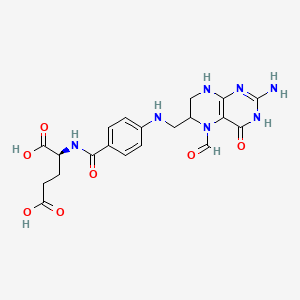
Leucovorin
"The active metabolite of FOLIC ACID. Leucovorin is used principally as its calcium salt as an antidote to folic acid antagonists which block the conversion of folic acid to folinic acid." (MeSH 2013)
Found this page useful?
 Web Resources: Leucovorin
Web Resources: Leucovorin Latest Research Publications
Latest Research PublicationsWeb Resources: Leucovorin (5 links)
Macmillan Cancer Support
NHS Evidence
 Leucovorin - Substance Summary
Leucovorin - Substance Summary
PubChem
Irish Cancer Society
MedlinePlus
Latest Research Publications
This list of publications is regularly updated (Source: PubMed).
Ulusakarya A, Teyar N, Karaboué A, et al.
Patient-tailored FOLFIRINOX as first line treatment of patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(16):e15341 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Patient-tailored FOLFIRINOX as first line treatment of patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(16):e15341 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
FOLFIRINOX is one of the most effective reference regimens in the 1st line treatment of locally advanced (LA) and metastatic pancreatic cancer (mPC), despite its high toxicity. We evaluated our real-life experience with "patient-tailored intent to treat FOLFIRINOX" in patients with LA or mPC compared to other reports along with the pivotal phase III trial.We analyzed data from all consecutive patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma treated with dose-modified FOLFIRINOX in 2016 at Paul Brousse University Hospital. Irinotecan was administered whenever initial serum bilirubin was <1.5 × upper limit of normal. Oxaliplatin was stopped for severe sensory neuropathy. Initial dose reductions were made according to patient profile (eg, age, comorbidities) and later due to toxicity. The treatment was continued until surgery or disease progression. Endpoints were time to progression (TTP), overall survival (OS), objective response rate (ORR), and secondary complete resection (R0R1).Thirty-seven patients with unresectable LA or mPC received patient-tailored FOLFIRINOX as 1st line chemotherapy. There were 22 male (59%) and 15 female patients (41%) aged 44 to 81 years with LA (18 patients, 49%) and mPC (19 patients, 51%). They had World Health Organization-performance status of 0 (59%) or 1 (41%). A total of 384 cycles were administered. Median dose intensities (mg/m/w) were 28.9 for oxaliplatin, 56.8 for irinotecan, and 886.2 for 5-fluorouracil. Thirty-four patients were assessed for response; ORR and disease control rates were 47% and 85%, respectively. R0R1 rate was 30%. Median TTP and OS were 9.6 and 14.6 months. LA disease was associated with significantly longer TTP and OS (P < .001).FOLFIRINOX with patient-tailored dose adaptations seems to offer better results in patients with advanced PC. This approach in the neoadjuvant setting results in a macroscopic R0R1 in 61% of patients with initially unresectable disease. It deserves prospective evaluation to further improve outcomes in the management of advanced PC.
Sadahiro S, Suzuki T, Tanaka A, et al.
Induction of CD3+ and FoxP3+ T Cells in Left-sided Colorectal Tumors After UFT/LV Chemotherapy.
Anticancer Res. 2019; 39(4):1997-2005 [PubMed] Related Publications
Induction of CD3+ and FoxP3+ T Cells in Left-sided Colorectal Tumors After UFT/LV Chemotherapy.
Anticancer Res. 2019; 39(4):1997-2005 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND/AIM: Immune checkpoint inhibitors are mainly used for right-sided, microsatellite instability-high colorectal tumors. In this study, the effects of oral uracil-tegafur plus leucovorin (UFT/LV) chemotherapy on the gene expressions of four immunotherapy targets and the amounts of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) were investigated.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Data of 260 patients with stage II or stage III colorectal cancer were analyzed. Gene expression and amount of TILs were evaluated using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (CRT-PCR) assay and immunohistochemical staining, respectively.
RESULTS: Expression of CTLA4 and LAG3 in tumor tissues was significantly increased after UFT/LV chemotherapy, but only in left-sided tumors. The percentage of high-TIL, high-CD3 and high-FoxP3 patients in the UFT/LV group was significantly higher than that in the control group, only in left-sided tumors.
CONCLUSION: The increase in TILs count, especially of CD3+ T cells and FoxP3+ regulatory T cells, after UFT/LV chemotherapy were specific to left-sided colorectal cancers.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Data of 260 patients with stage II or stage III colorectal cancer were analyzed. Gene expression and amount of TILs were evaluated using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (CRT-PCR) assay and immunohistochemical staining, respectively.
RESULTS: Expression of CTLA4 and LAG3 in tumor tissues was significantly increased after UFT/LV chemotherapy, but only in left-sided tumors. The percentage of high-TIL, high-CD3 and high-FoxP3 patients in the UFT/LV group was significantly higher than that in the control group, only in left-sided tumors.
CONCLUSION: The increase in TILs count, especially of CD3+ T cells and FoxP3+ regulatory T cells, after UFT/LV chemotherapy were specific to left-sided colorectal cancers.
Lyu N, Kong Y, Pan T, et al.
Hepatic Arterial Infusion of Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin in Hepatocellular Cancer with Extrahepatic Spread.
J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019; 30(3):349-357.e2 [PubMed] Related Publications
Hepatic Arterial Infusion of Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin in Hepatocellular Cancer with Extrahepatic Spread.
J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019; 30(3):349-357.e2 [PubMed] Related Publications
PURPOSE: To compare treatment with hepatic arterial infusion of chemotherapy (HAIC) in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with both extrahepatic spread (EHS) and intrahepatic tumor and patients with intrahepatic tumor only.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This single-center retrospective study comprised 116 patients with advanced HCC with both intrahepatic tumor and EHS (EHS group; n = 50) or with intrahepatic tumor only (non-EHS group; n = 66) treated with HAIC including oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin between June 2014 and July 2016. Overall survival (OS) and radiologic responses to treatment were determined and compared between the 2 groups.
RESULTS: Both the objective response rate and the clinical benefit rate were higher in the non-EHS group than in the EHS group (37.9% vs 16% objective response rate, P = .010; 81.8% vs 62% clinical benefit rate, P = .017). Median OS was not statistically different between the 2 groups (14.8 months vs 9.8 months, P = .068). Subgroup analysis of OS found that patients with lung metastases survived for a shorter time (OS 7 months) than patients with other metastatic sites (P = .003) and patients free of metastases (P = .001).
CONCLUSIONS: HAIC is a potential treatment option for advanced HCC with limited extrahepatic metastases in a population with hepatitis B virus infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: This single-center retrospective study comprised 116 patients with advanced HCC with both intrahepatic tumor and EHS (EHS group; n = 50) or with intrahepatic tumor only (non-EHS group; n = 66) treated with HAIC including oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin between June 2014 and July 2016. Overall survival (OS) and radiologic responses to treatment were determined and compared between the 2 groups.
RESULTS: Both the objective response rate and the clinical benefit rate were higher in the non-EHS group than in the EHS group (37.9% vs 16% objective response rate, P = .010; 81.8% vs 62% clinical benefit rate, P = .017). Median OS was not statistically different between the 2 groups (14.8 months vs 9.8 months, P = .068). Subgroup analysis of OS found that patients with lung metastases survived for a shorter time (OS 7 months) than patients with other metastatic sites (P = .003) and patients free of metastases (P = .001).
CONCLUSIONS: HAIC is a potential treatment option for advanced HCC with limited extrahepatic metastases in a population with hepatitis B virus infection.
Guler Y, Ovey IS
Synergic and comparative effect of 5-fluorouracil and leucoverin on breast and colon cancer cells through TRPM2 channels.
Bratisl Lek Listy. 2018; 119(11):692-700 [PubMed] Related Publications
Synergic and comparative effect of 5-fluorouracil and leucoverin on breast and colon cancer cells through TRPM2 channels.
Bratisl Lek Listy. 2018; 119(11):692-700 [PubMed] Related Publications
OBJECTIVES: We aimed to reveal the role of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and Leucovorin (LV) along with transient receptor potential protein melastatin 2 (TRPM2) channels in breast and colon cancer cells during the treatment process.
BACKGROUND: 5-FU and LV are widely used in breast and colon cancers for chemotherapy. It has been reported that the expression of TRPM2 channels increased intensively in cancer cells.
METHODS: Breast (MCF7) and colon (Caco-2) cells were cultured and divided into seven main groups. The cells in the group were incubated with 5-FU and LV for 24 hrs and then incubated with Antranilic acid. The effects of medicines were investigated on all molecular pathways of apoptosis.
RESULTS: It was found that 5FU and LCV, administered separately and together on breast cancer cell culture and colon cancer cell culture increased the intracellular calcium levels by stimulation of TRPM2 channels in both cancer cells.
CONCLUSION: As the result of our study, it has been shown that apoptotic effects of 5FU and LV on both colon and breast cancer cells were directly related to TRPM2 channels and that TRPM2 channels played an important role in the whole molecular pathway of apoptosis leading to increased intracellular Ca2+ (Ca2+) levels and increased mitochondrial depolarisation (Fig. 6, Ref. 43).
BACKGROUND: 5-FU and LV are widely used in breast and colon cancers for chemotherapy. It has been reported that the expression of TRPM2 channels increased intensively in cancer cells.
METHODS: Breast (MCF7) and colon (Caco-2) cells were cultured and divided into seven main groups. The cells in the group were incubated with 5-FU and LV for 24 hrs and then incubated with Antranilic acid. The effects of medicines were investigated on all molecular pathways of apoptosis.
RESULTS: It was found that 5FU and LCV, administered separately and together on breast cancer cell culture and colon cancer cell culture increased the intracellular calcium levels by stimulation of TRPM2 channels in both cancer cells.
CONCLUSION: As the result of our study, it has been shown that apoptotic effects of 5FU and LV on both colon and breast cancer cells were directly related to TRPM2 channels and that TRPM2 channels played an important role in the whole molecular pathway of apoptosis leading to increased intracellular Ca2+ (Ca2+) levels and increased mitochondrial depolarisation (Fig. 6, Ref. 43).
Lee KY, Park JW, Lee KY, et al.
Oncologic outcomes after adjuvant chemotherapy with capecitabine compared to 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin for geriatric stage II colon cancer: a retrospective cohort study.
Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019; 34(4):629-639 [PubMed] Related Publications
Oncologic outcomes after adjuvant chemotherapy with capecitabine compared to 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin for geriatric stage II colon cancer: a retrospective cohort study.
Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019; 34(4):629-639 [PubMed] Related Publications
PURPOSE: After curative resection of stage II colon cancer, adjuvant chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin (FL) or capecitabine is selectively recommended. However, there is little evidence of the effect of capecitabine on oncologic outcome in geriatric patients with stage II colon cancer compared to that of FL. The aim of this study was to determine the difference in recurrence-free survival (RFS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), and overall survival (OS) in patients older than 70 years of age with stage II colon cancer receiving capecitabine and FL.
METHODS: Patients over 70 years of age diagnosed with primary pathologic stage II colon cancer at the Seoul National University Hospital from January 2005 to December 2015 were included. A prospectively collected database was analyzed retrospectively. Patients were separated into an FL group and a capecitabine group. The primary outcomes were RFS, CSS, and OS.
RESULTS: Of the 154 included patients, 96 patients received FL and 58 patients received capecitabine. There was no difference between the two groups in RFS, CSS, or OS (p = 0.763, p = 0.221, and p = 0.470, respectively) as measured by Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank test. Administration of capecitabine as compared to FL was not a factor affecting RFS (hazard ratio [HR] 0.503, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.145-1.745), CSS (HR 1.519, 95% CI 0.348-6.629), or OS (HR 0.941, 95% CI 0.290-3.053) on multivariable analysis.
CONCLUSIONS: Capecitabine is a safe regimen in terms of oncologic outcomes compared with FL in older patients with stage II colon cancer.
METHODS: Patients over 70 years of age diagnosed with primary pathologic stage II colon cancer at the Seoul National University Hospital from January 2005 to December 2015 were included. A prospectively collected database was analyzed retrospectively. Patients were separated into an FL group and a capecitabine group. The primary outcomes were RFS, CSS, and OS.
RESULTS: Of the 154 included patients, 96 patients received FL and 58 patients received capecitabine. There was no difference between the two groups in RFS, CSS, or OS (p = 0.763, p = 0.221, and p = 0.470, respectively) as measured by Kaplan-Meier analysis with log-rank test. Administration of capecitabine as compared to FL was not a factor affecting RFS (hazard ratio [HR] 0.503, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.145-1.745), CSS (HR 1.519, 95% CI 0.348-6.629), or OS (HR 0.941, 95% CI 0.290-3.053) on multivariable analysis.
CONCLUSIONS: Capecitabine is a safe regimen in terms of oncologic outcomes compared with FL in older patients with stage II colon cancer.
Vogl UM, Andalibi H, Klaus A, et al.
Nab-paclitaxel and gemcitabine or FOLFIRINOX as first-line treatment in patients with unresectable adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: does sequence matter?
BMC Cancer. 2019; 19(1):28 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Nab-paclitaxel and gemcitabine or FOLFIRINOX as first-line treatment in patients with unresectable adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: does sequence matter?
BMC Cancer. 2019; 19(1):28 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Locally advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas remains - despite the implementation of new chemotherapy protocols - a disease with short overall survival (OS).
METHODS: Eighty-three patients were treated with locally advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas with either FOLFIRINOX or nab-Paclitxel and Gemcitabine (nabPGem) as first- or second line therapy. We analysed the outcome for OS and progression-free survival (PFS) in terms of treatment regimen and sequence.
RESULTS: The majority of patients presented in good performance status (PS) with a median age of 68 years. Fourty-two patients received FOLFIRINOX as first-line therapy, 41 patients were treated with nabPGem as first line therapy. Forty-eight patients received both treatments. The OS of all 83 patients was 12.6 months (95% CI: 10.7-14.6), resulting in a 1-year OS of 54%. Forty-eight patients received FOLFIRINOX followed by nabPGem or vice versa. There was no significant difference in OS or PFS for either of the two sequences (p = 0.9). The OS for FOLFIRINOX followed by nabPGem or nabPGem followed by FOLFIRINOX was 13.7 months (95% CI: 12.6-14.7) and 13.8 months (95% CI: 8.6-19), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS: The sequence FOLFIRINOX followed by nab-Paclitaxel and Gemcitabine or vice versa lead to an equal OS outcome.
METHODS: Eighty-three patients were treated with locally advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas with either FOLFIRINOX or nab-Paclitxel and Gemcitabine (nabPGem) as first- or second line therapy. We analysed the outcome for OS and progression-free survival (PFS) in terms of treatment regimen and sequence.
RESULTS: The majority of patients presented in good performance status (PS) with a median age of 68 years. Fourty-two patients received FOLFIRINOX as first-line therapy, 41 patients were treated with nabPGem as first line therapy. Forty-eight patients received both treatments. The OS of all 83 patients was 12.6 months (95% CI: 10.7-14.6), resulting in a 1-year OS of 54%. Forty-eight patients received FOLFIRINOX followed by nabPGem or vice versa. There was no significant difference in OS or PFS for either of the two sequences (p = 0.9). The OS for FOLFIRINOX followed by nabPGem or nabPGem followed by FOLFIRINOX was 13.7 months (95% CI: 12.6-14.7) and 13.8 months (95% CI: 8.6-19), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS: The sequence FOLFIRINOX followed by nab-Paclitaxel and Gemcitabine or vice versa lead to an equal OS outcome.
Sasaki T, Kanata R, Yamada I, et al.
Improvement of Treatment Outcomes for Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: A Real-world Data Analysis.
In Vivo. 2019 Jan-Feb; 33(1):271-276 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Improvement of Treatment Outcomes for Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: A Real-world Data Analysis.
In Vivo. 2019 Jan-Feb; 33(1):271-276 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND/AIM: FOLFIRINOX (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, irinotecan, oxaliplatin) and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel therapy have recently been introduced for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer. Herein, overall treatment outcomes of metastatic pancreatic cancer after introduction of FOLFIRINOX and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel therapy were evaluated, in daily practice.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Metastatic pancreatic cancer patients (n=321) who started systemic chemotherapy between January 2011 and December 2016 were included and were divided into two groups: group A (2011-2013) and group B (2014-2016). Treatment outcomes were evaluated retrospectively.
RESULTS: Patient characteristics were similar between the two groups except for the rates of distant lymph node metastasis and peritoneal metastasis. The preferred regimens in groups A and B were gemcitabine monotherapy and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel therapy, respectively. The response rates, median progression-free survival, and median overall survival of groups A and B were 7.8% and 28.4% (p<0.01), 3.1 months and 5.4 months (p<0.01), and 6.7 months and 10.2 months (p<0.01), respectively.
CONCLUSION: Overall treatment outcomes for metastatic pancreatic cancer were significantly improved after introduction of FOLFIRINOX and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel combination therapy in daily practice.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Metastatic pancreatic cancer patients (n=321) who started systemic chemotherapy between January 2011 and December 2016 were included and were divided into two groups: group A (2011-2013) and group B (2014-2016). Treatment outcomes were evaluated retrospectively.
RESULTS: Patient characteristics were similar between the two groups except for the rates of distant lymph node metastasis and peritoneal metastasis. The preferred regimens in groups A and B were gemcitabine monotherapy and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel therapy, respectively. The response rates, median progression-free survival, and median overall survival of groups A and B were 7.8% and 28.4% (p<0.01), 3.1 months and 5.4 months (p<0.01), and 6.7 months and 10.2 months (p<0.01), respectively.
CONCLUSION: Overall treatment outcomes for metastatic pancreatic cancer were significantly improved after introduction of FOLFIRINOX and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel combination therapy in daily practice.
Conroy T, Hammel P, Hebbar M, et al.
FOLFIRINOX or Gemcitabine as Adjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer.
N Engl J Med. 2018; 379(25):2395-2406 [PubMed] Related Publications
FOLFIRINOX or Gemcitabine as Adjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer.
N Engl J Med. 2018; 379(25):2395-2406 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Among patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer, combination chemotherapy with fluorouracil, leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin (FOLFIRINOX) leads to longer overall survival than gemcitabine therapy. We compared the efficacy and safety of a modified FOLFIRINOX regimen with gemcitabine as adjuvant therapy in patients with resected pancreatic cancer.
METHODS: We randomly assigned 493 patients with resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma to receive a modified FOLFIRINOX regimen (oxaliplatin [85 mg per square meter of body-surface area], irinotecan [180 mg per square meter, reduced to 150 mg per square meter after a protocol-specified safety analysis], leucovorin [400 mg per square meter], and fluorouracil [2400 mg per square meter] every 2 weeks) or gemcitabine (1000 mg per square meter on days 1, 8, and 15 every 4 weeks) for 24 weeks. The primary end point was disease-free survival. Secondary end points included overall survival and safety.
RESULTS: At a median follow-up of 33.6 months, the median disease-free survival was 21.6 months in the modified-FOLFIRINOX group and 12.8 months in the gemcitabine group (stratified hazard ratio for cancer-related event, second cancer, or death, 0.58; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.46 to 0.73; P<0.001). The disease-free survival rate at 3 years was 39.7% in the modified-FOLFIRINOX group and 21.4% in the gemcitabine group. The median overall survival was 54.4 months in the modified-FOLFIRINOX group and 35.0 months in the gemcitabine group (stratified hazard ratio for death, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.48 to 0.86; P=0.003). The overall survival rate at 3 years was 63.4% in the modified-FOLFIRINOX group and 48.6% in the gemcitabine group. Adverse events of grade 3 or 4 occurred in 75.9% of the patients in the modified-FOLFIRINOX group and in 52.9% of those in the gemcitabine group. One patient in the gemcitabine group died from toxic effects (interstitial pneumonitis).
CONCLUSIONS: Adjuvant therapy with a modified FOLFIRINOX regimen led to significantly longer survival than gemcitabine among patients with resected pancreatic cancer, at the expense of a higher incidence of toxic effects. (Funded by R&D Unicancer and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01526135 ; EudraCT number, 2011-002026-52 .).
METHODS: We randomly assigned 493 patients with resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma to receive a modified FOLFIRINOX regimen (oxaliplatin [85 mg per square meter of body-surface area], irinotecan [180 mg per square meter, reduced to 150 mg per square meter after a protocol-specified safety analysis], leucovorin [400 mg per square meter], and fluorouracil [2400 mg per square meter] every 2 weeks) or gemcitabine (1000 mg per square meter on days 1, 8, and 15 every 4 weeks) for 24 weeks. The primary end point was disease-free survival. Secondary end points included overall survival and safety.
RESULTS: At a median follow-up of 33.6 months, the median disease-free survival was 21.6 months in the modified-FOLFIRINOX group and 12.8 months in the gemcitabine group (stratified hazard ratio for cancer-related event, second cancer, or death, 0.58; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.46 to 0.73; P<0.001). The disease-free survival rate at 3 years was 39.7% in the modified-FOLFIRINOX group and 21.4% in the gemcitabine group. The median overall survival was 54.4 months in the modified-FOLFIRINOX group and 35.0 months in the gemcitabine group (stratified hazard ratio for death, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.48 to 0.86; P=0.003). The overall survival rate at 3 years was 63.4% in the modified-FOLFIRINOX group and 48.6% in the gemcitabine group. Adverse events of grade 3 or 4 occurred in 75.9% of the patients in the modified-FOLFIRINOX group and in 52.9% of those in the gemcitabine group. One patient in the gemcitabine group died from toxic effects (interstitial pneumonitis).
CONCLUSIONS: Adjuvant therapy with a modified FOLFIRINOX regimen led to significantly longer survival than gemcitabine among patients with resected pancreatic cancer, at the expense of a higher incidence of toxic effects. (Funded by R&D Unicancer and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01526135 ; EudraCT number, 2011-002026-52 .).
Lee J, Lee JC, Gromski MA, et al.
Clinical outcomes of FOLFIRINOX in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A single center experience.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(50):e13592 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Clinical outcomes of FOLFIRINOX in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A single center experience.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(50):e13592 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Systemic chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy is the initial primary option for patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC). This study analyzed the effect of FOLFIRINOX and assessed the factors influencing conversion to surgical resectability for LAPC.Sixty-four patients with LAPC who received FOLFIRINOX as initial chemotherapy were enrolled retrospectively. Demographic characteristics, tumor status, interval/dosage/cumulative relative dose intensity (cRDI) of FOLFIRINOX, conversion to resection, and clinical outcomes were reviewed and factors associated with conversion to resectability after FOLFIRINOX were analyzed.After administration of FOLFIRINOX (median 9 cycles, 70% of cRDI), the median patient overall survival (OS) was 17.0 months. Fifteen of 64 patients underwent surgery and R0 resection was achieved in 11 patients. During a median follow-up time of 9.4 months after resection, cumulative recurrence rate was 28.5% at 18 months after resection. The estimated median OS was significantly longer for the resected group (>40 months vs 13 months). There were no statistical differences between the resected and non-resected groups in terms of baseline characteristics, tumor status and hematologic adverse effects. The patients who received standard dose of FOLFIRINOX had higher probability of subsequent resection compared with patients who received reduced dose, although cRDIs did not differ between groups.FOLFIRINOX is an active regimen in patients with LAPC, given acceptable resection rates and promising R0 resection rates. Additionally, our data demonstrate it is advantageous for obtaining resectability to administer FOLFIRINOX without dose reduction.
Xu X, Wu Q, Wang Z, et al.
Meta-analysis of FOLFIRINOX regimen as the first-line chemotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer.
Clin Exp Med. 2019; 19(1):149-157 [PubMed] Related Publications
Meta-analysis of FOLFIRINOX regimen as the first-line chemotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer.
Clin Exp Med. 2019; 19(1):149-157 [PubMed] Related Publications
The study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of the first-line chemotherapy FOLFIRINOX in treating pancreatic cancer. Pertinent studies were derived from the PubMed, Cochrane Library and EMBASE. The outcomes were analyzed according to resection rate and radical (R0) resection rate. Data were expressed as weighted commix proportions with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Twenty-three studies, involving 968 patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC) and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (BRPC), were examined. After treatment, 55% (95% CI 52-58%) of the patients underwent resection and 40% (95% CI 37-43%) underwent R0 resection, and the median overall survival ranged from 15.5 to 35.4 months, with a 10.0-27.1 months' median progression-free survival. The meta-analysis shows that FOLFIRINOX, as the first-line therapy, has significant down-staging effects in patients with LAPC or BRPC, with a 40% R0 resection rate and the adverse events under control.
Liu W, Wang F, Zhu Y, et al.
Galactosylated Chitosan-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Loading by Calcium Leucovorin for Colon Cancer Cell-Targeted Drug Delivery.
Molecules. 2018; 23(12) [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Galactosylated Chitosan-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Loading by Calcium Leucovorin for Colon Cancer Cell-Targeted Drug Delivery.
Molecules. 2018; 23(12) [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Targeted drug delivery to colon cancer cells can significantly improve the efficiency of treatment. We firstly synthesized carboxyl-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN⁻COOH) via two-step synthesis, and then developed calcium leucovorin (LV)-loaded carboxyl-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles based on galactosylated chitosan (GC), which are galectin receptor-mediated materials for colon-specific drug delivery systems. Both unmodified and functionalized nanoparticles were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), nitrogen sorption, and dynamic light scattering (DLS). Drug release properties and drug loading capacity were determined by ultraviolet spectrophotometry (UV). LV@MSN⁻COOH/GC had a high LV loading and a drug loading of 18.07%. In vitro, its release, mainly by diffusion, was sustained release. Cell experiments showed that in SW620 cells with the galectin receptor, the LV@MSN⁻COOH/GC metabolized into methyl tetrahydrofolic acid (MTHF) and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)@MSN⁻NH₂/GC metabolized into FdUMP in vivo. MTHF and 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine 5'-monophosphate (FdUMP) had combined inhibition and significantly downregulated the expression of thymidylate synthase (TS). Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry experiments show that MSN⁻COOH/GC has tumor cell targeting, which specifically recognizes and binds to the galectin receptor in tumor cells. The results show that the nano-dosing system based on GC can increase the concentrations of LV and 5-FU tumor cells and enhance their combined effect against colon cancer.
Kurita Y, Kobayashi N, Tokuhisa M, et al.
Sarcopenia is a reliable prognostic factor in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer receiving FOLFIRINOX chemotherapy.
Pancreatology. 2019; 19(1):127-135 [PubMed] Related Publications
Sarcopenia is a reliable prognostic factor in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer receiving FOLFIRINOX chemotherapy.
Pancreatology. 2019; 19(1):127-135 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES: FOLFIRINOX is the reliable treatments for pancreatic cancer, but it has a relatively high toxicity and the selection of suitable patients for this regimen remains challenge. On the other hand, sarcopenia is one of the important prognostic factors of pancreatic cancer. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of sarcopenia on overall survival (OS) and time to treatment failure (TTF) in patients with pancreatic cancer who received FOLFIRINOX.
METHODS: Clinical data of consecutive patients treated with FOLFIRINOX at our institution from 2011 to 2017 was retrospectively reviewed. Skeletal muscle index (SMI) and adipose tissue index (ATI) at the third lumbar spine level was calculated from computed tomography (CT) images. The association between clinical factors (SMI and ATI), and OS and TTF were determined using univariate and multivariate analyses.
RESULTS: We assessed 82 patients. The median OS of sarcopenia and the non-sarcopenia patients were 11.3 and 17.0 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR], 2.49; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.43-4.32; p = 0.001). Median TTF was 3.0 and 6.1 months in the sarcopenia and the non-sarcopenia patients, respectively (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.03-2.71; p = 0.032). Multivariate analyses revealed that sarcopenia (HR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.01-1.87; p = 0.045) was an independent prognostic factor of OS. High ATI (p = 0.022) and sarcopenic obesity (p = 0.008) were significantly associated with hematologic toxicity.
CONCLUSIONS: Sarcopenia is an independent indicator of poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer who received FOLFIRINOX, while ATI and sarcopenic obesity predicted severe hematologic toxicity.
METHODS: Clinical data of consecutive patients treated with FOLFIRINOX at our institution from 2011 to 2017 was retrospectively reviewed. Skeletal muscle index (SMI) and adipose tissue index (ATI) at the third lumbar spine level was calculated from computed tomography (CT) images. The association between clinical factors (SMI and ATI), and OS and TTF were determined using univariate and multivariate analyses.
RESULTS: We assessed 82 patients. The median OS of sarcopenia and the non-sarcopenia patients were 11.3 and 17.0 months, respectively (hazard ratio [HR], 2.49; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.43-4.32; p = 0.001). Median TTF was 3.0 and 6.1 months in the sarcopenia and the non-sarcopenia patients, respectively (HR, 1.67; 95% CI, 1.03-2.71; p = 0.032). Multivariate analyses revealed that sarcopenia (HR, 1.37; 95% CI, 1.01-1.87; p = 0.045) was an independent prognostic factor of OS. High ATI (p = 0.022) and sarcopenic obesity (p = 0.008) were significantly associated with hematologic toxicity.
CONCLUSIONS: Sarcopenia is an independent indicator of poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer who received FOLFIRINOX, while ATI and sarcopenic obesity predicted severe hematologic toxicity.
Shirasu H, Todaka A, Omae K, et al.
Impact of UGT1A1 genetic polymorphism on toxicity in unresectable pancreatic cancer patients undergoing FOLFIRINOX.
Cancer Sci. 2019; 110(2):707-716 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Impact of UGT1A1 genetic polymorphism on toxicity in unresectable pancreatic cancer patients undergoing FOLFIRINOX.
Cancer Sci. 2019; 110(2):707-716 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Studies have indicated an association between UDP-glucuronosyltransferase-1A1 (UGT1A1) genetic polymorphisms and irinotecan-induced toxicity. We undertook this study to investigate the association between UGT1A1 genetic polymorphisms and toxicity in patients treated with the FOLFIRINOX (comprising oxaliplatin, irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin) chemotherapy regimen in the JASPAC 06 study. Patients screened for UGT1A1*6 and UGT1A1*28, and treated with either the original FOLFIRINOX (oxaliplatin 85 mg/m
Schlick K, Magnes T, Ratzinger L, et al.
Novel models for prediction of benefit and toxicity with FOLFIRINOX treatment of pancreatic cancer using clinically available parameters.
PLoS One. 2018; 13(11):e0206688 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Novel models for prediction of benefit and toxicity with FOLFIRINOX treatment of pancreatic cancer using clinically available parameters.
PLoS One. 2018; 13(11):e0206688 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Despite modern chemotherapy regimens, survival of pancreatic cancer patients remains dismal. Toxicity is a major concern and it is a challenge to upfront identify patients with the highest benefit from aggressive polychemotherapy. We aimed to evaluate ORR and side effects of the FOLFIRINOX regimen, highlighting dose modification and to explore possible prognostic response factors as a clinical tool.
METHODS: This retrospective study includes 123 patients with metastatic PC that were treated with FOLFIRINOX between the years 2007 to 2016 in a single academic institution. Survival rates were analysed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Prognostic models including laboratory and clinical parameters were calculated using Cox proportional models in univariate and multivariate analyses.
RESULTS: Median age at diagnosis was 64 years (47-78 years), 71 (57, 7%) were male and the majority had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1 (63 patients; 83.7%). After a median follow up of 17.8 months, median progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 5.7 (4.55-6.84; 95%CI) and 11.8 months (9.35-14.24; 95%CI) respectively. Overall response rate with FOLFIRINOX was 34.9% and stable disease rate was 21.9%. Regarding Grade 3/4 side effects, 62 events, were reported in 37 patients. Looking at risk factors e.g. patient characteristics, tumor marker, inflammatory markers and body composition multivariate analyses proved CEA >4 elevation and BMI > 25 at the time point before palliative chemotherapy to be independent negative prognostic factors for OS. Grouping patients with no risk factor, one or two of these risk factors we analyzed a median OS of 17.4 moths, 9.6 months and 6.7 months (p<0.001) respectively. In addition we identified thrombocytosis and low BMI as predictors of early toxicity.
CONCLUSION: This study identifies two easily available factors influencing overall survival with FOLFIRINOX therapy. By combining these two factors to create a score for OS, we propose a prognostic tool for physicians to identify patients, who are unlikely to benefit more from FOLFIRINOX or likely to experience toxicity.
METHODS: This retrospective study includes 123 patients with metastatic PC that were treated with FOLFIRINOX between the years 2007 to 2016 in a single academic institution. Survival rates were analysed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Prognostic models including laboratory and clinical parameters were calculated using Cox proportional models in univariate and multivariate analyses.
RESULTS: Median age at diagnosis was 64 years (47-78 years), 71 (57, 7%) were male and the majority had an ECOG performance status of 0 or 1 (63 patients; 83.7%). After a median follow up of 17.8 months, median progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 5.7 (4.55-6.84; 95%CI) and 11.8 months (9.35-14.24; 95%CI) respectively. Overall response rate with FOLFIRINOX was 34.9% and stable disease rate was 21.9%. Regarding Grade 3/4 side effects, 62 events, were reported in 37 patients. Looking at risk factors e.g. patient characteristics, tumor marker, inflammatory markers and body composition multivariate analyses proved CEA >4 elevation and BMI > 25 at the time point before palliative chemotherapy to be independent negative prognostic factors for OS. Grouping patients with no risk factor, one or two of these risk factors we analyzed a median OS of 17.4 moths, 9.6 months and 6.7 months (p<0.001) respectively. In addition we identified thrombocytosis and low BMI as predictors of early toxicity.
CONCLUSION: This study identifies two easily available factors influencing overall survival with FOLFIRINOX therapy. By combining these two factors to create a score for OS, we propose a prognostic tool for physicians to identify patients, who are unlikely to benefit more from FOLFIRINOX or likely to experience toxicity.
Taflin H, Odin E, Derwinger K, et al.
Relationship between folate concentration and expression of folate-associated genes in tissue and plasma after intraoperative administration of leucovorin in patients with colorectal cancer.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018; 82(6):987-997 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Relationship between folate concentration and expression of folate-associated genes in tissue and plasma after intraoperative administration of leucovorin in patients with colorectal cancer.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018; 82(6):987-997 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
PURPOSE: The aim of study was to investigate the relationship between folate concentration and expression of folate-associated genes in tumour, mucosa and plasma of patients with colorectal cancer, after intraoperative administration of bolus leucovorin (LV).
METHODS: Eighty patients were randomized into four groups to receive 0, 60, 200, or 500 mg/m
RESULTS: The folate concentration in tumour increased with increasing dosage of LV. Half of the patients treated with 60 mg/m
CONCLUSIONS: The results indicate the possibility of using the individual plasma 5-MTHF/LV ratio after LV injection as a surrogate marker for tissue folate concentration. Expression of several folate-associated genes is associated with folate concentration in tissue and plasma and may become useful when predicting response to LV treatment.
METHODS: Eighty patients were randomized into four groups to receive 0, 60, 200, or 500 mg/m
RESULTS: The folate concentration in tumour increased with increasing dosage of LV. Half of the patients treated with 60 mg/m
CONCLUSIONS: The results indicate the possibility of using the individual plasma 5-MTHF/LV ratio after LV injection as a surrogate marker for tissue folate concentration. Expression of several folate-associated genes is associated with folate concentration in tissue and plasma and may become useful when predicting response to LV treatment.
Barenboim A, Lahat G, Geva R, et al.
Neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: An intention to treat analysis.
Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018; 44(10):1619-1623 [PubMed] Related Publications
Neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: An intention to treat analysis.
Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018; 44(10):1619-1623 [PubMed] Related Publications
OBJECTIVE: To assess clinical and pathologic efficacy of neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced (LAPC) and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (BRPC).
METHODS: Patients receiving neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX for LAPC and BRPC treated between 2014 and 2017 were identified. Post-treatment patients achieving resectability were referred for surgery, whereas unresectable patients continued chemotherapy. Clinical and pathological data were retrospectively compared with control group consisting of 47 consecutive patients with BRPC undergoing pancreatic and portal vein resection between 2008 and 2017.
RESULTS: Thirty LAPC and 23 BRPC patients were identified. Reasons for unresectability included disease progression (70%), locally unresectable disease (18%), and poor performance status (11%). Three patients (10%) with LAPC, and 20 (87%) with BRPC underwent curative surgery. Compared with control group, perioperative complication rate (4.3% versus 28.9%, p = 0.016), and pancreatic fistula rate (0 versus 14.8%, p = 0.08) were lower. Peripancreatic fat invasion (52.2% vs 97.8%, p = 0.001), lymph node involvement (22% vs 54.3%, p = 0.01), and surgical margin involvement (0 vs 17.4%, p = 0.04) were higher in the control group. Median survival was 34.3 months in BRPC patients operated after FOLFIRINOX and 26.1 months in the control group (p = 0.07). Three patients (13%) with complete pathological response are disease-free after mean follow-up of 19 months.
CONCLUSIONS: Whereas neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX rarely achieves resectability in patients with LAPC (10%), most BRPC undergo resection (87%). Neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX leads to complete pathological response in 13% of cases, tumor downstaging, and a trend towards improved survival compared with patients undergoing up-front surgery.
METHODS: Patients receiving neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX for LAPC and BRPC treated between 2014 and 2017 were identified. Post-treatment patients achieving resectability were referred for surgery, whereas unresectable patients continued chemotherapy. Clinical and pathological data were retrospectively compared with control group consisting of 47 consecutive patients with BRPC undergoing pancreatic and portal vein resection between 2008 and 2017.
RESULTS: Thirty LAPC and 23 BRPC patients were identified. Reasons for unresectability included disease progression (70%), locally unresectable disease (18%), and poor performance status (11%). Three patients (10%) with LAPC, and 20 (87%) with BRPC underwent curative surgery. Compared with control group, perioperative complication rate (4.3% versus 28.9%, p = 0.016), and pancreatic fistula rate (0 versus 14.8%, p = 0.08) were lower. Peripancreatic fat invasion (52.2% vs 97.8%, p = 0.001), lymph node involvement (22% vs 54.3%, p = 0.01), and surgical margin involvement (0 vs 17.4%, p = 0.04) were higher in the control group. Median survival was 34.3 months in BRPC patients operated after FOLFIRINOX and 26.1 months in the control group (p = 0.07). Three patients (13%) with complete pathological response are disease-free after mean follow-up of 19 months.
CONCLUSIONS: Whereas neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX rarely achieves resectability in patients with LAPC (10%), most BRPC undergo resection (87%). Neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX leads to complete pathological response in 13% of cases, tumor downstaging, and a trend towards improved survival compared with patients undergoing up-front surgery.
Mizusawa J, Fukutomi A, Katayama H, et al.
Protocol digest of randomized phase II study of modified FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel combination therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Japan clinical oncology group study (JCOG1407).
Pancreatology. 2018; 18(7):841-845 [PubMed] Related Publications
Protocol digest of randomized phase II study of modified FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel combination therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Japan clinical oncology group study (JCOG1407).
Pancreatology. 2018; 18(7):841-845 [PubMed] Related Publications
Gemcitabine is one of the standard treatments for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Recent studies on metastatic pancreatic cancer have shown that combination chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFIRINOX) and gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel (GnP) prolonged the overall survival compared with gemcitabine alone. To select the most promising chemotherapy, a randomized phase II selection design trial was started in July 2016 to compare between modified FOLFIRINOX and GnP for patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. A total of 124 patients will be enrolled from 36 Japanese institutions within 2.5 years. The primary endpoint is the proportion of 1-year overall survival, and secondary endpoints are progression-free survival, distant metastasis-free survival, response rate in patients with target lesions, CA19-9 response, adverse events, treatment-related death, early death, grade 4 non-hematological toxicity, and dose intensity. This trial has been registered with the UMIN Clinical Trials Registry [http://www.umin.ac.jp/ctr/index.htm], and the registration number is UMIN000023143.
Schwarz L, Vernerey D, Bachet JB, et al.
Resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma neo-adjuvant FOLF(IRIN)OX-based chemotherapy - a multicenter, non-comparative, randomized, phase II trial (PANACHE01-PRODIGE48 study).
BMC Cancer. 2018; 18(1):762 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma neo-adjuvant FOLF(IRIN)OX-based chemotherapy - a multicenter, non-comparative, randomized, phase II trial (PANACHE01-PRODIGE48 study).
BMC Cancer. 2018; 18(1):762 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND: At time of diagnosis, less than 10% of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinomas (PDAC) are considered to be immediately operable (i.e. resectable). Considering their poor overall survival (OS), only tumours without vascular invasion (NCCN 2017) should be considered for resection, i.e. those for which resection with disease-free margins (R0) is theoretically possible in absence of presurgery treatment. With regard to high R1 rates and undetectable locoregional and/or metastatic spreading prior to surgery explain (at least in part) the observed 1-year relapse and mortality rates of 50 and 25%, respectively. Today, upfront surgery followed by adjuvant chemotherapy is the reference treatment in Europe. The main limitation of the adjuvant approach is the low rate of completion of the full therapeutic sequence. Indeed, only 47 to 60% patients received any adjuvant therapy after resection compared to more than 75% for neoadjuvant therapy. No previous prospective study has compared this approach to a neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX or FOLFOX chemotherapy for resectable PDAC.
METHODS: PANACHE01-PRODIGE48 is a prospective multicentre controlled randomized non comparative Phase II trial, evaluating the safety and efficacy of two regimens of neo-adjuvant chemotherapy (4 cycles of mFOLFIRINOX or FOLFOX) relative to the current reference treatment (surgery and then adjuvant chemotherapy) in patients with resectable PDAC. The main co-primary endpoints are OS rate at 12 months and the rate of patients undergoing the full therapeutic sequence.
DISCUSSION: The "ideal" cancer treatment for resectable PDAC would have the following characteristics: administration to the highest possible proportion of patients, ability to identify fast-progressing patients (i.e. poor candidates for surgery), a low rate of R1 resections (through optimisation of local disease control), and an acceptable toxicity profile. The neoadjuvant approach may meet all these criteria. With respect to published data on the efficacy of FOLFOX and mFOLFIRINOX, these two regimens are potential candidates for neoadjuvant use in the aim to optimising oncological outcomes in resectable PDAC.
TRIAL REGISTRATION: ClinicalTrials.gov , NCT02959879 . Trial registration date: November 9, 2016.
METHODS: PANACHE01-PRODIGE48 is a prospective multicentre controlled randomized non comparative Phase II trial, evaluating the safety and efficacy of two regimens of neo-adjuvant chemotherapy (4 cycles of mFOLFIRINOX or FOLFOX) relative to the current reference treatment (surgery and then adjuvant chemotherapy) in patients with resectable PDAC. The main co-primary endpoints are OS rate at 12 months and the rate of patients undergoing the full therapeutic sequence.
DISCUSSION: The "ideal" cancer treatment for resectable PDAC would have the following characteristics: administration to the highest possible proportion of patients, ability to identify fast-progressing patients (i.e. poor candidates for surgery), a low rate of R1 resections (through optimisation of local disease control), and an acceptable toxicity profile. The neoadjuvant approach may meet all these criteria. With respect to published data on the efficacy of FOLFOX and mFOLFIRINOX, these two regimens are potential candidates for neoadjuvant use in the aim to optimising oncological outcomes in resectable PDAC.
TRIAL REGISTRATION: ClinicalTrials.gov , NCT02959879 . Trial registration date: November 9, 2016.
Kawai K, Sunami E, Hata K, et al.
Phase I/II Study of Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy With TEGAFIRI for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer.
Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018; 17(3):240-246 [PubMed] Related Publications
Phase I/II Study of Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy With TEGAFIRI for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer.
Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018; 17(3):240-246 [PubMed] Related Publications
INTRODUCTION: Chemoradiotherapy (CRT) is the standard treatment for locally advanced rectal cancer; however, the optimal chemotherapy sequence to administer simultaneously with radiotherapy remains unclear. We conducted a phase I/II study to test a new regimen, TEGAFIRI (combination tegafur, uracil [UFT], leucovorin [LV], irinotecan), for patients with locally advanced rectal cancer.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: A total of 22 patients with locally advanced lower rectal adenocarcinoma were enrolled in the present study. The radiation dose was 50.4 Gy in 28 fractions. UFT (300 mg/m
RESULTS: Dose-limiting toxicity was not observed at any dosing level. The most frequent adverse event was leukopenia (50%), followed by diarrhea (45.5%), anal pain (31.8%), and neutropenia (27.3%). All were well-managed with the appropriate drugs. The total pathologic complete response rate was 22.7%, and the proportion of good responders was 28.6%, 50%, and 71.4% at levels 1, 2, and 3, respectively. None of the patients experienced local recurrence. The 5-year relapse-free and overall survival rates were 80.4% and 80.8%, respectively.
CONCLUSION: TEGAFIRI is a promising CRT regimen that results in marked tumor regression and good local control. Moreover, its adverse events are well-tolerated.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: A total of 22 patients with locally advanced lower rectal adenocarcinoma were enrolled in the present study. The radiation dose was 50.4 Gy in 28 fractions. UFT (300 mg/m
RESULTS: Dose-limiting toxicity was not observed at any dosing level. The most frequent adverse event was leukopenia (50%), followed by diarrhea (45.5%), anal pain (31.8%), and neutropenia (27.3%). All were well-managed with the appropriate drugs. The total pathologic complete response rate was 22.7%, and the proportion of good responders was 28.6%, 50%, and 71.4% at levels 1, 2, and 3, respectively. None of the patients experienced local recurrence. The 5-year relapse-free and overall survival rates were 80.4% and 80.8%, respectively.
CONCLUSION: TEGAFIRI is a promising CRT regimen that results in marked tumor regression and good local control. Moreover, its adverse events are well-tolerated.
Erstad DJ, Sojoodi M, Taylor MS, et al.
Orthotopic and heterotopic murine models of pancreatic cancer and their different responses to FOLFIRINOX chemotherapy.
Dis Model Mech. 2018; 11(7) [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Orthotopic and heterotopic murine models of pancreatic cancer and their different responses to FOLFIRINOX chemotherapy.
Dis Model Mech. 2018; 11(7) [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Syngeneic, immunocompetent allograft tumor models recapitulate important aspects of the tumor microenvironment and have short tumor latency with predictable growth kinetics, making them useful for trialing novel therapeutics. Here, we describe surgical techniques for orthotopic and heterotopic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tumor implantation and characterize phenotypes based on implantation site.Mice (
Machover D, Goldschmidt E, Mollicone R, et al.
Enhancement of 5-Fluorouracil Cytotoxicity by Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate and Folinic Acid in Tandem.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018; 366(2):238-243 [PubMed] Related Publications
Enhancement of 5-Fluorouracil Cytotoxicity by Pyridoxal 5'-Phosphate and Folinic Acid in Tandem.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018; 366(2):238-243 [PubMed] Related Publications
The current study originates from the assumption that, in tumors, levels of naturally occurring pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) are too small to allow conversion of tetra hydro pteroylglutamate (H
Saito K, Isayama H, Sakamoto Y, et al.
A phase II trial of gemcitabine, S-1 and LV combination (GSL) neoadjuvant chemotherapy for patients with borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer.
Med Oncol. 2018; 35(7):100 [PubMed] Related Publications
A phase II trial of gemcitabine, S-1 and LV combination (GSL) neoadjuvant chemotherapy for patients with borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer.
Med Oncol. 2018; 35(7):100 [PubMed] Related Publications
There has been a pressing need to develop optimal regimen for neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for pancreatic cancer (PC). The safety and efficacy of gemcitabine, S-1, and LV combination (GSL) therapy as NAC for borderline resectable (BR) and locally advanced (LA) PC was evaluated in this phase II study. Patients with pathologically proven BR or LA PC were enrolled and gemcitabine 1000 mg/m
Vaishnavi K, Bansal D, Trehan A, et al.
Improving the safety of high-dose methotrexate for children with hematologic cancers in settings without access to MTX levels using extended hydration and additional leucovorin.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2018; 65(12):e27241 [PubMed] Related Publications
Improving the safety of high-dose methotrexate for children with hematologic cancers in settings without access to MTX levels using extended hydration and additional leucovorin.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2018; 65(12):e27241 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: A lack of access to methotrexate levels is common in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC), relevant for 80% of children with cancer worldwide. We evaluated whether high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX) can be administered safely with extended hydration and leucovorin rescue, with monitoring of serum creatinine and urine pH.
METHODS: The prospective study was conducted at a single centre in Chandigarh, India in 2015. Patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) or with T-cell ALL or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (T-NHL) were administered 3 and 5 gm/m
RESULTS: The study included 100 cycles of HD-MTX in 53 patients: B-ALL 25 patients (51 cycles), T-ALL 16 patients (28 cycles), T-NHL 10 patients (18 cycles), and relapsed ALL 2 patients (3 cycles). The mean age was 6.8 ± 3.2 years. Patients were underweight in 15 (15%) cycles. Patients in 23% of cycles had a rise in creatinine to >1.25 times the baseline. Toxicities (NCI CTCAE v4.0) included mucositis (32%), diarrhoea (10%), and febrile neutropenia (9%). One patient died from dengue shock syndrome.
CONCLUSIONS: It is safe to administer 3 or 5 gm/m
METHODS: The prospective study was conducted at a single centre in Chandigarh, India in 2015. Patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) or with T-cell ALL or non-Hodgkin lymphoma (T-NHL) were administered 3 and 5 gm/m
RESULTS: The study included 100 cycles of HD-MTX in 53 patients: B-ALL 25 patients (51 cycles), T-ALL 16 patients (28 cycles), T-NHL 10 patients (18 cycles), and relapsed ALL 2 patients (3 cycles). The mean age was 6.8 ± 3.2 years. Patients were underweight in 15 (15%) cycles. Patients in 23% of cycles had a rise in creatinine to >1.25 times the baseline. Toxicities (NCI CTCAE v4.0) included mucositis (32%), diarrhoea (10%), and febrile neutropenia (9%). One patient died from dengue shock syndrome.
CONCLUSIONS: It is safe to administer 3 or 5 gm/m
Marchegiani G, Todaro V, Boninsegna E, et al.
Surgery after FOLFIRINOX treatment for locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: increase in tumour attenuation on CT correlates with R0 resection.
Eur Radiol. 2018; 28(10):4265-4273 [PubMed] Related Publications
Surgery after FOLFIRINOX treatment for locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: increase in tumour attenuation on CT correlates with R0 resection.
Eur Radiol. 2018; 28(10):4265-4273 [PubMed] Related Publications
OBJECTIVES: To assess factors associated with radical resection (R0) of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) after induction treatment with FOLFIRINOX.
METHODS: Patients with either locally advanced (LA) and borderline resectable (BR) PDAC undergoing surgical exploration after FOLFIRINOX were retrospectively enrolled. Two pancreatic radiologists reviewed the CT blinded to the final outcome and assessed chemotherapy response and resectability. Patients were then divided into R0 resected (group A) and not resected/R1 resected (group B), which were compared.
RESULTS: Of 59 patients included, 19 were defined as unresectable (32%), 33 borderline resectable (56%) and 7 resectable (12%) during the blind radiological evaluation after FOLFIRINOX. Once in a surgical setting, 27% were non-resectable, whereas 73% received surgical resection with a 70% R0 rate. Consequent sensitivity and specificity were 86% and 29%. At imaging review, significant decreases in longest tumour dimension were observed in both groups: from 32 mm (95% CI 15-55) to 21 (10-44) in group A and from 34 (18-70) to 26 (7-60) in group B, p < 0.05. However, a significant increase in tumour attenuation in all phases was only observed for R0 resected, from 52 HU (26-75) to 65 (35-92) in arterial phase (p < 0.001) and from 62 (36-96) to 78 (40-120) in the venous (p = 0.001).
CONCLUSION: After neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX, CT predicted resectability with acceptable sensitivity but low specificity. The observation of increased tumour attenuation at CT scan after FOLFIRINOX treatment might represent a reliable predictor of R0 resection.
KEY POINTS: • CT drives the assessment of PDAC resectability after FOLFIRINOX • CT predicts resectability with acceptable sensitivity but low specificity • Significant increase in tumour attenuation was only observed for R0 resected PDAC • Tumour attenuation after FOLFIRINOX represents a reliable predictor of R0 resection.
METHODS: Patients with either locally advanced (LA) and borderline resectable (BR) PDAC undergoing surgical exploration after FOLFIRINOX were retrospectively enrolled. Two pancreatic radiologists reviewed the CT blinded to the final outcome and assessed chemotherapy response and resectability. Patients were then divided into R0 resected (group A) and not resected/R1 resected (group B), which were compared.
RESULTS: Of 59 patients included, 19 were defined as unresectable (32%), 33 borderline resectable (56%) and 7 resectable (12%) during the blind radiological evaluation after FOLFIRINOX. Once in a surgical setting, 27% were non-resectable, whereas 73% received surgical resection with a 70% R0 rate. Consequent sensitivity and specificity were 86% and 29%. At imaging review, significant decreases in longest tumour dimension were observed in both groups: from 32 mm (95% CI 15-55) to 21 (10-44) in group A and from 34 (18-70) to 26 (7-60) in group B, p < 0.05. However, a significant increase in tumour attenuation in all phases was only observed for R0 resected, from 52 HU (26-75) to 65 (35-92) in arterial phase (p < 0.001) and from 62 (36-96) to 78 (40-120) in the venous (p = 0.001).
CONCLUSION: After neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX, CT predicted resectability with acceptable sensitivity but low specificity. The observation of increased tumour attenuation at CT scan after FOLFIRINOX treatment might represent a reliable predictor of R0 resection.
KEY POINTS: • CT drives the assessment of PDAC resectability after FOLFIRINOX • CT predicts resectability with acceptable sensitivity but low specificity • Significant increase in tumour attenuation was only observed for R0 resected PDAC • Tumour attenuation after FOLFIRINOX represents a reliable predictor of R0 resection.
Ozaka M, Ishii H, Sato T, et al.
A phase II study of modified FOLFIRINOX for chemotherapy-naïve patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018; 81(6):1017-1023 [PubMed] Related Publications
A phase II study of modified FOLFIRINOX for chemotherapy-naïve patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018; 81(6):1017-1023 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: We evaluated the efficacy and safety of a modified FOLFIRINOX regimen for chemotherapy-naïve patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer.
METHODS: Patients with untreated metastatic pancreatic cancer (MPC) received modified FOLFIRINOX (intravenous oxaliplatin 85 mg/m
RESULTS: Sixty-nine pts. were enrolled from 39 institutions in Japan. The median overall survival was 11.2 months [95% confidence interval (CI) 9.0-]. The median progression-free survival was 5.5 months (95% CI 4.1-6.7). The response rate was 37.7% (95% CI 26.3-50.2), and the disease control rate was 78.3% (95% CI 66.7-87.3). The incidence of grade 3 or higher neutropenia was 47.8%. Serious adverse events occurred in six patients (8.7%). All AE proportions were less than those in the previous Japanese full-dose phase II study. One patient died due to interstitial pneumonia related to treatment.
CONCLUSION: This is the first prospective study of modified FOLFIRINOX in Asia. Modified FOLFIRINOX in this study has an improved safety profile with maintained efficacy in MPC without prophylactic pegfilgrastim.
METHODS: Patients with untreated metastatic pancreatic cancer (MPC) received modified FOLFIRINOX (intravenous oxaliplatin 85 mg/m
RESULTS: Sixty-nine pts. were enrolled from 39 institutions in Japan. The median overall survival was 11.2 months [95% confidence interval (CI) 9.0-]. The median progression-free survival was 5.5 months (95% CI 4.1-6.7). The response rate was 37.7% (95% CI 26.3-50.2), and the disease control rate was 78.3% (95% CI 66.7-87.3). The incidence of grade 3 or higher neutropenia was 47.8%. Serious adverse events occurred in six patients (8.7%). All AE proportions were less than those in the previous Japanese full-dose phase II study. One patient died due to interstitial pneumonia related to treatment.
CONCLUSION: This is the first prospective study of modified FOLFIRINOX in Asia. Modified FOLFIRINOX in this study has an improved safety profile with maintained efficacy in MPC without prophylactic pegfilgrastim.
Zhang H, Kellett C, Lambert P, Kim CA
Efficacy and Tolerability of Second-line Nab-paclitaxel and Gemcitabine After Failure of First-line FOLFIRINOX for Advanced Pancreas Cancer: A Single-institution Experience.
Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018; 17(3):e451-e456 [PubMed] Related Publications
Efficacy and Tolerability of Second-line Nab-paclitaxel and Gemcitabine After Failure of First-line FOLFIRINOX for Advanced Pancreas Cancer: A Single-institution Experience.
Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018; 17(3):e451-e456 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Advanced pancreatic cancer (APC) has a poor prognosis. Current first-line chemotherapy options include FOLFIRINOX (5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, oxaliplatin), NG (nab-paclitaxel, gemcitabine), and GEM (gemcitabine) alone. The optimal second-line regimen is unclear. For patients with disease progression with FOLFIRINOX who have a good performance status, NG might be a reasonable second-line option.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Patients in whom APC was diagnosed from 2012 to 2016 who underwent chemotherapy at CancerCare Manitoba were identified from the Manitoba Cancer Registry. Pharmacy records were used to identified those patients who had received first-line FOLFIRINOX, followed by second-line NG, GEM alone, or best supportive care. A retrospective analysis was performed to identify the patient and treatment characteristics, toxicity, radiologic response, and survival. Edmonton Symptom Assessment System, revised, scores were analyzed to assess symptom control.
RESULTS: A total of 146 patients had received first-line FOLFIRINOX. Of those with disease progression who were offered second-line therapy, 30 received NG, 8 GEM alone, and 22 best supportive care. NG was more toxic than GEM alone; however, the dose intensity was similar between the 2 groups. The median progression-free survival was 3.61 months in the NG group and 2.51 months in the GEM-alone group. The median overall survival was 5.69 months in the NG group and 3.82 months in the GEM-alone group. No significant differences were found in the Edmonton Symptom Assessment System, revised, scores when stratified by the treatment received.
CONCLUSION: For select patients with APC in whom first-line FOLFIRINOX fails, a role might exist for second-line NG. In our institution, second-line NG was associated with improvement in survival compared with second-line GEM alone, with a manageable toxicity profile.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Patients in whom APC was diagnosed from 2012 to 2016 who underwent chemotherapy at CancerCare Manitoba were identified from the Manitoba Cancer Registry. Pharmacy records were used to identified those patients who had received first-line FOLFIRINOX, followed by second-line NG, GEM alone, or best supportive care. A retrospective analysis was performed to identify the patient and treatment characteristics, toxicity, radiologic response, and survival. Edmonton Symptom Assessment System, revised, scores were analyzed to assess symptom control.
RESULTS: A total of 146 patients had received first-line FOLFIRINOX. Of those with disease progression who were offered second-line therapy, 30 received NG, 8 GEM alone, and 22 best supportive care. NG was more toxic than GEM alone; however, the dose intensity was similar between the 2 groups. The median progression-free survival was 3.61 months in the NG group and 2.51 months in the GEM-alone group. The median overall survival was 5.69 months in the NG group and 3.82 months in the GEM-alone group. No significant differences were found in the Edmonton Symptom Assessment System, revised, scores when stratified by the treatment received.
CONCLUSION: For select patients with APC in whom first-line FOLFIRINOX fails, a role might exist for second-line NG. In our institution, second-line NG was associated with improvement in survival compared with second-line GEM alone, with a manageable toxicity profile.
Kang J, Hwang I, Yoo C, et al.
Nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine versus FOLFIRINOX as the first-line chemotherapy for patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer: retrospective analysis.
Invest New Drugs. 2018; 36(4):732-741 [PubMed] Related Publications
Nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine versus FOLFIRINOX as the first-line chemotherapy for patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer: retrospective analysis.
Invest New Drugs. 2018; 36(4):732-741 [PubMed] Related Publications
Purpose nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine (AG) and FOLFIRINOX have been established as standard first-line treatment in metastatic pancreatic cancer (mPC). We performed retrospective analysis comparing the efficacies of AG and FOLFIRINOX in daily practice setting. Materials and Methods We analyzed 308 patients who presented initially as mPC and received AG (n = 149) or FOLFIRINOX (n = 159) as first-line treatment between 2013 and 2016. Primary endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Result There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of baseline characteristics, except older age and higher Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score in AG group. The response rates (34% vs 34%) and median PFS (6.8 vs 5.1 months) were comparable between two groups (p = 0.88 and p = 0.19, respectively), while median OS was significantly better with AG than FOLFIRINOX (11.4 vs 9.6 months; p = 0.002). Elevated baseline CA19-9 level and liver metastasis were independent adverse prognostic factors for PFS and OS. In subgroup analyses, PFS with AG was better in patients with age ≥ 65 years, peritoneal metastasis, and higher CCI than that with FOLFIRINOX. Conclusion Both AG and FOLFIRINOX showed comparable efficacy outcomes in daily practice setting. AG might be preferentially considered in patients with peritoneal metastasis, comorbid medical conditions or old age.
Usón Junior PLS, Rother ET, Maluf FC, Bugano DDG
Meta-analysis of Modified FOLFIRINOX Regimens for Patients With Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer.
Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018; 17(3):187-197 [PubMed] Related Publications
Meta-analysis of Modified FOLFIRINOX Regimens for Patients With Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer.
Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018; 17(3):187-197 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: We performed a meta-analysis of previous reports evaluating the effect of mFIO (modified FOLFIRINOX; leucovorin, 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, oxaliplatin) regimens in advanced pancreatic cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We performed a meta-analysis of reported studies in PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science (1950-2016) in December 2016. The inclusion criteria were randomized trials, prospective or retrospective cohorts, patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma, the use of mFIO or FOLFIRINOX (FIO) chemotherapy, and available information for ≥ 1 efficacy endpoint (response rate, progression-free survival, and/or overall survival). The outcomes were compared according to the chemotherapy regimen using a random effects model. We also performed a meta-regression analysis to evaluate the effect of dose reductions on outcomes.
RESULTS: Of 2525 abstracts, 32 were considered eligible. Modifications in the FIO regimen included omission of the 5-fluorouracil bolus and/or dose reductions in infusional 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, and/or oxaliplatin. mFIO was not associated with inferior response rates (32% vs. 33%; P = .879), lower rates of survival at 11 months (47% vs. 50%; P = .38), or lower 6-month progression-free survival rates (47% vs. 53%; P = .38). The meta-regression of the percentage of dose reduction failed to show any association.
CONCLUSION: The results of the present meta-analysis with a combined sample size of 1461 patients suggest that it is reasonable to consider mFIO regimens for patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We performed a meta-analysis of reported studies in PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science (1950-2016) in December 2016. The inclusion criteria were randomized trials, prospective or retrospective cohorts, patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma, the use of mFIO or FOLFIRINOX (FIO) chemotherapy, and available information for ≥ 1 efficacy endpoint (response rate, progression-free survival, and/or overall survival). The outcomes were compared according to the chemotherapy regimen using a random effects model. We also performed a meta-regression analysis to evaluate the effect of dose reductions on outcomes.
RESULTS: Of 2525 abstracts, 32 were considered eligible. Modifications in the FIO regimen included omission of the 5-fluorouracil bolus and/or dose reductions in infusional 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, and/or oxaliplatin. mFIO was not associated with inferior response rates (32% vs. 33%; P = .879), lower rates of survival at 11 months (47% vs. 50%; P = .38), or lower 6-month progression-free survival rates (47% vs. 53%; P = .38). The meta-regression of the percentage of dose reduction failed to show any association.
CONCLUSION: The results of the present meta-analysis with a combined sample size of 1461 patients suggest that it is reasonable to consider mFIO regimens for patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Byrne JD, Jajja MRN, O'Neill AT, et al.
Impact of formulation on the iontophoretic delivery of the FOLFIRINOX regimen for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018; 81(6):991-998 [PubMed] Related Publications
Impact of formulation on the iontophoretic delivery of the FOLFIRINOX regimen for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018; 81(6):991-998 [PubMed] Related Publications
PURPOSE: Effective treatment of patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer is a significant unmet clinical need. One major hurdle that exists is inadequate drug delivery due to the desmoplastic stroma and poor vascularization that is characteristic of pancreatic cancer. The local iontophoretic delivery of chemotherapies provides a novel way of improving treatment. With the growing practice of highly toxic combination therapies in the treatment of pancreatic cancer, the use of iontophoresis for local delivery can potentiate the anti-cancer effects of these therapies while sparing unwanted toxicity. The objective of this study was to investigate the impact of formulation on the electro-transport of the FOLFIRINOX regimen for the development of a new treatment for pancreatic cancer.
METHODS: Three formulations of the FOLFIRINOX regimen (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin) were generated at a fixed pH of 6.0 and were referred to as formulation A (single drug solution with all four drugs combined), formulation B (two drug solutions with two drugs per solution), and formulation C (four individual drug solutions). Anodic iontophoresis of the three different formulations was evaluated in orthotopic patient-derived xenografts of pancreatic cancer.
RESULTS: Iontophoretic transport of the FOLFIRINOX drugs was characterized according to organ exposure after a single device treatment in vivo. We report that the co-iontophoresis of two drug solutions, leucovorin + oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil + irinotecan, resulted in the highest levels of cytotoxic drugs in the tumor compared to drugs delivered individually or combined into one solution. There was no significant difference in plasma, pancreas, kidney, and liver exposure to the cytotoxic drugs delivered by the three different formulations. In addition, we found that reducing the duration of iontophoretic treatment from 10 to 5 min per solution resulted in a significant decrease in drug concentrations.
CONCLUSIONS: Underlying the difference in drug transport of the formulations was electrolyte concentrations, which includes both active and inactive components. Electrolyte concentrations can hinder or improve drug electro-transport. Overall, balancing electrolyte concentration is needed for optimal electro-transport.
METHODS: Three formulations of the FOLFIRINOX regimen (5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin) were generated at a fixed pH of 6.0 and were referred to as formulation A (single drug solution with all four drugs combined), formulation B (two drug solutions with two drugs per solution), and formulation C (four individual drug solutions). Anodic iontophoresis of the three different formulations was evaluated in orthotopic patient-derived xenografts of pancreatic cancer.
RESULTS: Iontophoretic transport of the FOLFIRINOX drugs was characterized according to organ exposure after a single device treatment in vivo. We report that the co-iontophoresis of two drug solutions, leucovorin + oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil + irinotecan, resulted in the highest levels of cytotoxic drugs in the tumor compared to drugs delivered individually or combined into one solution. There was no significant difference in plasma, pancreas, kidney, and liver exposure to the cytotoxic drugs delivered by the three different formulations. In addition, we found that reducing the duration of iontophoretic treatment from 10 to 5 min per solution resulted in a significant decrease in drug concentrations.
CONCLUSIONS: Underlying the difference in drug transport of the formulations was electrolyte concentrations, which includes both active and inactive components. Electrolyte concentrations can hinder or improve drug electro-transport. Overall, balancing electrolyte concentration is needed for optimal electro-transport.
Katada E, Mitsui A, Sasaki S, et al.
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after a Variety of Combined Chemotherapies Containing Bevacizumab for Metastatic Colon Cancer.
Intern Med. 2018; 57(16):2403-2407 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after a Variety of Combined Chemotherapies Containing Bevacizumab for Metastatic Colon Cancer.
Intern Med. 2018; 57(16):2403-2407 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
A 44-year-old woman with advanced metastatic colon cancer received chemotherapies comprising oxaliplatin and capecitabine (XELOX), irinotecan hydrochloride, leucovorin calcium and fluorouracil irinotecan (FOLFIRI)/panitumumab and mFOLFOX6/bevacizumab. Fifteen months later, she presented with the acute onset of a headache, drowsiness and seizure with a fever and hypertension. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) indicated bilateral regions of signal hyperintensity in the white matter with spasms of bilateral cerebral arteries apparent on magnetic resonance angiography. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) was diagnosed, and treatments resulted in improvement of the MRI findings, but the patient experienced cerebral infarction and ultimately died of deterioration of cancer on day 26 after the onset of PRES.


 Fluorouracil
Fluorouracil