-ion trap mass spectrometer. The identified proteins were grouped into overrepresented functional categories with the PANTHER classification system.
RESULTS: We found 135 proteins exclusively expressed in the presence of vincristine. The most represented functional categories were: Toll receptor signaling pathway, Ras Pathway, B and T cell activation, CCKR signaling map, cytokine-mediated signaling pathway, and oxidative phosphorylation.
CONCLUSIONS: Our study indicates that signal transduction and mitochondrial ATP production are essential during adaptation of leukemic cells to vincristine, these processes represent potential therapeutic targets.
METHODS: The B-lineage pediatric ALL cell line CCRF-SB was gradually exposed to the chemotherapeutic vincristine until proliferation was observed at 6nM, control cells were cultured in the absence of vincristine. The proteome from each group was analyzed by nanoHPLC coupled to an ESI-ion trap mass spectrometer. The identified proteins were grouped into overrepresented functional categories with the PANTHER classification system.
RESULTS: We found 135 proteins exclusively expressed in the presence of vincristine. The most represented functional categories were: Toll receptor signaling pathway, Ras Pathway, B and T cell activation, CCKR signaling map, cytokine-mediated signaling pathway, and oxidative phosphorylation.
CONCLUSIONS: Our study indicates that signal transduction and mitochondrial ATP production are essential during adaptation of leukemic cells to vincristine, these processes represent potential therapeutic targets.
Gutierrez-Camino Á, Umerez M, Martin-Guerrero I, et al.
Mir-pharmacogenetics of Vincristine and peripheral neurotoxicity in childhood B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Pharmacogenomics J. 2018; 18(6):704-712 [PubMed] Related Publications
Mir-pharmacogenetics of Vincristine and peripheral neurotoxicity in childhood B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Pharmacogenomics J. 2018; 18(6):704-712 [PubMed] Related Publications
Vincristine (VCR), an important component of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) therapy, can cause sensory and motor neurotoxicity. This neurotoxicity could lead to dose reduction or treatment discontinuation, which could in turn reduce survival. In this line, several studies associated peripheral neurotoxicity and polymorphisms in genes involved in pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of VCR. Nowadays, it is well known that these genes are regulated by microRNAs (miRNAs) and SNPs in miRNAs could modify their levels or function. Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine whether SNPs in miRNAs could be associated with VCR-induced neurotoxicity. To achieve this aim, we analyzed all the SNPs in miRNAs (minor allele frequency (MAF) ≥ 0.01) which could regulate VCR-related genes in a large cohort of Spanish children with B-cell precursor ALL (B-ALL) homogeneously treated with LAL/SHOP protocols. We identified the A allele of rs12402181 in the seed region of miR-3117-3p, that could affect the binding with ABCC1 and RALBP1 gene, and C allele of rs7896283 in pre-mature sequence of miR-4481, which could be involved in peripheral nerve regeneration, significantly associated with VCR-induced neurotoxicity. These findings point out the possible involvement of two SNPs in miRNA associated with VCR-related neurotoxicity.


 Apoptosis
Apoptosis