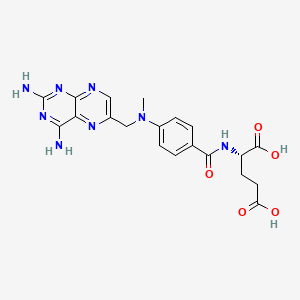
Methotrexate
"An antineoplastic antimetabolite with immunosuppressant properties. It is an inhibitor of TETRAHYDROFOLATE DEHYDROGENASE and prevents the formation of tetrahydrofolate, necessary for synthesis of thymidylate, an essential component of DNA." (MeSH 2013)
Found this page useful?
 Web Resources: Methotrexate
Web Resources: Methotrexate Latest Research Publications
Latest Research PublicationsWeb Resources: Methotrexate (6 links)
Cancer Research UK
Irish Cancer Society
Macmillan Cancer Support
NHS Evidence
 Methotrexate - Substance Summary
Methotrexate - Substance Summary
PubChem
MedlinePlus
Latest Research Publications
This list of publications is regularly updated (Source: PubMed).
Wińska P, Widło Ł, Skierka K, et al.
Simultaneous Inhibition of Protein Kinase CK2 and Dihydrofolate Reductase Results in Synergistic Effect on Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells.
Anticancer Res. 2019; 39(7):3531-3542 [PubMed] Related Publications
Simultaneous Inhibition of Protein Kinase CK2 and Dihydrofolate Reductase Results in Synergistic Effect on Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells.
Anticancer Res. 2019; 39(7):3531-3542 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND/AIM: Recently, we demonstrated the ability of inhibitors of protein kinase 2 (casein kinase II; CK2) to enhance the efficacy of 5-fluorouracil, a thymidylate synthase (TYMS)-directed drug for anticancer treatment. The present study aimed to investigate the antileukemic effect of simultaneous inhibition of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR), another enzyme involved in the thymidylate biosynthesis cycle, and CK2 in CCRF-CEM acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The influence of combined treatment on apoptosis and cell-cycle progression, as well as the endocellular level of DHFR protein and inhibition of CK2 were determined using flow cytometry and western blot analysis, respectively. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to examine the influence of silmitasertib (CX-4945), a selective inhibitor of CK2 on the expression of DHFR and TYMS genes.
RESULTS: The synergistic effect was correlated with the increase of annexin V-binding cell fraction, caspase 3/7 activation and a significant reduce in the activity of CK2. An increase of DHFR protein level was observed in CCRF-CEM cells after CX-4945 treatment, with the mRNA level remaining relatively constant.
CONCLUSION: The obtained results demonstrate a possibility to improve methotrexate-based anti-leukemia therapy by simultaneous inhibition of CK2. The effect of CK2 inhibition on DHFR expression suggests the important regulatory role of CK2-mediated phosphorylation of DHFR inside cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The influence of combined treatment on apoptosis and cell-cycle progression, as well as the endocellular level of DHFR protein and inhibition of CK2 were determined using flow cytometry and western blot analysis, respectively. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to examine the influence of silmitasertib (CX-4945), a selective inhibitor of CK2 on the expression of DHFR and TYMS genes.
RESULTS: The synergistic effect was correlated with the increase of annexin V-binding cell fraction, caspase 3/7 activation and a significant reduce in the activity of CK2. An increase of DHFR protein level was observed in CCRF-CEM cells after CX-4945 treatment, with the mRNA level remaining relatively constant.
CONCLUSION: The obtained results demonstrate a possibility to improve methotrexate-based anti-leukemia therapy by simultaneous inhibition of CK2. The effect of CK2 inhibition on DHFR expression suggests the important regulatory role of CK2-mediated phosphorylation of DHFR inside cells.
Zang YN, Wang SZ, Qin Y, et al.
Population pharmacokinetic study of delayed methotrexate excretion in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia .
Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019; 57(8):402-407 [PubMed] Related Publications
Population pharmacokinetic study of delayed methotrexate excretion in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia .
Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019; 57(8):402-407 [PubMed] Related Publications
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the population pharmacokinetics of delayed methotrexate (MTX) excretion in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A total of 1,659 plasma concentration samples of MTX from 190 patients with 1 - 4 courses (plasma concentrations > 0.1 µmol/L) were collected in this study. The data analysis was performed using Phoenix NLME 1.3 software. The covariates included age, body surface area (BSA), body weight, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), total bilirubin (TBIL), and serum creatinine (SCr). The final model was validated by bootstrap resampling procedures (1,000 runs) and visual predictive check (VPC) method.
RESULTS: The data were best described by a two-compartment linear pharmacokinetic model. The mean values of clearance (CL) and distribution volume (V
CONCLUSION: The final model was demonstrated as appropriate and effective for assessing the pharmacokinetic parameters of delayed MTX excretion in children with ALL.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: A total of 1,659 plasma concentration samples of MTX from 190 patients with 1 - 4 courses (plasma concentrations > 0.1 µmol/L) were collected in this study. The data analysis was performed using Phoenix NLME 1.3 software. The covariates included age, body surface area (BSA), body weight, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), total bilirubin (TBIL), and serum creatinine (SCr). The final model was validated by bootstrap resampling procedures (1,000 runs) and visual predictive check (VPC) method.
RESULTS: The data were best described by a two-compartment linear pharmacokinetic model. The mean values of clearance (CL) and distribution volume (V
CONCLUSION: The final model was demonstrated as appropriate and effective for assessing the pharmacokinetic parameters of delayed MTX excretion in children with ALL.
Kang HL, Zhao Q, Yang SL, Duan W
Efficacy of Combination Therapy with Actinomycin D and Methotrexate in the Treatment of Low-Risk Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia.
Chemotherapy. 2019; 64(1):42-47 [PubMed] Related Publications
Efficacy of Combination Therapy with Actinomycin D and Methotrexate in the Treatment of Low-Risk Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia.
Chemotherapy. 2019; 64(1):42-47 [PubMed] Related Publications
OBJECTIVES: We aimed to identify an optimal regimen for low-risk gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (LR-GTN) providing reduction in dosage and toxicity/side effects, enhancement of therapeutic efficacy, and a shorter treatment duration.
METHODS: A total of 149 LR-GTN patients were enrolled in the affiliated Beijing Maternity Hospital of Capital Medical University from January 2014 to January 2017 and randomly divided into 3 groups with 50 cases in the methotrexate (MTX) group, 49 in actinomycin D (ACT-D) group, and 50 in ACT-D+MTX group. Follow-up recorded symptoms, physical and bimanual gynecological examinations, routine blood test, serum β-HCG level, liver and renal functions, electrolytes, electrocardiogram before each treatment course, and pelvic and abdominal B-mode ultrasound or pelvic/abdominal/chest computed tomography.
RESULTS: Serum complete remission (SCR) was 96.0, 87.8, and 83.7% for the ACT-D+MTX, ACT-D, and MTX groups, respectively, with SCR being highest in the ACT-D+MTX group, statistically higher than in the MTX group. Vomiting was the only side effect differing significantly by chemotherapy regimen, with a distinctly higher incidence in the ACT-D+MTX group compared with the MTX group (p = 0.028). The reduction rate of serum β-HCG in the ACT-D+MTX group was significantly greater than in the other 2 groups.
CONCLUSION: Combined ACT-D+MTX chemotherapy achieved overall better efficacy and showed less toxicity than ACT-D or MTX alone, and thus can be prioritized for the treatment of LR-GTN.
METHODS: A total of 149 LR-GTN patients were enrolled in the affiliated Beijing Maternity Hospital of Capital Medical University from January 2014 to January 2017 and randomly divided into 3 groups with 50 cases in the methotrexate (MTX) group, 49 in actinomycin D (ACT-D) group, and 50 in ACT-D+MTX group. Follow-up recorded symptoms, physical and bimanual gynecological examinations, routine blood test, serum β-HCG level, liver and renal functions, electrolytes, electrocardiogram before each treatment course, and pelvic and abdominal B-mode ultrasound or pelvic/abdominal/chest computed tomography.
RESULTS: Serum complete remission (SCR) was 96.0, 87.8, and 83.7% for the ACT-D+MTX, ACT-D, and MTX groups, respectively, with SCR being highest in the ACT-D+MTX group, statistically higher than in the MTX group. Vomiting was the only side effect differing significantly by chemotherapy regimen, with a distinctly higher incidence in the ACT-D+MTX group compared with the MTX group (p = 0.028). The reduction rate of serum β-HCG in the ACT-D+MTX group was significantly greater than in the other 2 groups.
CONCLUSION: Combined ACT-D+MTX chemotherapy achieved overall better efficacy and showed less toxicity than ACT-D or MTX alone, and thus can be prioritized for the treatment of LR-GTN.
Yu D, Zhang S, Feng A, et al.
Methotrexate, doxorubicin, and cisplatinum regimen is still the preferred option for osteosarcoma chemotherapy: A meta-analysis and clinical observation.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(19):e15582 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Methotrexate, doxorubicin, and cisplatinum regimen is still the preferred option for osteosarcoma chemotherapy: A meta-analysis and clinical observation.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(19):e15582 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND: We designed the study to investigate whether methotrexate, doxorubicin, and cisplatinum (MAP) chemotherapy strategy was still the preferred option for the survival of osteosarcoma patients.
METHOD: We collected some trials of osteosarcoma to make a meta-analysis first. Then, we retrospectively collected data from 115 patients with osteosarcoma and performed further analysis to verify the impact of MAP regimen on the survival of patients.
RESULTS: Seven studies including 3433 participants met the preliminary inclusion criteria. Meta-analysis of the 3-year disease-free survival (odds ratio [OR] = 1.06, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.88-1.28; P = .52) and overall survival (OR = 1.21, 95% CI: 0.70-2.11; P = .54), 5-year disease-free survival (OR = 1.07, 95% CI: 0.87-1.30; P = .54) and overall survival (OR = 0.86, 95% CI: 0.65-1.12; P = .26), and mortality rate (OR = 0.90, 95% CI: 0.70-1.17; P = .44), showed no statistically significant differences. The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were neutropenia (498 [85.9%] patients in MAP vs 533 [93.3%] in MAP plus ifosfamide and etoposide, or other adjuvant therapy drugs [MAP]). MAP was associated with less frequent toxicities than MAP group with statistical significance in thrombocytopenia, febrile neutropenia, anemia, and hypophosphatemia. The same phenomenon could also be seen in the analysis of clinical data.
CONCLUSION: MAP regimen remains the preferred option for osteosarcoma chemotherapy.
METHOD: We collected some trials of osteosarcoma to make a meta-analysis first. Then, we retrospectively collected data from 115 patients with osteosarcoma and performed further analysis to verify the impact of MAP regimen on the survival of patients.
RESULTS: Seven studies including 3433 participants met the preliminary inclusion criteria. Meta-analysis of the 3-year disease-free survival (odds ratio [OR] = 1.06, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.88-1.28; P = .52) and overall survival (OR = 1.21, 95% CI: 0.70-2.11; P = .54), 5-year disease-free survival (OR = 1.07, 95% CI: 0.87-1.30; P = .54) and overall survival (OR = 0.86, 95% CI: 0.65-1.12; P = .26), and mortality rate (OR = 0.90, 95% CI: 0.70-1.17; P = .44), showed no statistically significant differences. The most common grade 3/4 adverse events were neutropenia (498 [85.9%] patients in MAP vs 533 [93.3%] in MAP plus ifosfamide and etoposide, or other adjuvant therapy drugs [MAP]). MAP was associated with less frequent toxicities than MAP group with statistical significance in thrombocytopenia, febrile neutropenia, anemia, and hypophosphatemia. The same phenomenon could also be seen in the analysis of clinical data.
CONCLUSION: MAP regimen remains the preferred option for osteosarcoma chemotherapy.
Park JE, Lee KM, Choi HY, et al.
Methotrexate-associated primary hepatic lymphoma and cranial neuropathy in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis: A case report with clinical follow-up over a 7-year period.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(17):e14997 [PubMed] Related Publications
Methotrexate-associated primary hepatic lymphoma and cranial neuropathy in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis: A case report with clinical follow-up over a 7-year period.
Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(17):e14997 [PubMed] Related Publications
RATIONALE: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) shows a variable clinical expression in patients. Articular disease is common manifestation, but patients may rarely present with extra-articular manifestation such as cranial neuropathy. Also, primary hepatic lymphoma (PHL) has rarely been reported in patient treated with immunosuppressive drug such as methotrexate (MTX) for RA. We herein describe a case of cranial neuropathy and MTX-related PHL in a woman receiving MTX for RA.
PATIENT CONCERNS: A 73-year-old women received MTX treatment for more than 5 years, presented with recurrent cranial neuropathies. During therapy of cranial neuropathies, liver enzyme levels were elevated.
DIAGNOSES: The patient was diagnosed as RA by laboratory examination. A series of examinations had been launched to evaluate any possible cause of the extra-articular manifestation of the patient including ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance image (MRI) and positron emission tomography of the liver and MRI of the brain. Finally, the patient diagnosed as MTX-associated PHL and cranial neuropathy.
INTERVENTIONS: The patient underwent 4-year MTX therapy for RA at first with prednisolone. After that, she had been treated with cyclophosphamide therapy for cranial neuropathy. The liver biopsy was performed for hepatic lesion.
OUTCOMES: MTX was discontinued, but no improvement of PHL and elevated liver enzyme was observed during the 3 weeks. The patient received 6 cycles of chemotherapy for 3 months and achieved complete remission including PHL and cranial neuronal lesion with symptom. No instances of relapse have occurred in 2 years of follow-up.
LESSONS: The present case is the extremely rare case in which MTX-related PHL and cranial neuropathy were involved together in the RA patient. It is necessary to examine long-term follow up hepatic and neurologic examinations that patient had a long history of receiving MTX therapy for RA.
PATIENT CONCERNS: A 73-year-old women received MTX treatment for more than 5 years, presented with recurrent cranial neuropathies. During therapy of cranial neuropathies, liver enzyme levels were elevated.
DIAGNOSES: The patient was diagnosed as RA by laboratory examination. A series of examinations had been launched to evaluate any possible cause of the extra-articular manifestation of the patient including ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance image (MRI) and positron emission tomography of the liver and MRI of the brain. Finally, the patient diagnosed as MTX-associated PHL and cranial neuropathy.
INTERVENTIONS: The patient underwent 4-year MTX therapy for RA at first with prednisolone. After that, she had been treated with cyclophosphamide therapy for cranial neuropathy. The liver biopsy was performed for hepatic lesion.
OUTCOMES: MTX was discontinued, but no improvement of PHL and elevated liver enzyme was observed during the 3 weeks. The patient received 6 cycles of chemotherapy for 3 months and achieved complete remission including PHL and cranial neuronal lesion with symptom. No instances of relapse have occurred in 2 years of follow-up.
LESSONS: The present case is the extremely rare case in which MTX-related PHL and cranial neuropathy were involved together in the RA patient. It is necessary to examine long-term follow up hepatic and neurologic examinations that patient had a long history of receiving MTX therapy for RA.
Hansen MF, Abel I, Clasen-Linde E
Primary malignant melanoma of the urethra in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate.
BMJ Case Rep. 2019; 12(4) [PubMed] Related Publications
Primary malignant melanoma of the urethra in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate.
BMJ Case Rep. 2019; 12(4) [PubMed] Related Publications
We report a case of a 79-year-old woman with urinary incontinence who presented at a urogynaecology appointment. Her medical history included rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treated with methotrexate (MXT) for 22 years. A polypoidal lesion was protruding from the meatus urethrae. The histoimmunocytology confirmed a primary superficial spreading malignant melanoma. The tumour was extensively excised, but 8 months later, due to a lymphatic nodal swelling, a positron emission tomography/CT was performed showing a process suspicious of malignant melanoma and multiple distant metastasis. The subsequent treatment was palliative and 1 year later, the patient died. The aetiology of malignant melanomas in the urethra is poorly understood. There is consistent evidence that RA is associated with a number of cancers, but it remains controversial whether this risk is increased with MXT. This case emphasises the importance of gynaecological examination even in patients with only weak symptoms from the pelvic region, especially in patients undergoing immunosuppressive treatment.
Bhandari A, Bansal A, Singh A, et al.
Comparison of transport of chemotherapeutic drugs in voxelized heterogeneous model of human brain tumor.
Microvasc Res. 2019; 124:76-90 [PubMed] Related Publications
Comparison of transport of chemotherapeutic drugs in voxelized heterogeneous model of human brain tumor.
Microvasc Res. 2019; 124:76-90 [PubMed] Related Publications
Systemic administration of chemotherapeutic drugs is widely used in the treatment of cancer. However, a good understanding of drug transport barriers that influence the treatment efficacy is still lacking. In this study, a voxelized numerical model based on dynamic contrast enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is employed to study the transport and efficacy of three different chemotherapeutic drugs, namely methotrexate, doxorubicin and cisplatin in human brain tumors. DCE-MRI data provides realistic heterogeneous vasculature of the tumor, the permeability of tissue to contrast agent, interstitial volume fraction (porosity) of the tissue and patient-specific arterial input function (AIF). The permeability of tissue to aforementioned drugs is determined by correlating it with the permeability of tissue to the contrast agent. The model is employed to simulate drug concentration in the tissue and compare the effect of heterogeneous vasculature on the distribution of the drugs in the tumor. The drug accumulation is observed to be higher in high permeability areas initially, and in higher porosity areas at later times. Furthermore, it is observed that methotrexate remains in the interstitial space of the tumor in higher concentration for a longer duration as compared to other two drugs, facilitating more tumor cell killing.
Abdelrady H, Hathout RM, Osman R, et al.
Exploiting gelatin nanocarriers in the pulmonary delivery of methotrexate for lung cancer therapy.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019; 133:115-126 [PubMed] Related Publications
Exploiting gelatin nanocarriers in the pulmonary delivery of methotrexate for lung cancer therapy.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019; 133:115-126 [PubMed] Related Publications
Gelatin has many merits that encourage its use in the pulmonary delivery of anticancer drugs. It is a biodegradable denatured protein which possesses several functional groups that could be modified. Additionally, it has balanced hydrophilic and hydrophobic characters, which facilitate the loading of chemotherapeutic agents. Accordingly, the purpose of the current work was to exploit this valuable biomaterial in the efficient pulmonary delivery of methotrexate in case of lung cancer. Gelatin nanoparticles were prepared via a desolvation method and the fabrication process was optimized using Box Behnken design of experiment. A comparative study on uptake of gelatin nanoparticles by lung adenocarcinoma cells and macrophages was implemented using flow cytometry. Investigation of the effect of different methotrexate loading techniques: encapsulation, post loading and chemical conjugation on the nanoparticles characteristics and cellular cytotoxicity was performed. Nano-in-microparticles were prepared by co-spray drying optimized nanoparticles with leucine. Results showed that Box Behnken design was able to optimize preparation parameters to yield uniform nanoparticles with suitable particle size for cancer cells uptake. The prepared nanoparticles demonstrated a preferential uptake by lung cancer cells. Additionally, methotrexate loaded nanoparticles demonstrated up to four fold significant reduction in methotrexate IC
Jastaniah W, Elimam N, Abdalla K, et al.
Intrathecal dose intensification by CNS status at diagnosis in the treatment of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Hematology. 2019; 24(1):369-377 [PubMed] Related Publications
Intrathecal dose intensification by CNS status at diagnosis in the treatment of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Hematology. 2019; 24(1):369-377 [PubMed] Related Publications
OBJECTIVES: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) with CNS2 status predicts inferior outcome and a high rate of CNS relapse, similar to overt CNS leukemia (CNS3). The purpose of this study was to determine if intrathecal (IT) dose intensification during induction would improve outcomes and reduce CNS relapse for CNS2 disease.
METHODS: From January 2001 to December 2014, children (1-14 years) with newly diagnosed ALL were treated at the Princess Noorah Oncology Centre (PNOC) following modifications of the Children's Oncology Group (COG) protocols. We intensified IT methotrexate (ITM) during induction for patients with CNS2 disease. Patients were evaluated for overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), and cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR).
RESULTS: 449 children with T-cell (14.3%) or B-cell (85.7%) ALL were treated using PNOC-SR or PNOC-HR regimens (Jan 2001- Dec 2007) or CALL08 regimens (Arm A [SR], Arm B [IR], and Arm C [HR]) (Jan 2008 - Dec 2014). The 5-year OS, DFS, and CIR were 87.2 ± 1.6%, 81.7 ± 1.9%, and 13.0 ± 1.7%, respectively. The OS and DFS of patients with CNS2 were significantly superior to that of patients with CNS3 (P = 0.025 and P = 0.019, respectively). Patients with CNS2 had similar OS and DFS to those with CNS1. None of the patients with CNS2 at initial diagnosis experienced CNS relapse.
CONCLUSIONS: ITM intensification during induction was associated with elimination of CNS recurrence in patients with CNS2 disease and childhood ALL. Controlled studies are needed to confirm this observation.
METHODS: From January 2001 to December 2014, children (1-14 years) with newly diagnosed ALL were treated at the Princess Noorah Oncology Centre (PNOC) following modifications of the Children's Oncology Group (COG) protocols. We intensified IT methotrexate (ITM) during induction for patients with CNS2 disease. Patients were evaluated for overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), and cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR).
RESULTS: 449 children with T-cell (14.3%) or B-cell (85.7%) ALL were treated using PNOC-SR or PNOC-HR regimens (Jan 2001- Dec 2007) or CALL08 regimens (Arm A [SR], Arm B [IR], and Arm C [HR]) (Jan 2008 - Dec 2014). The 5-year OS, DFS, and CIR were 87.2 ± 1.6%, 81.7 ± 1.9%, and 13.0 ± 1.7%, respectively. The OS and DFS of patients with CNS2 were significantly superior to that of patients with CNS3 (P = 0.025 and P = 0.019, respectively). Patients with CNS2 had similar OS and DFS to those with CNS1. None of the patients with CNS2 at initial diagnosis experienced CNS relapse.
CONCLUSIONS: ITM intensification during induction was associated with elimination of CNS recurrence in patients with CNS2 disease and childhood ALL. Controlled studies are needed to confirm this observation.
Kobayashi H, Yamaguchi S, Motegi H, et al.
Long-Term Evaluation of Combination Treatment of Single Agent HD-MTX Chemotherapy up to Three Cycles and Moderate Dose Whole Brain Irradiation for Primary CNS Lymphoma.
J Chemother. 2019; 31(1):35-41 [PubMed] Related Publications
Long-Term Evaluation of Combination Treatment of Single Agent HD-MTX Chemotherapy up to Three Cycles and Moderate Dose Whole Brain Irradiation for Primary CNS Lymphoma.
J Chemother. 2019; 31(1):35-41 [PubMed] Related Publications
High-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX)-based chemotherapy in combination with whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) has been a common therapy for primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). The aim of this study was to evaluate the survival benefit of a minimized cycle of HD-MTX monotherapy prior to WBRT. A maximum of three cycles of HD-MTX was combined with a WBRT dose of 30 Gy and an additional localized boost was administered where remnant was observed. A total of 54 patients with newly diagnosed PCNSL were enrolled in this study. The objective response rate for HD-MTX was 80% and the median overall survival was 58.4 months. Responders to HD-MTX demonstrated better survival than patients with resistance. The concentration of MTX in serum and cerebrospinal fluid was not related the chemotherapeutic response. This study demonstrated the efficacy of HD-MTX prior to WBRT and indicated that three cycles of HD-MTX monotherapy may be sufficient in combination with radiotherapy.
Inose R, Takahashi K, Nanno S, et al.
Calcium Channel Blockers Possibly Delay the Elimination of Plasma Methotrexate in Patients Receiving High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy.
J Chemother. 2019; 31(1):30-34 [PubMed] Related Publications
Calcium Channel Blockers Possibly Delay the Elimination of Plasma Methotrexate in Patients Receiving High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy.
J Chemother. 2019; 31(1):30-34 [PubMed] Related Publications
Delayed elimination of plasma methotrexate (MTX), which leads to elevated toxicity, is often observed in patients receiving high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX) therapy, despite of the preventive measures. In this study, we investigated the factors that delay elimination of plasma MTX in patients on HD-MTX therapy. Fifteen patients who received HD-MTX therapy (21 cycles) were classified into two groups: delayed elimination of plasma MTX (38.1%, 8/21) and normal elimination of plasma MTX (61.9%, 13/21). Patient characteristics, plasma MTX concentrations, laboratory values, and adverse reactions were compared between the two groups using Fisher's exact test. Univariate analysis showed that co-administration of calcium channel blockers was significantly associated with delayed elimination of plasma MTX (p = 0.042). This is the first report demonstrating that co-administration of calcium channel blockers may be a predictive factor of delayed elimination of plasma MTX in patients receiving HD-MTX therapy.
Kern S, Truebenbach I, Höhn M, et al.
Combined antitumoral effects of pretubulysin and methotrexate.
Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019; 7(1):e00460 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Combined antitumoral effects of pretubulysin and methotrexate.
Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019; 7(1):e00460 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Pretubulysin (PT), a potent tubulin-binding antitumoral drug, and the well-established antimetabolite methotrexate (MTX) were tested separately or in combination (PT+MTX) for antitumoral activity in L1210 leukemia cells or KB cervix carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo in NMRI-nu/nu tumor mouse models. In cultured L1210 cells, treatment with PT or MTX displays strong antitumoral effects in vitro
Grinich E, Koon SM, Cascio MJ, Fett N
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma responsive to combination therapy with methotrexate and corticosteroids.
Dermatol Online J. 2018; 24(9) [PubMed] Related Publications
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma responsive to combination therapy with methotrexate and corticosteroids.
Dermatol Online J. 2018; 24(9) [PubMed] Related Publications
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) is a rare condition that falls underneath the umbrella of primary cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTCLs). SPTCL can be very difficult to diagnose as it may mimic other subtypes of CTCL, such as γ/δ T-cell lymphoma (TCL), or other forms of panniculitis. Confirmation of diagnosis often requires immunohistochemical analysis and is essential for proper prognosis and therapeutic management. Herein, we present a case of SPTCL that mimicked lupus panniculitis and was successfully treated with prednisone taper and methotrexate.
Wormdal OM, Flægstad T, Stokland T
Treatment of two cases on the same day of intrathecal methotrexate overdose using cerebrospinal fluid exchange and intrathecal instillation of carboxypeptidase-G2.
Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2018 Aug - Sep; 35(5-6):350-354 [PubMed] Related Publications
Treatment of two cases on the same day of intrathecal methotrexate overdose using cerebrospinal fluid exchange and intrathecal instillation of carboxypeptidase-G2.
Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2018 Aug - Sep; 35(5-6):350-354 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Two 14-year old boys with acute lymphocytic leukemia were treated according to the NOPHO-ALL-08 protocol with intrathecal methotrexate (MTX) on the same day. Due to a preparation error in the hospital pharmacy, they were both given 240 mg of MTX instead of the prescribed 12 mg. Treatment (or methods): Both patients developed acute neurotoxicity with confusion, pain and seizures. Intravenous dexamethasone and folinic acid (leucovorin) was given. Exchange of cerebrospinal fluid was performed. Intrathecal glucarpidase (carboxypeptidase-G2) was administered after 11 h.
RESULTS: One patient developed a toxic arachnoiditis. Three years after the incident, one patient has no neurological or neuropsychological sequelae after the overdose, while the other reports some loss of short-term memory.
CONCLUSION: Fast recognition and treatment of intrathecal MTX overdose is critical to survival and outcome. Efforts to prevent such overdoses are of vital importance.
RESULTS: One patient developed a toxic arachnoiditis. Three years after the incident, one patient has no neurological or neuropsychological sequelae after the overdose, while the other reports some loss of short-term memory.
CONCLUSION: Fast recognition and treatment of intrathecal MTX overdose is critical to survival and outcome. Efforts to prevent such overdoses are of vital importance.
Nagy G, Király G, Veres P, et al.
Controlled release of methotrexate from functionalized silica-gelatin aerogel microparticles applied against tumor cell growth.
Int J Pharm. 2019; 558:396-403 [PubMed] Related Publications
Controlled release of methotrexate from functionalized silica-gelatin aerogel microparticles applied against tumor cell growth.
Int J Pharm. 2019; 558:396-403 [PubMed] Related Publications
Methotrexate functionalized silica-gelatin hybrid aerogel (SGM) was synthesized by the sol-gel method and co-gelation. The drug methotrexate (MTX) is covalently linked to the collagen molecules of the hybrid aerogel backbone by amide-bond. The characteristic MTX content of the functionalized hybrid aerogel is ca. 6 wt% by the dry weight. The micronization of SGM aerogel in water yields cell sized (d = 10-20 µm) particles. The cytotoxicity of these microparticles against tumor cell lines (SCC VII and HL-60) is unprecedentedly high, it is approximately equivalent to that of an equal dose of free (dissolved) MTX, as proved by in vitro experiments. Thus, the activity of MTX is intact after aerogel functionalization, and the mass specific cytotoxicity of SGM is high enough for medical applications. Drug release studies verified that MTX cannot be liberated from this drug delivery system solely by chemical hydrolysis, however, collagenase enzymatic activity releases MTX from the functionalized hybrid aerogel. The cytotoxicity of SGM towards various cancerous and non-cancerous cell lines correlates with the collagenase activities of cells. Therefore, conjugation with the hybrid aerogel provides a controlled release system for the antineoplastic agent MTX. The morphology of the delivery vehicle was chosen to adapt the size of cancer cells; thus the metastatic pathways of the tumor cells can get flooded.
Tabata R, Tabata C, Uesugi H, Takei Y
Highly aggressive plasmablastic neoplasms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2019; 68:213-217 [PubMed] Related Publications
Highly aggressive plasmablastic neoplasms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate.
Int Immunopharmacol. 2019; 68:213-217 [PubMed] Related Publications
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis occasionally develop lymphoproliferative disorders. Methotrexate-associated lymphoproliferative disorders is a lymphoproliferative disease or lymphoma in patients treated with methotrexate for autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Here we report two rare cases of highly aggressive plasmablastic lymphoproliferative disorders in rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate. Case 1 is a 68-year-old female patient with leukemic transformation of malignant lymphoma. She received methotrexate therapy for rheumatoid arthritis for >6 years. The patient showed rapid progressive course and died on the 2nd hospital day. After the death, we diagnosed the patient as plasmablastic lymphoma. Case 2 is an 80-year-old female patient with plasmablastic plasma cell myeloma, with a history of methotrexate treatment for rheumatoid arthritis for >5 years. Although M-protein was decreased by chemotherapy, bone marrow examination revealed the further increase of plasmablastic cells and she died 2 months later. The present cases were difficult to diagnose because proliferation of malignant plasmablasts was hardly predicted because neither lymph node enlargement nor an evident M-protein was observed. Both cases showed aggressive features and extremely poor prognosis. Clinicians should be aware of the underlying malignant plasmablastic proliferation when inexplicable inflammatory findings are observed in inactive rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Wei CW, Yu YL, Chen YH, et al.
Anticancer effects of methotrexate in combination with α‑tocopherol and α‑tocopherol succinate on triple‑negative breast cancer.
Oncol Rep. 2019; 41(3):2060-2066 [PubMed] Related Publications
Anticancer effects of methotrexate in combination with α‑tocopherol and α‑tocopherol succinate on triple‑negative breast cancer.
Oncol Rep. 2019; 41(3):2060-2066 [PubMed] Related Publications
Triple‑negative breast cancers (TNBCs) lack the estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). Therefore, hormone or targeted therapies are not effective in the treatment of TNBC and thus the development of novel therapeutic strategies is crucial. Methotrexate (MTX), a folate antagonist, has been used in the treatment of various types of cancer; however, the anticancer effects of MTX treatment on breast cancer have thus far been ineffective. Vitamin E variants and derivatives have been applied for cancer therapy. Previous studies have indicated that vitamin E variants and derivatives exert distinct anticancer effects on different types of cancer. However, whether MTX plus vitamin E variants or its derivatives can inhibit TNBC remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to examine the anticancer effects and mechanisms of action of MTX in combination with vitamin E variants (α‑tocopherol) and derivatives (α‑tocopherol succinate) on TNBC. In the present study, MTT assay and western blot analysis were used to determine the cell survival rates and protein levels. The results demonstrated that combination treatment with MTX and α‑tocopherol suppressed TNBC cell proliferation. In addition, various concentrations of MTX exerted distinct cytotoxic effects on α‑tocopherol succinate‑treated cells. Furthermore, high‑dose MTX enhanced α‑tocopherol succinate‑induced anticancer activity; however, low‑dose MTX inhibited α‑tocopherol succinate‑induced anticancer activity. The present study also demonstrated that caspase‑3 activation and poly(adenosine diphosphate‑ribose) polymerase cleavage were observed in the α‑tocopherol succinate/MTX‑treated cells. In conclusion, the findings of the present study demonstrated that high‑dose MTX enhanced anticancer activity in α‑TOS‑treated TNBC, while low‑dose MTX reduced anticancer activity in α‑TOS‑treated TNBC.
Kobayashi H, Abe Y, Miura D, et al.
Limited efficacy of high-dose methotrexate in patients with neurolymphomatosis.
Int J Hematol. 2019; 109(3):286-291 [PubMed] Related Publications
Limited efficacy of high-dose methotrexate in patients with neurolymphomatosis.
Int J Hematol. 2019; 109(3):286-291 [PubMed] Related Publications
Neurolymphomatosis (NL) is a rare manifestation of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, in which malignant cells infiltrate the peripheral nerves. Most patients are treated with high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX)-based systemic chemotherapy regimens similar to patients with central nervous system lymphoma. However, because NL is rare, the efficacy of HD-MTX is largely unknown. We reviewed medical records of patients diagnosed with NL over the past 10 years and identified 18 patients. The underlying hematological malignancy was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in 10 patients (55.6%), intravascular large B-cell lymphoma in six (33.3%), and other types in two patients. Ten patients were treated with HD-MTX-based systemic chemotherapy; the response rates with and without HD-MTX-based chemotherapy were 100% (n = 10) and 85.7% (n = 6), respectively (P = 0.41). The median progression-free and overall survival rates of patients with versus without HD-MTX treatment were 6.4 vs. 8.5 months (P = 0.97) and 13.5 vs. 8.5 months (P = 0.63), respectively. Despite the initial favorable responses, rapid disease recurrence was observed in most patients administered HD-MTX-based chemotherapy. Our observations suggest that HD-MTX-based chemotherapy may have insufficient efficacy against NL, and that other therapeutic approaches are required to improve the outcomes of patients with this rare disease.
Katiyar SS, Kushwah V, Dora CP, Jain S
Novel biosurfactant and lipid core-shell type nanocapsular sustained release system for intravenous application of methotrexate.
Int J Pharm. 2019; 557:86-96 [PubMed] Related Publications
Novel biosurfactant and lipid core-shell type nanocapsular sustained release system for intravenous application of methotrexate.
Int J Pharm. 2019; 557:86-96 [PubMed] Related Publications
In an attempt to prepare novel core shell nanocapsules, lipid and Stearic acid-Valine conjugate (Biosurfactant) based nanosystem was prepared to attain high drug loading of hydrophilic drug methotrexate (MTX), with sustained release. Antisolvent nanoprecipitation technique was employed for the formulation of nanoparticles (NPs). Optimized formulation depicted 209.6 ± 31.3 nm particle size, 0.209 ± 0.072 PDI and 14.98 ± 1.33 %w/w drug loading. In vitro release depicted biphasic release for 12 h with initial burst phase followed by sustained release phase. In vitro Haemolytic study on RBCs revealed haemocompatible nature of MTX-Biosurfactant NPs compared to Biotrexate® (Zydus). In vitro cell culture studies showed 3.33 folds and 3.50 folds increase in cellular uptake of MTX at 10 µg/ml and 15 µg/ml concentration respectively for developed nanoparticles with 4.16 folds decrease in IC
Inose R, Hosomi K, Takahashi K, et al.
Risk of malignant lymphoma in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and methotrexate .
Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019; 57(2):63-72 [PubMed] Related Publications
Risk of malignant lymphoma in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and methotrexate .
Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019; 57(2):63-72 [PubMed] Related Publications
OBJECTIVE: This study investigated whether using biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) further increases the risk of malignant lymphoma in patients with rheumatoid arthritis undergoing methotrexate therapy using spontaneous adverse reaction databases in different countries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Patient data were acquired from the US Food and Drug Administration's Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS), the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER), and the Canada Vigilance Adverse Reaction Online Database (CVARD) from the first quarter of 2004 to the end of 2015. Data subset analysis was performed to investigate whether the use of bDMARDs further increased the risk of malignant lymphoma in patients receiving methotrexate therapy.
RESULTS: The FAERS subset data indicated a significant association between Hodgkin lymphoma and methotrexate with infliximab (reporting odds ratio (ROR): 8.28. 95% CI: 5.70 - 12.02; information component (IC): 2.04, 95% CI: 1.59 - 2.49). In addition, signal scores suggested that methotrexate with infliximab (ROR: 3.26. 95% CI: 2.68 - 3.98; IC: 1.31, 95% CI: 1.04 - 1.58) was significantly associated with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). The CVARD subset data also indicated a significant association between NHL and methotrexate with infliximab (ROR: 22.82. 95% CI: 5.02 - 103.78; IC: 1.77, 95% CI: 0.13 - 3.41). However, the JADER subset data revealed no significant associations.
CONCLUSION: The present study shows that using infliximab further increases the risk of malignant lymphoma in patients receiving methotrexate therapy. .
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Patient data were acquired from the US Food and Drug Administration's Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS), the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER), and the Canada Vigilance Adverse Reaction Online Database (CVARD) from the first quarter of 2004 to the end of 2015. Data subset analysis was performed to investigate whether the use of bDMARDs further increased the risk of malignant lymphoma in patients receiving methotrexate therapy.
RESULTS: The FAERS subset data indicated a significant association between Hodgkin lymphoma and methotrexate with infliximab (reporting odds ratio (ROR): 8.28. 95% CI: 5.70 - 12.02; information component (IC): 2.04, 95% CI: 1.59 - 2.49). In addition, signal scores suggested that methotrexate with infliximab (ROR: 3.26. 95% CI: 2.68 - 3.98; IC: 1.31, 95% CI: 1.04 - 1.58) was significantly associated with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). The CVARD subset data also indicated a significant association between NHL and methotrexate with infliximab (ROR: 22.82. 95% CI: 5.02 - 103.78; IC: 1.77, 95% CI: 0.13 - 3.41). However, the JADER subset data revealed no significant associations.
CONCLUSION: The present study shows that using infliximab further increases the risk of malignant lymphoma in patients receiving methotrexate therapy. .
Xu W, Li Z, Zhu X, et al.
miR-29 Family Inhibits Resistance to Methotrexate and Promotes Cell Apoptosis by Targeting COL3A1 and MCL1 in Osteosarcoma.
Med Sci Monit. 2018; 24:8812-8821 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
miR-29 Family Inhibits Resistance to Methotrexate and Promotes Cell Apoptosis by Targeting COL3A1 and MCL1 in Osteosarcoma.
Med Sci Monit. 2018; 24:8812-8821 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a crucial role in regulating diverse biological processes, including drug resistance. We investigated the potential roles of the miR-29 family in methotrexate (MTX) resistance in osteosarcoma. MATERIAL AND METHODS Two MTX-resistant osteosarcoma cell lines, MG-63/MTX and U2OS/MTX, were generated by continuous exposure to stepwise increasing concentrations of MTX. miR-29abc, COL3A1, and MCL1 mRNA expression levels were determined using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Protein expression levels of COL3A1 and MCL1 were detected by Western blot. Cell viability, IC50 value, and cell apoptosis were assessed by CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry, respectively. The target relationship between the miR-29 family and COL3A1 or MCL1 was confirmed by luciferase reporter assay. RESULTS miR-29a, miR-29b, and miR-29c were significantly downregulated in MG-63/MTX and U2OS/MTX cells and in chemotherapy poor-response osteosarcoma tissues. Overexpression of the miR-29 family sensitized MG-63/MTX and U2OS/MTX cells to MTX and obviously promoted cell apoptosis compared with negative control. COL3A1 and MCL1 were identified to be target genes of the miR-29 family, and transfection with miR-29abc mimics in MG-63/MTX and U2OS/MTX cells decreased COL3A1 and MCL1 mRNA and protein expression. Meanwhile, overexpression of COL3A1 and MCL1 partly neutralized the effects of the miR-29 family on MTX resistance and cell apoptosis. CONCLUSIONS Taken together, our findings suggested a tumor-suppressor role of the miR-29 family in control of MTX resistance and cell apoptosis through regulating COL3A1 or MCL1. Targeting the miR-29 family might provide new strategies to overcome the high-dosage MTX-induced cytotoxicity in osteosarcoma treatment.
Bidram E, Sulistio A, Cho HJ, et al.
Targeted Graphene Oxide Networks: Cytotoxicity and Synergy with Anticancer Agents.
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018; 10(50):43523-43532 [PubMed] Related Publications
Targeted Graphene Oxide Networks: Cytotoxicity and Synergy with Anticancer Agents.
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018; 10(50):43523-43532 [PubMed] Related Publications
An effective strategy to inhibit endocytosis in cancer cells is presented where modified net-type graphene oxide (GO) sheets, bound with multiple cell surface receptors, are introduced and synthesized as novel anticancer agents. The results suggest that the binding connects GO sheets with neighboring lipid rafts, neutralizes endocytosis, and causes metabolic deprivation. As a result, tumor cell survival and proliferation are reduced. Live cell confocal microscopy imaging reveals that GO-PEGFA (folate-PEGylated GO) (PEG, polyethylene glycol) is internalized by tumor cells, while GO-PEGRGD (tripeptide Arg-Gly-Asp PEGylated GO) associates with the external cell membrane (not internalized). In vitro exposure of tumor cells to GO-PEGFA or GO-PEGRGD reduces the cell viability by 35%, compared to 50% reduction using methotrexate (100 μM). The combination of modified GO sheets with methotrexate or doxorubicin shows a greater toxicity (80% reduction in cell viability) than the individual agents. The proposed setup demonstrates a significant synergy in limiting tumor cell growth.
Chen J, Yang X, Huang L, et al.
Development of dual-drug-loaded stealth nanocarriers for targeted and synergistic anti-lung cancer efficacy.
Drug Deliv. 2018; 25(1):1932-1942 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Development of dual-drug-loaded stealth nanocarriers for targeted and synergistic anti-lung cancer efficacy.
Drug Deliv. 2018; 25(1):1932-1942 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Combination chemotherapy is widely exploited for suppressing drug resistance and achieving synergistic anticancer efficacy in the clinic. In this paper, the nanostructured targeting methotrexate (MTX) plus pemetrexed (PMX) chitosan nanoparticles (CNPs) were developed by modifying methoxy polye (thylene glycol) (mPEG), in which PEGylation CNPs was used as stealth nanocarriers (PCNPs) and MTX was employed as a targeting ligand and chemotherapeutic agent as well. Studies were undertaken on human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial (A549) and Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cell lines, revealing the anti-tumor efficacy of nanoparticle drug delivery system. The co-delivery nanoparticles (MTX-PMX-PCNPs) had well-dispersed with sustained release behavior. Cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) has been used to measure A549 cell viability and the research showed that MTX-PMX-PCNPs were much more effective than free drugs when it came to the inhibition of growth and proliferation. Cell cycle assay by flow cytometry manifested that the MTX-PMX-PCNPs exhibited stronger intracellular taken up ability than free drugs at the same concentration. In vivo anticancer effect results indicated that MTX-PMX-PCNPs exhibited a significantly prolong blood circulation, more tumoral location accumulation, and resulted in a robust synergistic anticancer efficacy in lung cancer in mice. The results clearly demonstrated that such unique synergistic anticancer efficacy of co-delivery of MTX and PMX via stealth nanocarriers, providing a prospective strategy for lung cancer treatment.
Ishigaki S, Masaoka T, Kameyama H, et al.
Methotrexate-associated Lymphoproliferative Disorder of the Stomach Presumed to Be Mucosa-associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma.
Intern Med. 2018; 57(22):3249-3254 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Methotrexate-associated Lymphoproliferative Disorder of the Stomach Presumed to Be Mucosa-associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma.
Intern Med. 2018; 57(22):3249-3254 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
The number of patients with methotrexate-associated lymphoproliferative disorder (MTX-LPD) is increasing. We describe a case of MTX-LPD of the stomach. After treatment with methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis, the patient developed left cervical lymphadenopathy and an ulcerative lesion in the stomach, which was presumed to be a mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma. However, we suspected MTX-LPD, based on the clinical course and the positivity of in situ hybridization for the detection of the Epstein-Barr encoding region. After the cessation of MTX, the left cervical lymphadenopathy and the gastric lesion disappeared. This is first report of gastric MTX-LPD that was presumed to be MALT lymphoma.
Hassanein EHM, Shalkami AS, Khalaf MM, et al.
The impact of Keap1/Nrf2, P
Biomed Pharmacother. 2019; 109:47-56 [PubMed] Related Publications
The impact of Keap1/Nrf2, P
Biomed Pharmacother. 2019; 109:47-56 [PubMed] Related Publications
Berberine (BBR) is a natural compound of plant origin belonging to isoquinoline type of alkaloid. Methotrexate (MTX) is an anti-metabolite used widely for a variety of tumors and autoimmune conditions. Clinical uses of MTX were severely limited by its concomitant renal intoxication. The current study was designed to investigate the efficacy of BBR against MTX-induced nephrotoxicity and for exploring the underlying molecular mechanisms through examining the Keap1/Nrf2, NF-κB/P
Sherief LM, Sanad R, ElHaddad A, et al.
A Cross-sectional Study of Two Chemotherapy Protocols on Long Term Neurocognitive Functions in Egyptian Children Surviving Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.
Curr Pediatr Rev. 2018; 14(4):253-260 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
A Cross-sectional Study of Two Chemotherapy Protocols on Long Term Neurocognitive Functions in Egyptian Children Surviving Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.
Curr Pediatr Rev. 2018; 14(4):253-260 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
INTRODUCTION: Subtle neurocognitive deficits have been recently observed in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) survivors.
AIM: We aim to assess the neurocognitive functions of ALL survivors who had been treated with chemotherapy only using two different protocols, and to identify treatment-related risk factors.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: We carried a multicenter study involving 3 pediatric oncology centers on 100 children who were treated for ALL. Fifty patients were treated by the modified Children's Cancer Group (CCG) 1991 protocol with low dose methotrexate and 50 children were treated by Total XV protocol with high dose methotrexate. Fifty healthy children were included as a control group. Psychometric assessment using Arabic version of Wechsler intelligence scale for children (WISC III) was performed for all patients and controls.
RESULTS: Patients had significantly lower mean full scale IQ, performance IQ and verbal IQ than controls. Patients ≤ 5 years at diagnosis had significantly lower mean full scale IQ and performance IQ than patients>5 years at diagnosis, while the verbal IQ showed no significant difference between both age groups. Female patients had significantly lower mean full scale IQ, performance IQ and verbal IQthan males. Patients who received Total XV protocol with high dose methotrexate had significantly lower mean full scale IQ, performance IQ and verbal IQ than patients who received modified CCG 1991 protocol with low dose methotrexate.
CONCLUSIONS: CNS directed chemotherapy might appear to affect neurocognitive functions in children with ALL, which is more significant in young children at diagnosis, in girls and in those receiving high dose methotrexate.
AIM: We aim to assess the neurocognitive functions of ALL survivors who had been treated with chemotherapy only using two different protocols, and to identify treatment-related risk factors.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: We carried a multicenter study involving 3 pediatric oncology centers on 100 children who were treated for ALL. Fifty patients were treated by the modified Children's Cancer Group (CCG) 1991 protocol with low dose methotrexate and 50 children were treated by Total XV protocol with high dose methotrexate. Fifty healthy children were included as a control group. Psychometric assessment using Arabic version of Wechsler intelligence scale for children (WISC III) was performed for all patients and controls.
RESULTS: Patients had significantly lower mean full scale IQ, performance IQ and verbal IQ than controls. Patients ≤ 5 years at diagnosis had significantly lower mean full scale IQ and performance IQ than patients>5 years at diagnosis, while the verbal IQ showed no significant difference between both age groups. Female patients had significantly lower mean full scale IQ, performance IQ and verbal IQthan males. Patients who received Total XV protocol with high dose methotrexate had significantly lower mean full scale IQ, performance IQ and verbal IQ than patients who received modified CCG 1991 protocol with low dose methotrexate.
CONCLUSIONS: CNS directed chemotherapy might appear to affect neurocognitive functions in children with ALL, which is more significant in young children at diagnosis, in girls and in those receiving high dose methotrexate.
Yang Y, Wang X, Tian J, Wang Z
Renal Function and Plasma Methotrexate Concentrations Predict Toxicities in Adults Receiving High-Dose Methotrexate.
Med Sci Monit. 2018; 24:7719-7726 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Renal Function and Plasma Methotrexate Concentrations Predict Toxicities in Adults Receiving High-Dose Methotrexate.
Med Sci Monit. 2018; 24:7719-7726 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND Methotrexate (MTX) is an effective drug for the treatment of adult malignancies, but toxicity remains a significant problem. Toxic reactions may occur when patients use high-dose MTX (HD-MTX), but the correlation between its toxicity and concentration in adults is controversial. The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between MTX concentration and renal function, as well as to assess toxic reactions to MTX in Chinese adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). MATERIAL AND METHODS This retrospective study enrolled 97 patients who had been diagnosed with ALL or NHL, and who were treated at the Hemopathology Department of Shanghai Changhai Hospital from January 2015 to June 2016. RESULTS Forty-one (27.5%) episodes of elimination delay were observed. We found negative correlations between creatinine clearance rate before MTX infusion and the plasma concentrations of MTX at 36 h after MTX infusion (P=0.005). The serum creatinine at 48 h and plasma concentrations of MTX at 48 h and72 h were significantly and positively correlated (both p=0.000). High blood concentration of MTX was positively associated with nephrotoxicity > grade 1 (P<0.01). Infection > grade 1 was more likely to occur if a patient had high MTX levels at 36 h,48 h, and 72 h (P<0.01). CONCLUSIONS Our results show that renal function is associated with MTX concentration, and high MTX concentration can predict the occurrence of renal toxicity and infection related to MTX.
AlQahtani AD, Al-Mansoori L, Bashraheel SS, et al.
Production of "biobetter" glucarpidase variants to improve drug detoxification and antibody directed enzyme prodrug therapy for cancer treatment.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019; 127:79-91 [PubMed] Related Publications
Production of "biobetter" glucarpidase variants to improve drug detoxification and antibody directed enzyme prodrug therapy for cancer treatment.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019; 127:79-91 [PubMed] Related Publications
Recombinant glucarpidase (formerly: Carboxypeptidase G2, CPG2) is used in Antibody Directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy (ADEPT) for the treatment of cancer. In common with many protein therapeutics, glucarpidase has a relatively short half-life in serum and, due to the need for the repeated cycles of the ADEPT, its bioavailability may be further diminished by neutralizing antibodies produced by patients. PEGylation and fusion with human serum albumin (HSA) are two approaches that are commonly employed to increase the residency time of protein therapeutics in blood, and also to increase the half-lives of the proteins in vivo. To address this stability and the immunogenicity problems, 'biobetter' glucarpidase variants, mono-PEGylated glucarpidase, and HSA fused glucarpidase by genetic fusion with albumin, were produced. Biochemical and bioactivity analyses, including anti-proliferation, bioassays, circular dichroism, and in vitro stability using human blood serum and immunoassays, demonstrated that the functional activities of the designed glucarpidase conjugates were maintained. The immunotoxicity studies indicated that the PEGylated glucarpidase did not significantly induce T-cell proliferation, suggesting that glucarpidase epitopes were masked by the PEG moiety. However, free glucarpidase and HSA-glucarpidase significantly increased T-cell proliferation compared with the negative control. In the latter case, this might be due to the type of expression system used or due to trace impurities associated with the highly purified (99.99%) recombinant HSA-glucarpidase. Both PEGylated glucarpidase and HAS-glucarpidase exhibit more stability in human serum and were more resistant to key human proteases relative to native glucarpidase. To our knowledge, this study is the first to report stable and less immunogenic glucarpidase variants produced by PEGylation and fusion with HSA. The results suggest that they may have better efficacy in drug detoxification and ADEPT, thereby improving this cancer treatment strategy.
Matsubayashi RN, Iwasaki H, Iwakuma N, Momosaki S
Methotrexate (MTX)-associated malignant lymphoma of the bilateral breast: imaging features in comparison to other nipple-areolar tumors.
Clin Imaging. 2019 Jan - Feb; 53:120-125 [PubMed] Related Publications
Methotrexate (MTX)-associated malignant lymphoma of the bilateral breast: imaging features in comparison to other nipple-areolar tumors.
Clin Imaging. 2019 Jan - Feb; 53:120-125 [PubMed] Related Publications
Tumors originating from the nipple-areolar complex of the breast are rare. We herein report the case of a patient with metachronous bilateral areolar methotrexate (MTX)-associated lymphoma. The patient was a 67-year-old woman who presented with a rapidly enlarging tumor in the areolar region of her left breast. She had a long history of rheumatoid arthritis and had taken MTX for many years. On ultrasonography, the tumor showed well-demarcated margins and hyper-vascularity. On magnetic resonance imaging, the tumor showed a homogeneous low-to-moderate signal intensity that was similar to that of the nipple on both T1- and T2-weighted imaging; the diffusion was significantly reduced on diffusion-weighted images. The tumor showed a medium-plateau pattern on dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging. No necrotic change was observed. Based on the imaging findings, we considered the tumor to have originated from the areola. According to the internal homogeneity, the rapid growth and hyper-cellularity, the potential diagnoses included a small round cell tumor (including malignant lymphoma) and a mesenchymal neoplasm (especially leiomyoma or leiomyosarcoma, which frequently originate from the areolar region). An excisional biopsy of the tumor was performed. The pathological diagnosis was diffuse large, non GC B-cell lymphoma that we suspected was associated with MTX. The tumor shrank rapidly after the withdrawal of MTX. After three months, we detected a B-cell lymphoma of the same type originating in the contralateral areola. We compared the characteristics of the imaging findings of the MTX-associated lymphoma with the nipple-areolar or periareolar tumors and primary breast lymphoma.
Xu D, Lu ST, Li YS, et al.
Evaluation of methotrexate-conjugated gadolinium(III) for cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018; 12:3301-3309 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Evaluation of methotrexate-conjugated gadolinium(III) for cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018; 12:3301-3309 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Background: Gliomas are one of the most common types of primary brain tumors. It is usually evaluated by gadolinium(III)-based contrast agents by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the clinic. Methotrexate (MTX), as a type of folate analog that inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase, is widely used as a chemotherapeutic agent to treat gliomas in the experiment.
Purpose: In this study, a novel theranostic agent MTX-DOTA-Gd (MTX-Gd) was synthesized, which integrates magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with anticancer treatment.
Methods: MTX-Gd was synthesized by connecting MTX and Gd through 1,4,7,10-tetraazacy-clododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA). The characterization of MTX-Gd was detected by ultraviolet (UV) and infrared spectroscopy (IR). To confirm the antitumor effect of MTX-Gd, the cytotoxicity of MTX-Gd was examined by the MTT assay. The contrast enhancement of the MTX-Gd was measured through MRI in vitro. Then, nude mice bearing C6 tumor xenografts were used to study in vivo imaging capabilities.
Results: The ultraviolet-visible-near infrared radiation (UV-NIR) absorption curve indicated that MTX-Gd had a broad absorption in the region of 500-700 nm. The formation of MTX-Gd was confirmed from the characteristic bands of MTX-DOTA-Gd in the 1413 cm
Conclusion: A novel stable and unique theranostic agent (MTX-Gd) was successfully synthe-sized, and it has good stability, strong anticancer ability and excellent magnetic capacity. The methotrexate component of MTX-Gd, as a chemotherapeutic agent, played an important role in targeted therapies of cancer. The DOTA-Gd component of MTX-Gd performed as the MRI contrast agent. The superior MRI imaging performance and synergetic chemical antineoplastic ability of MTX-Gd was revealed, and it has great potential in the diagnosis and treatment of glioma and potentially other cancers, with prospects of clinical application in the near future.
Purpose: In this study, a novel theranostic agent MTX-DOTA-Gd (MTX-Gd) was synthesized, which integrates magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with anticancer treatment.
Methods: MTX-Gd was synthesized by connecting MTX and Gd through 1,4,7,10-tetraazacy-clododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA). The characterization of MTX-Gd was detected by ultraviolet (UV) and infrared spectroscopy (IR). To confirm the antitumor effect of MTX-Gd, the cytotoxicity of MTX-Gd was examined by the MTT assay. The contrast enhancement of the MTX-Gd was measured through MRI in vitro. Then, nude mice bearing C6 tumor xenografts were used to study in vivo imaging capabilities.
Results: The ultraviolet-visible-near infrared radiation (UV-NIR) absorption curve indicated that MTX-Gd had a broad absorption in the region of 500-700 nm. The formation of MTX-Gd was confirmed from the characteristic bands of MTX-DOTA-Gd in the 1413 cm
Conclusion: A novel stable and unique theranostic agent (MTX-Gd) was successfully synthe-sized, and it has good stability, strong anticancer ability and excellent magnetic capacity. The methotrexate component of MTX-Gd, as a chemotherapeutic agent, played an important role in targeted therapies of cancer. The DOTA-Gd component of MTX-Gd performed as the MRI contrast agent. The superior MRI imaging performance and synergetic chemical antineoplastic ability of MTX-Gd was revealed, and it has great potential in the diagnosis and treatment of glioma and potentially other cancers, with prospects of clinical application in the near future.


 Apoptosis
Apoptosis