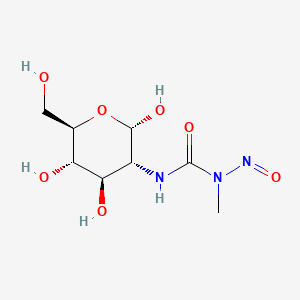
Streptozocin
"An antibiotic that is produced by Stretomyces achromogenes. It is used as an antineoplastic agent and to induce diabetes in experimental animals." (MeSH 2013)
Found this page useful?
 Web Resources: Streptozocin
Web Resources: Streptozocin Latest Research Publications
Latest Research PublicationsWeb Resources: Streptozocin (6 links)
Cancer Research UK
Macmillan Cancer Support
MedlinePlus
NHS Evidence
 Streptozocin - Substance Summary
Streptozocin - Substance Summary
PubChem
Irish Cancer Society
Latest Research Publications
This list of publications is regularly updated (Source: PubMed).
Krug S, Boch M, Daniel H, et al.
Streptozocin-Based Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Neuroendocrine Neoplasms--Predictive and Prognostic Markers for Treatment Stratification.
PLoS One. 2015; 10(12):e0143822 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Streptozocin-Based Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Neuroendocrine Neoplasms--Predictive and Prognostic Markers for Treatment Stratification.
PLoS One. 2015; 10(12):e0143822 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND AND AIM: Chemotherapy with streptozocin (STZ) in combination with 5-FU or doxorubicin (Dox) represents a standard of care for patients with metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (pNEN). However, predictive markers for patient selection are still missing. The aim of this study was a retrospective evaluation of the clinicopathological characteristics of pNEN patients receiving STZ-based chemotherapies and to identify predictive and prognostic markers.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: We retrospectively analyzed 77 patients treated at our center between 1995 and 2013. The median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were calculated using Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression methods, respectively. Uni- and multivariate analyses were performed.
RESULTS: The median PFS (mPFS) in patients receiving STZ/5-FU/Dox was 16 months with a median OS (mOS) of 28 months. Objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) were 34% and 72%, respectively. Biochemical response and positive octreotide scintigraphy predicted objective response. Univariate analysis revealed Ki-67 > 10% and the absence of biochemical or objective response by imaging as independent risk factors for shorter PFS. Additionally, performance status (PS) and resection of the primary tumor were observed to influence mOS. Treatment was well tolerated with less than 10% grade 3 and 4 toxicities.
CONCLUSIONS: STZ-based chemotherapy is an effective and well-tolerated treatment option in patients with well differentiated neuroendocrine neoplasms. Positive octreotide scintigraphy and biochemical response predict objective response.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: We retrospectively analyzed 77 patients treated at our center between 1995 and 2013. The median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were calculated using Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression methods, respectively. Uni- and multivariate analyses were performed.
RESULTS: The median PFS (mPFS) in patients receiving STZ/5-FU/Dox was 16 months with a median OS (mOS) of 28 months. Objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) were 34% and 72%, respectively. Biochemical response and positive octreotide scintigraphy predicted objective response. Univariate analysis revealed Ki-67 > 10% and the absence of biochemical or objective response by imaging as independent risk factors for shorter PFS. Additionally, performance status (PS) and resection of the primary tumor were observed to influence mOS. Treatment was well tolerated with less than 10% grade 3 and 4 toxicities.
CONCLUSIONS: STZ-based chemotherapy is an effective and well-tolerated treatment option in patients with well differentiated neuroendocrine neoplasms. Positive octreotide scintigraphy and biochemical response predict objective response.
Aoki T, Kokudo N, Komoto I, et al.
Streptozocin chemotherapy for advanced/metastatic well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors: an analysis of a multi-center survey in Japan.
J Gastroenterol. 2015; 50(7):769-75 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Streptozocin chemotherapy for advanced/metastatic well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors: an analysis of a multi-center survey in Japan.
J Gastroenterol. 2015; 50(7):769-75 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are believed to be relatively rare and to follow a generally indolent course. However, liver metastases are common in NET patients and the outcome of NET liver metastasis is poor. In Western countries, streptozocin (STZ) has been established as a first-line anticancer drug for unresectable NET; however, STZ cannot be used in daily practice in Japan. The aim of the present study was to determine the status of STZ usage in Japan and to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of STZ chemotherapy in Japanese NET patients.
METHODS: A retrospective multi-center survey was conducted. Five institutions with experience performing STZ chemotherapy participated in the study. The patient demographics, tumor characteristics, context of STZ chemotherapy, and patient outcome were collected and assessed.
RESULTS: Fifty-four patients were enrolled. The main recipients of STZ chemotherapy were middle-aged patients with pancreatic NET and unresectable liver metastases. The predominant regimen was the weekly/bi-weekly intravenous administration of STZ combined with other oral anticancer agents. STZ monotherapy was used in one-fourth of the patients. The median progression-free and overall survival periods were 11.8 and 38.7 months, respectively, and sustained stable disease was obtained in some selected patients. The adverse events profile was mild and tolerable.
CONCLUSIONS: Our survey showed the clinical benefit and safety of STZ therapy for Japanese patients with unresectable NET. Therefore, we recommend that STZ, which is the only cytotoxic agent available against NET, should be used in daily practice in Japan.
METHODS: A retrospective multi-center survey was conducted. Five institutions with experience performing STZ chemotherapy participated in the study. The patient demographics, tumor characteristics, context of STZ chemotherapy, and patient outcome were collected and assessed.
RESULTS: Fifty-four patients were enrolled. The main recipients of STZ chemotherapy were middle-aged patients with pancreatic NET and unresectable liver metastases. The predominant regimen was the weekly/bi-weekly intravenous administration of STZ combined with other oral anticancer agents. STZ monotherapy was used in one-fourth of the patients. The median progression-free and overall survival periods were 11.8 and 38.7 months, respectively, and sustained stable disease was obtained in some selected patients. The adverse events profile was mild and tolerable.
CONCLUSIONS: Our survey showed the clinical benefit and safety of STZ therapy for Japanese patients with unresectable NET. Therefore, we recommend that STZ, which is the only cytotoxic agent available against NET, should be used in daily practice in Japan.
Berends M, Lesterhuis WJ, van Laarhoven HW
Streptozotocin-induced diabetic ketoacidosis in a patient with metastatic islet-cell carcinoma.
Neth J Med. 2013; 71(10):541-2 [PubMed] Related Publications
Streptozotocin-induced diabetic ketoacidosis in a patient with metastatic islet-cell carcinoma.
Neth J Med. 2013; 71(10):541-2 [PubMed] Related Publications
Here we report a severe life-threatening complication of treatment with streptozotocin in a patient with pancreatic island-cell carcinoma. The patient was admitted to the intensive care unit with severe diabetic ketoacidosis which needed aggressive fluid resuscitation and insulin therapy. We believe it is critical to be aware of the symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis and monitor glucose levels during streptozotocin treatment.
Weatherstone K, Meyer T
Streptozocin-based chemotherapy is not history in neuroendocrine tumours.
Target Oncol. 2012; 7(3):161-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Streptozocin-based chemotherapy is not history in neuroendocrine tumours.
Target Oncol. 2012; 7(3):161-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Streptozocin (STZ)-based chemotherapy has been used for over 30 years in the treatment of neuroendocrine tumours (NET); however, there have been few randomised trials in homogeneous and well-characterised patient populations. With the recent approval of sunitinib and everolimus for pancreatic NET (PNET) and the emergence of a more stratified approach to cancer therapy, it is timely to reevaluate the role of chemotherapy. Here we review the evidence base for STZ-based chemotherapy, the toxicity associated with treatment and the role of predictive markers such as Ki67 to select patients who may benefit most from therapy. Although there are no trials comparing chemotherapy with best supportive care, there is evidence that multi-agent STZ-containing regimens are associated with improved survival compared with control therapy. Compared with other therapies, chemotherapy appears to be associated with the highest response rate, particularly in PNET and remains the first-line treatment of choice for those patients in whom response is required. This includes those who are symptomatic from tumour burden and those with locally advanced disease who may be down-staged for resection. The role of Ki67 and other predictive markers requires further assessment in prospective studies as does the relative efficacy of alternative agents such as temozolomide.
Naidoo J, O'Toole D, Kennedy MJ, et al.
A single institution experience of streptozocin/fluorouracil combination chemotherapy: a case series.
Ir J Med Sci. 2012; 181(2):211-4 [PubMed] Related Publications
A single institution experience of streptozocin/fluorouracil combination chemotherapy: a case series.
Ir J Med Sci. 2012; 181(2):211-4 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: The combination chemotherapy regimen of streptozocin and 5-fluorouracil (FU/STZ) has been used for the treatment of metastatic neuroendocrine tumours.
AIM: The aim of this study was to analyse the use of this regimen in a tertiary oncology referral centre over a 10-year period.
METHOD: We retrospectively analysed nine cases from February 2000 to May 2010. Patient demographics, chemotherapy schedule, toxicities, progression-free and overall survival were tabulated for each patient.
RESULT: The median progression-free survival was 17 months (range 3-48+ months), and overall survival 31 months (range 12-53+ months) with no toxicity related deaths.
CONCLUSION: FU/STZ was a well-tolerated regimen that produced significant benefit in the setting of metastatic and progressive disease. Our case series demonstrated comparable progression-free survival and overall survival in relation to randomized controlled studies and previous case series.
AIM: The aim of this study was to analyse the use of this regimen in a tertiary oncology referral centre over a 10-year period.
METHOD: We retrospectively analysed nine cases from February 2000 to May 2010. Patient demographics, chemotherapy schedule, toxicities, progression-free and overall survival were tabulated for each patient.
RESULT: The median progression-free survival was 17 months (range 3-48+ months), and overall survival 31 months (range 12-53+ months) with no toxicity related deaths.
CONCLUSION: FU/STZ was a well-tolerated regimen that produced significant benefit in the setting of metastatic and progressive disease. Our case series demonstrated comparable progression-free survival and overall survival in relation to randomized controlled studies and previous case series.
Dong XD, Carr BI
Hepatic artery chemoembolization for the treatment of liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors: a long-term follow-up in 123 patients.
Med Oncol. 2011; 28 Suppl 1:S286-90 [PubMed] Related Publications
Hepatic artery chemoembolization for the treatment of liver metastases from neuroendocrine tumors: a long-term follow-up in 123 patients.
Med Oncol. 2011; 28 Suppl 1:S286-90 [PubMed] Related Publications
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) of the gastrointestinal tract have a propensity for hepatic metastases. Surgical resection for hepatic metastases remains the gold standard for long-term survival, but many patients present with multifocal tumors, precluding surgery with increasing use of chemoembolization. However, there are few studies examining long-term survival factors. We reviewed our 15-year experience with chemoembolization in 123 patients with unresectable NET liver metastases, whose prognosis was evaluated upon baseline clinical factors. There were 64 males (53%) and 59 females (47%). Average age at presentation was 56 years (range: 14.3-85.5 years). Abdominal pain (44%) was the most common presenting symptom, followed by diarrhea (30%) and weight lost (22%). Patients underwent an average 7.3 cycles of chemoembolization (range 1-32 cycles). Responses: 62% of patients had PR; 24% had stable disease and 14% had tumor progression. Overall 3-, 5- and 10-year survivals were 59, 36 and 20% of patients with a mean follow-up of 3.2 years (range 2 weeks-18.3 years) and mean survival of 3.3 years. Univariate analysis showed that age greater than 60 years had worse outcome (P < 0.01), as did baseline serum albumin of ≤ 3.5 g/dL and prothrombin time >13 s. Location of the primary tumor (P = 0.68), gender (P = 0.4) and serum NET peptide levels did not influence survival. However, multivariate analysis showed that a low baseline serum albumin level was an independent factor for prognosis (P = 0.003). Chemoembolization for unresectable NETs metastatic to liver is useful for tumor size reduction, symptom palliation and can be associated with prolonged survival.
Turner NC, Strauss SJ, Sarker D, et al.
Chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin and streptozocin for neuroendocrine tumours.
Br J Cancer. 2010; 102(7):1106-12 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin and streptozocin for neuroendocrine tumours.
Br J Cancer. 2010; 102(7):1106-12 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND: The role of chemotherapy for neuroendocrine tumours remains controversial and there is no standard regimen.
METHOD: We report the outcome for a consecutive series of chemonaive patients with metastatic or locally advanced neuroendocrine tumours treated with a combination of 5-fluorouracil (500 mg m(-2)), cisplatin (70 mg m(-2)) and streptozocin (1000 mg m(-2)) (FCiSt) administered three weekly for up to six cycles. Patients were assessed for radiological response, toxicity and survival.
RESULTS: In the 79 patients assessable for response, treatment with FCiSt was associated with an overall response rate of 33% (38% for pancreatic primary sites and 25% for non-pancreatic primary sites). Stable disease occurred in a further 51%, with progression in 16%. The median time to progression was 9.1 months and median overall survival was 31.5 months. The most common grade 3-4 toxicity was neutropaenia (28% patients) but grade 3-4 infection was rare (7%). The most frequent non-haematological grade 3-4 toxicity was nausea and vomiting (17%). Prognostic factors included Ki-67, mitotic index, grade and chromogranin A, whereas response to chemotherapy was predicted by mitotic index, grade and alpha-fetoprotein.
CONCLUSIONS: FCiSt is an effective regimen for neuroendocrine tumours with an acceptable toxicity profile. Grade and mitotic index are the best predictors of response.
METHOD: We report the outcome for a consecutive series of chemonaive patients with metastatic or locally advanced neuroendocrine tumours treated with a combination of 5-fluorouracil (500 mg m(-2)), cisplatin (70 mg m(-2)) and streptozocin (1000 mg m(-2)) (FCiSt) administered three weekly for up to six cycles. Patients were assessed for radiological response, toxicity and survival.
RESULTS: In the 79 patients assessable for response, treatment with FCiSt was associated with an overall response rate of 33% (38% for pancreatic primary sites and 25% for non-pancreatic primary sites). Stable disease occurred in a further 51%, with progression in 16%. The median time to progression was 9.1 months and median overall survival was 31.5 months. The most common grade 3-4 toxicity was neutropaenia (28% patients) but grade 3-4 infection was rare (7%). The most frequent non-haematological grade 3-4 toxicity was nausea and vomiting (17%). Prognostic factors included Ki-67, mitotic index, grade and chromogranin A, whereas response to chemotherapy was predicted by mitotic index, grade and alpha-fetoprotein.
CONCLUSIONS: FCiSt is an effective regimen for neuroendocrine tumours with an acceptable toxicity profile. Grade and mitotic index are the best predictors of response.
Maire F, Hammel P, Kianmanesh R, et al.
Is adjuvant therapy with streptozotocin and 5-fluorouracil useful after resection of liver metastases from digestive endocrine tumors?
Surgery. 2009; 145(1):69-75 [PubMed] Related Publications
Is adjuvant therapy with streptozotocin and 5-fluorouracil useful after resection of liver metastases from digestive endocrine tumors?
Surgery. 2009; 145(1):69-75 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: In patients with digestive endocrine tumors (DET) and liver metastases (LM) surgical resection is the only curative treatment. However, 5-year recurrence occurs in 50-80% of patients in the literature. The effect of adjuvant chemotherapy (CT) on relapse-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) is unknown.
AIM: To assess the safety and the efficacy of systemic adjuvant CT with streptozotocin and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) following LM resection in patients with DET.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Between 1996 and 2006, 52 consecutive patients (23 males, median age 54 years [21-69]) underwent surgery for LM of well-differentiated DET in our center. The primary tumor was resected. After R0 resection of LM, patients were considered for adjuvant CT if the primary tumor was pancreatic, if LM was >or=10, or if the patient was <50 years old, in patients with other primary tumors. Twenty-nine patients received adjuvant CT and 23 were in the observation group. Adjuvant CT included 4 postoperative courses of i.v. streptozotocin-5-FU (500 and 400 mg/m(2), respectively, daily for 5 days every 42 days). RFS, OS and toxicity were evaluated. Log rank and chi-square analysis were used to identify prognostic factors.
RESULTS: Median post-operative follow-up was 47 months (4-162). In the adjuvant CT group, all patients except one received the 4 cycles. Two patients had grade 3-4 toxicity, including 1 febrile neutropenia resulting in death. Recurrence occurred in 43% and 65% of patients in the observation and adjuvant CT groups, respectively. RFS at 3 and 5 years was 51% and 38% in the observation group and 40% and 20% in the adjuvant CT group, respectively (P = .36). In univariate analysis, the significant prognostic factors associated with RFS were the number of LM (>or=10) and synchronous LM. Administration of adjuvant CT was not correlated with RFS. OS at 3 and 5 years was 90% and 76% in the observation group and 96% and 96% in the adjuvant CT group, respectively (P = .58).
CONCLUSION: RFS in patients receiving adjuvant CT was similar to that reported in the observation group and in historical cohorts without adjuvant CT. Thus, administration of streptozotocin-5-FU cannot be recommended in this indication.
AIM: To assess the safety and the efficacy of systemic adjuvant CT with streptozotocin and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) following LM resection in patients with DET.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Between 1996 and 2006, 52 consecutive patients (23 males, median age 54 years [21-69]) underwent surgery for LM of well-differentiated DET in our center. The primary tumor was resected. After R0 resection of LM, patients were considered for adjuvant CT if the primary tumor was pancreatic, if LM was >or=10, or if the patient was <50 years old, in patients with other primary tumors. Twenty-nine patients received adjuvant CT and 23 were in the observation group. Adjuvant CT included 4 postoperative courses of i.v. streptozotocin-5-FU (500 and 400 mg/m(2), respectively, daily for 5 days every 42 days). RFS, OS and toxicity were evaluated. Log rank and chi-square analysis were used to identify prognostic factors.
RESULTS: Median post-operative follow-up was 47 months (4-162). In the adjuvant CT group, all patients except one received the 4 cycles. Two patients had grade 3-4 toxicity, including 1 febrile neutropenia resulting in death. Recurrence occurred in 43% and 65% of patients in the observation and adjuvant CT groups, respectively. RFS at 3 and 5 years was 51% and 38% in the observation group and 40% and 20% in the adjuvant CT group, respectively (P = .36). In univariate analysis, the significant prognostic factors associated with RFS were the number of LM (>or=10) and synchronous LM. Administration of adjuvant CT was not correlated with RFS. OS at 3 and 5 years was 90% and 76% in the observation group and 96% and 96% in the adjuvant CT group, respectively (P = .58).
CONCLUSION: RFS in patients receiving adjuvant CT was similar to that reported in the observation group and in historical cohorts without adjuvant CT. Thus, administration of streptozotocin-5-FU cannot be recommended in this indication.
Arnold R, Rinke A, Schmidt Ch, Hofbauer L
Endocrine tumours of the gastrointestinal tract: Chemotherapy.
Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2005; 19(4):649-56 [PubMed] Related Publications
Endocrine tumours of the gastrointestinal tract: Chemotherapy.
Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2005; 19(4):649-56 [PubMed] Related Publications
Malignant neuroendocrine tumours are less sensitive to chemotherapy than other epithelial malignancies. If chemotherapy is considered, tumours of pancreatic origin have a higher sensitivity than tumours from the gastrointestinal tract ('carcinoids'). Chemotherapy with streptozocin combinations and with dacarbazine should be considered in patients with progressive malignant neuroendocrine tumours of the pancreas. A favourable response to chemotherapy can be expected in up to 60% of patients receiving a combination of streptozocin plus doxorubicin, and in up to 40% of patients receiving dacarbazine. A survival benefit has been shown for streptozocin combinations. Treatment regimens are effective in functioning and non-functioning tumours. The response to treatment cannot be predicted. Poorly differentiated neuroendocrine tumours, independent of their origin, respond to a combination of etoposide plus cisplatin. Chemotherapy is, however, almost ineffective in patients with well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumours originating in the gastrointestinal tract ('carcinoids').
Starke A, Saddig C, Mansfeld L, et al.
Malignant metastatic insulinoma-postoperative treatment and follow-up.
World J Surg. 2005; 29(6):789-93 [PubMed] Related Publications
Malignant metastatic insulinoma-postoperative treatment and follow-up.
World J Surg. 2005; 29(6):789-93 [PubMed] Related Publications
The rarity of malignant insulinoma limits reports on therapeutic strategies and outcome. The treatment and follow-up of 10 patients, all presenting an insulinoma with metastatic disease of the liver and newly diagnosed between 1992 and 2002, is reported. Pancreatic surgery with successful removal of the primary tumor preferentially located in the tail was performed in 7 women and 3 men, median age 55 years (range 36-82 years). If appropriate, 5 patients underwent additional hepatic surgery and lymph node resections. Liver metastases as the major cause of postoperatively persistent hypoglycemia were subsequently treated by repeated transarterial hepatic chemoembolization and chemoperfusion protocols using high-dose transhepatic streptozocin perfusions (3-4 g per session). The current median survival time for all 10 patients is 2.6 years (range: 1.6-9.7 years). Six patients are currently alive with a median survival of 3.7 years (1.7-9.7 years), five of them with stable disease and free of hypoglycemia. Four patients died after a median survival of 1.8 years (range: 1.6-7.5 years) from complications of unmanageable hypoglycemia. It is concluded that the necessity to treat debiliating and life-threatening hypoglycemia in metastatic malignant insulinoma warrants the option of radical endocrine surgery in combination with extended and repeated postoperative chemoembolization of liver metastases.
Bolzán AD, Bianchi MS
Clastogenic effects of streptozotocin on human colon cancer cell lines with gene amplification.
J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2003; 22(4):281-6 [PubMed] Related Publications
Clastogenic effects of streptozotocin on human colon cancer cell lines with gene amplification.
J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2003; 22(4):281-6 [PubMed] Related Publications
We investigated the clastogenic effects of the methylating agent streptozotocin (STZ) on two human colon cancer cell lines. COLO320DM and COLO320HSR are cell lines derived from a human neuroendocrine colon carcinoma. STZ produced a dose-dependent increase in the frequency of chromosomal aberrations in both cell lines (p < 0.05) and induced fragmentation and/or pulverization of COLO320DM and COLO320HSR chromosomes. This effect was dose and time dependent. Severe chromosome damage was also found in cells that had progressed beyond the first metaphase, and a higher percentage of metaphases showing pulverized chromosomes were found in cells after the second than after the first division. This seems to indicate that STZ has a persistent and delayed clastogenic effect on COLO320DM and COLO320HSR cells. In addition, STZ produced a marked depression of the mitotic index in both cell lines. These results demonstrate that human colon cancer cell lines COLO320DM and COLO320HSR are highly sensitive to STZ, and suggest that this antibiotic has a good potential as a chemotherapeutic agent for colon cancer.
Khan TS, Imam H, Juhlin C, et al.
Streptozocin and o,p'DDD in the treatment of adrenocortical cancer patients: long-term survival in its adjuvant use.
Ann Oncol. 2000; 11(10):1281-7 [PubMed] Related Publications
Streptozocin and o,p'DDD in the treatment of adrenocortical cancer patients: long-term survival in its adjuvant use.
Ann Oncol. 2000; 11(10):1281-7 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: To evaluate the efficacy of streptozocin and o.p'DDD (SO) in adrenocortical cancer (ACC) patients since other chemotherapeutic regimens have limited effects.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: We performed a phase II study with SO therapy in 40 ACC patients (median age 44 years). Oral o,p'DDD administration (1-4 g/d, every day) was given together with intravenous streptozocin (1 g/d for five days, thereafter 2 g once every three weeks). 5HT3-receptor blocker was used as standard premedication for streptozocin.
RESULTS: The SO therapy was found to have significant effects on disease-free interval (P = 0.02) as well as on survival (P = 0.01) in adjuvantly treated cases (n = 17) in comparison to the patients who did not get any therapy after complete resection (n = 11). Complete or partial response was obtained in 36.4% of patients with measurable disease (n = 22). The overall two-year and five-year survival rates were 70% and 32.5%, respectively. The presence of metastases at diagnosis was identified as a poor prognostic factor (P = 0.02).
CONCLUSIONS: The present study necessitates further randomized clinical study of SO therapy in the treatment of ACC, mainly as adjuvant treatment immediately after curative intended surgery, and could be developed into a regular treatment regimen.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: We performed a phase II study with SO therapy in 40 ACC patients (median age 44 years). Oral o,p'DDD administration (1-4 g/d, every day) was given together with intravenous streptozocin (1 g/d for five days, thereafter 2 g once every three weeks). 5HT3-receptor blocker was used as standard premedication for streptozocin.
RESULTS: The SO therapy was found to have significant effects on disease-free interval (P = 0.02) as well as on survival (P = 0.01) in adjuvantly treated cases (n = 17) in comparison to the patients who did not get any therapy after complete resection (n = 11). Complete or partial response was obtained in 36.4% of patients with measurable disease (n = 22). The overall two-year and five-year survival rates were 70% and 32.5%, respectively. The presence of metastases at diagnosis was identified as a poor prognostic factor (P = 0.02).
CONCLUSIONS: The present study necessitates further randomized clinical study of SO therapy in the treatment of ACC, mainly as adjuvant treatment immediately after curative intended surgery, and could be developed into a regular treatment regimen.
Dominguez S, Denys A, Madeira I, et al.
Hepatic arterial chemoembolization with streptozotocin in patients with metastatic digestive endocrine tumours.
Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000; 12(2):151-7 [PubMed] Related Publications
Hepatic arterial chemoembolization with streptozotocin in patients with metastatic digestive endocrine tumours.
Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000; 12(2):151-7 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Hepatic arterial chemoembolization (CE) with anthracyclines is an effective treatment for progressive liver metastases of digestive endocrine tumours. Streptozotocin (STZ) is widely used for systemic chemotherapy, but its efficacy by the hepatic arterial route has not been evaluated.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Fifteen consecutive patients, mean age 57.8 years, were prospectively included between July 1993 and January 1997. All patients had progressive liver metastases from either a carcinoid tumour (eight patients) or an islet cell carcinoma (ICC) (seven patients) that had increased in size (> or = 25%) before CE. Five patients had the carcinoid syndrome. STZ was administered, as an emulsion with iodized oil, into the hepatic artery before embolization with gelatin sponge particles. Two to six procedures (median, 3) were performed in 12 patients (one in three patients). Changes in the size of the liver metastases were evaluated by CT scan or MRI according to WHO criteria. The median follow-up was 15 months (1-50).
RESULTS: An objective response was achieved in 8/15 patients (53%; median duration of 10.5 months) whatever the primary tumour (carcinoid or ICC). The carcinoid syndrome disappeared in 3/5 patients for 10, 11 and 17 months, respectively. CE effectively controlled hypoglycaemic attacks (decrease of > 50%) in the patient with insulinoma. The biological response was complete in four patients for a median duration of 7 months. CE induced minor side effects, namely nausea, fever and abdominal pain. Acute and reversible tubular necrosis due to CE was observed in one patient who had previously undergone a nephrectomy.
CONCLUSION: Hepatic arterial chemoembolization with STZ is an effective treatment for patients with liver metastases caused by digestive endocrine tumours.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Fifteen consecutive patients, mean age 57.8 years, were prospectively included between July 1993 and January 1997. All patients had progressive liver metastases from either a carcinoid tumour (eight patients) or an islet cell carcinoma (ICC) (seven patients) that had increased in size (> or = 25%) before CE. Five patients had the carcinoid syndrome. STZ was administered, as an emulsion with iodized oil, into the hepatic artery before embolization with gelatin sponge particles. Two to six procedures (median, 3) were performed in 12 patients (one in three patients). Changes in the size of the liver metastases were evaluated by CT scan or MRI according to WHO criteria. The median follow-up was 15 months (1-50).
RESULTS: An objective response was achieved in 8/15 patients (53%; median duration of 10.5 months) whatever the primary tumour (carcinoid or ICC). The carcinoid syndrome disappeared in 3/5 patients for 10, 11 and 17 months, respectively. CE effectively controlled hypoglycaemic attacks (decrease of > 50%) in the patient with insulinoma. The biological response was complete in four patients for a median duration of 7 months. CE induced minor side effects, namely nausea, fever and abdominal pain. Acute and reversible tubular necrosis due to CE was observed in one patient who had previously undergone a nephrectomy.
CONCLUSION: Hepatic arterial chemoembolization with STZ is an effective treatment for patients with liver metastases caused by digestive endocrine tumours.
Smith DC, Gerson SL, Liu L, et al.
Carmustine and streptozocin in refractory melanoma: an attempt at modulation of O-alkylguanine-DNA-alkyltransferase.
Clin Cancer Res. 1996; 2(7):1129-34 [PubMed] Related Publications
Carmustine and streptozocin in refractory melanoma: an attempt at modulation of O-alkylguanine-DNA-alkyltransferase.
Clin Cancer Res. 1996; 2(7):1129-34 [PubMed] Related Publications
The activity of the enzyme O6-alkylguanine-DNA-alkytransferase (AGAT) protects cells from the cytotoxic effects of alkylating agents. This Phase II trial was designed to assess the efficacy of a strategy designed to modulate the resistance to carmustine (BCNU) mediated by AGAT using streptozocin (STZ) in patients with advanced refractory melanoma. Seventeen patients who had failed prior chemotherapy were treated with STZ at 500 mg/m2 daily for 4 days with BCNU at 150 mg/m2 on day 3. Peripheral blood lymphocytes for assay of AGAT activity levels were collected prior to therapy and following the third dose of STZ. There were two partial responses in the 15 patients evaluable for response (13%). Most patients received only a single cycle of therapy due to rapidly progressive disease. Two patients developed fatal pulmonary toxicity, and one developed myelodysplasia. Other toxicities included transient rises in liver function tests. AGAT levels decreased by a mean of 53% in 9 patients but actually increased over baseline in 3 patients while on therapy. Based on these data, BCNU and STZ are not an effective combination for the therapy of advanced refractory melanoma, and pulmonary toxicity due to this combination appears to be increased compared with BCNU alone. STZ is not an effective modulator of AGAT activity when given on this schedule. New strategies designed to deplete AGAT activity using O6-benzylguanine or temozolomide should be explored with careful attention to the possibility that this approach may potentiate both the toxicity and efficacy of BCNU.
Bobola MS, Tseng SH, Blank A, et al.
Role of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase in resistance of human brain tumor cell lines to the clinically relevant methylating agents temozolomide and streptozotocin.
Clin Cancer Res. 1996; 2(4):735-41 [PubMed] Related Publications
Role of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase in resistance of human brain tumor cell lines to the clinically relevant methylating agents temozolomide and streptozotocin.
Clin Cancer Res. 1996; 2(4):735-41 [PubMed] Related Publications
We have analyzed the sensitivity of 14 human medulloblastoma- and glioma-derived cell lines to the clinically used methylating agents temozolomide and streptozotocin. The cell lines responded similarly to these agents, displaying a 3-fold range in cytotoxicity, assessed as the 10% survival dose (LD10). The contribution of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) to resistance, measured as reduction in the LD10 by O6-benzylguanine (O6-BG), varied among the lines by 1 order of magnitude for both agents. However, in all MGMT-expressing lines, O6-BG eliminated a threshold dose that accounted for up to one-half of the LD10. The effect of O6-BG on the rate of killing varied 13-fold for temozolomide and 14-fold for streptozotocin. Some lines displayed two subpopulations with different rates of killing, with one subpopulation that comprised 20-60% of cells showing essentially no dependence of the rate of killing on MGMT. O6-BG increased the range of the LD10 for both agents. The persistent, heightened variability in cytotoxicity in the absence of MGMT, the lack of correlation between MGMT content of the lines and cytoxicity (LD10), and the lack of correlation between MGMT content and the contribution of MGMT to resistance (O6-BG-mediated reduction of the LD10) reflect the operation of resistance mechanisms other than MGMT. We also analyzed sensitivity to methyl methanesulfonate, observing little dependence of resistance on MGMT and persistent variability in cytotoxicity in the presence of O6-BG. We discuss the implications for clinical use of methylators and O6-BG.
Willson JK, Haaga JR, Trey JE, et al.
Modulation of O6-alkylguanine alkyltransferase-directed DNA repair in metastatic colon cancers.
J Clin Oncol. 1995; 13(9):2301-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Modulation of O6-alkylguanine alkyltransferase-directed DNA repair in metastatic colon cancers.
J Clin Oncol. 1995; 13(9):2301-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
PURPOSE: Carmustine (BCNU) resistance has been correlated with tumor expression of the DNA repair enzyme O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (AT). It has been shown that streptozotocin will deplete AT activity of human colon cancer cells in vitro and potentiate BCNU cytotoxicity. This clinical trial was conducted to determine whether streptozotocin can be used as a modulator of AT in metastatic colorectal cancers and thereby overcome clinical resistance to BCNU.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Fifteen patients with fluorouracil-resistant metastatic colon or rectal cancers were treated sequentially with 2 g/m2 of streptozotocin followed 5 1/2 hours later by BCNU. Sequential biopsies of metastases before and after streptozotocin were conducted to determine whether streptozotocin depletes tumor AT. Peripheral-blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were evaluated as a surrogate tissue for prediction of baseline AT levels and streptozotocin posttreatment modulation of the AT in metastases.
RESULTS: Streptozotocin treatment led to a 78% (range, 69% to 89%) decrease in the AT levels in colon cancer metastases; however, myelosuppression and hepatic toxicity limited the BCNU dose to 130 mg/m2. A similar decrease in AT levels of PBMCs was found; however, the absolute levels of AT in PBMCs at baseline and following streptozotocin were not predictive of the levels expressed in metastases from the same patient. Despite the decrease in tumor levels of AT, no clinical responses were observed.
CONCLUSION: Streptozotocin decreases but does not fully deplete AT activity in metastatic colorectal cancers and the residual AT level in metastases is sufficient to maintain clinical resistance to BCNU. We have also demonstrated that sequential computed tomography (CT)-directed biopsies of colorectal cancer metastases can be used to evaluate strategies to investigate modulators of AT-directed repair. AT levels of PBMCs do not predict for the AT level or degree of modulation achieved in the metastatic tumor.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Fifteen patients with fluorouracil-resistant metastatic colon or rectal cancers were treated sequentially with 2 g/m2 of streptozotocin followed 5 1/2 hours later by BCNU. Sequential biopsies of metastases before and after streptozotocin were conducted to determine whether streptozotocin depletes tumor AT. Peripheral-blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were evaluated as a surrogate tissue for prediction of baseline AT levels and streptozotocin posttreatment modulation of the AT in metastases.
RESULTS: Streptozotocin treatment led to a 78% (range, 69% to 89%) decrease in the AT levels in colon cancer metastases; however, myelosuppression and hepatic toxicity limited the BCNU dose to 130 mg/m2. A similar decrease in AT levels of PBMCs was found; however, the absolute levels of AT in PBMCs at baseline and following streptozotocin were not predictive of the levels expressed in metastases from the same patient. Despite the decrease in tumor levels of AT, no clinical responses were observed.
CONCLUSION: Streptozotocin decreases but does not fully deplete AT activity in metastatic colorectal cancers and the residual AT level in metastases is sufficient to maintain clinical resistance to BCNU. We have also demonstrated that sequential computed tomography (CT)-directed biopsies of colorectal cancer metastases can be used to evaluate strategies to investigate modulators of AT-directed repair. AT levels of PBMCs do not predict for the AT level or degree of modulation achieved in the metastatic tumor.
Zhao KM, Chen JM, Zuo HZ, et al.
Modulation of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase-mediated nimustine resistance in recurrent malignant gliomas by streptozotocin--a preliminary report.
Anticancer Res. 1995 Mar-Apr; 15(2):645-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Modulation of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase-mediated nimustine resistance in recurrent malignant gliomas by streptozotocin--a preliminary report.
Anticancer Res. 1995 Mar-Apr; 15(2):645-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
This trial is based on the strategy of reversing O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT)-mediated nimustine resistance by depleting MGMT activity with streptozotocin (STZ) pretreatment. Eight patients with recurrent malignant gliomas refractory to previous nimustine chemotherapy were entered in this study. Patients received STZ (2g/m2) followed one hour with nimustine (2-3 mg/Kg) via the ipsilateral carotid artery. After 1-2 cycles of therapy, 3 patients responded, 4 stabilized, and 1 failed. Toxic effects were generally tolerated. The preliminary results indicated that nimustine-resistant tumor cells in vivo could also be sensitized by modulation of MGMT activity.
Eizirik DL, Björklund A, Cagliero E
Genotoxic agents increase expression of growth arrest and DNA damage--inducible genes gadd 153 and gadd 45 in rat pancreatic islets.
Diabetes. 1993; 42(5):738-45 [PubMed] Related Publications
Genotoxic agents increase expression of growth arrest and DNA damage--inducible genes gadd 153 and gadd 45 in rat pancreatic islets.
Diabetes. 1993; 42(5):738-45 [PubMed] Related Publications
Pancreatic beta-cells are able to repair themselves after some sublethal injuries in vitro. However, little is known of the nature of the repair mechanisms active in these cells. This study examined the expression of growth arrest and DNA damage--inducible genes gadd 153 and gadd 45 in pancreatic rat islets and in the clonal insulin secretory HIT-T15 cells. Rat pancreatic islets were exposed in vitro to the alkylating agents streptozocin or methyl methanesulfonate, or to the cytokine recombinant interleukin-1 beta. Islet exposure to STZ or MMS reduced insulin release by 40-50% over the next 4 h, whereas exposure to rIL-1 beta induced a 60% increase in insulin release over the same period. Both gadd 153 and gadd 45 mRNA were detectable in rat islets, and their levels were increased twofold after STZ exposure, whereas MMS induced a fivefold increase in gadd 153 and a twofold increase in gadd 45 mRNA. Islet exposure to rIL-1 beta did not affect the expression of gadd 153 or gadd 45. HIT cells exposed to STZ or MMS also exhibited an increased expression of both gadd 153 and gadd 45. Again, this increase in gadd mRNA was more marked after MMS exposure. Moreover, expression of both gadd 153 and gadd 45 after MMS exposure lasted for a longer period of time than after STZ treatment. The effects of MMS on the expression of both gadd genes were inhibited by actinomycin D, suggesting that transcription is necessary for acute gadd induction.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Goel R, McClay EF, Kirmani S, et al.
Pharmacokinetic study of intraperitoneal streptozotocin.
Clin Invest Med. 1992; 15(5):420-6 [PubMed] Related Publications
Pharmacokinetic study of intraperitoneal streptozotocin.
Clin Invest Med. 1992; 15(5):420-6 [PubMed] Related Publications
Streptozotocin, a nitrosourea, has limited antitumour activity. However, in concentrations and exposures higher than those achieved after intravenous dosing, streptozotocin has been reported to sensitize various cell lines in vitro to other nitrosoureas or alkylating agents. We hypothesized that the intraperitoneal administration of streptozotocin would achieve concentrations and exposures in the peritoneal cavity sufficient for this sensitization to take place. The pharmacokinetics of streptozotocin in the peritoneal cavity and in plasma were determined in patients who received 1 g of streptozotocin via the intraperitoneal route. Fifteen courses were administered to 12 patients. The mean total area under the concentration versus time curves (AUC) was 183 +/- 31 (SE) mM min in the peritoneal cavity (5 courses) and 5.3 +/- 1.1 (SE) mM min in plasma (6 courses). The mean peritoneal to plasma AUC ratio was 64 +/- 23 (5 courses). The mean peak streptozotocin concentrations in the peritoneal cavity (5 courses) and plasma (6 courses) were 1.9 +/- 0.4 mM and 0.03 +/- 0.01 mM, respectively. No significant toxicity was observed on any course. We conclude that intraperitoneal administration of streptozotocin is feasible, and that drug concentrations and exposures are in an appropriate range in the peritoneal cavity to cause sensitization to other nitrosoureas.
Janson ET, Rönnblom L, Ahlström H, et al.
Treatment with alpha-interferon versus alpha-interferon in combination with streptozocin and doxorubicin in patients with malignant carcinoid tumors: a randomized trial.
Ann Oncol. 1992; 3(8):635-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Treatment with alpha-interferon versus alpha-interferon in combination with streptozocin and doxorubicin in patients with malignant carcinoid tumors: a randomized trial.
Ann Oncol. 1992; 3(8):635-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
An open randomized trial was performed to compare the effect of recombinant interferon-alpha 2a (rIFN-alpha 2a) (group A, n = 12) versus rIFN-alpha 2a in combination with chemotherapy (group B, n = 11) in patients with malignant carcinoid tumors. Both groups received rIFN-alpha 2a at a dose of 3 MU/m2 s.c. three times weekly during the first 6 months. IFN was discontinued every third week in group B, followed by an i.v. injection of 2 g streptozocin and 40 mg/m2 doxorubicin. After 6 months group A showed one complete biochemical response (CR), 9 patients with stable disease (SD) and 2 who progressed (PD). Two patients had a partial reduction (PR) of tumor size, 9 showed SD and one PD. All patients in group B demonstrated SD. Chemotherapy was withdrawn after 6 months and all patients continued with rIFN-alpha 2a at an increased dose of 3 MU/m2 five days/week for a further 6 months. After 12 months 6 patients showed PR, 12 SD and one PD biochemically. Tumor size showed SD in 18 patients and PD in one. One patient died from cardiomyopathy, probably induced by doxorubicin. Antibodies against rIFN-alpha 2a developed in 41% of the patients. In conclusion, we detected no difference in response rates between the two treatment groups. Adverse reactions from the combination were considerable. The frequent development of IFN antibodies might have interfered with the therapeutic results.
Nesović M, Cirić J, Radojković S, et al.
Improvement of metastatic endocrine tumors of the pancreas by hepatic artery chemoembolization.
J Endocrinol Invest. 1992 Jul-Aug; 15(7):543-7 [PubMed] Related Publications
Improvement of metastatic endocrine tumors of the pancreas by hepatic artery chemoembolization.
J Endocrinol Invest. 1992 Jul-Aug; 15(7):543-7 [PubMed] Related Publications
We report the results of transcatheter intraarterial perfusion of liver with the emulsion of iodized oil and cytostatics performed as palliative treatment in three patients with hepatic metastases of pancreatic endocrine tumors. Two patients had insulinoma and one patient had glucagonoma. They were also treated by medical therapy from the time the diagnosis was made. Intraarterial perfusion of the liver was achieved by Lipiodol emulsified with streptozotocin and 5-fluorouracil. Regarding these three patients therapeutic responses were different in duration of hormone secretion decrease. Relief of hypoglycemic attacks and a significant decrease of plasma immunoreactive insulin concentration within 12 months without any additional therapy was observed in the patient with insulinoma (case no. 2). This patient had slightly increased immunoreactive glucagon concentration from the time of diagnosis. A decrease of immunoreactive insulin levels in other patient with insulinoma and an increase in plasma glucose to the euglycemic range during two months allowed a reduction of doses of somatostatin analogue and diazoxide. Due to rapid progression of the disease, intraarterial perfusion of liver was repeated three months later with the same results. Remission of symptoms was partial in the case of glucagonoma. Immunoreactive glucagon levels were not changed and there was no significant benefit of the treatment. Intraarterial perfusion of liver with iodized oil and cytostatics could be an effective, safe and repeatable method of palliating symptoms of malignant pancreatic tumors, especially in inoperable but nonterminal cases. It could allow reduction of additional medical therapy, but success of the treatment is not predictable.
Panella TJ, Smith DC, Schold SC, et al.
Modulation of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase-mediated carmustine resistance using streptozotocin: a phase I trial.
Cancer Res. 1992; 52(9):2456-9 [PubMed] Related Publications
Modulation of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase-mediated carmustine resistance using streptozotocin: a phase I trial.
Cancer Res. 1992; 52(9):2456-9 [PubMed] Related Publications
1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea (BCNU) resistance may be mediated by repair of chloroethylated guanine before stable cross-linking occurs. Guanine adducts may be repaired by the enzyme O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (O6-AGAT). Such repair irreversibly inactivates O6-AGAT. Streptozotocin (STZ) forms adducts at the O6 position of guanine; repair of these adducts consumes O6-AGAT. In vivo STZ potentiates BCNU cytotoxicity. The purpose of this trial was to determine the maximum tolerated dose of BCNU that can be administered together with STZ. The STZ dose was 500 mg/m2/day for 4 days and was not escalated. BCNU was given 4 h after the third dose of STZ at a starting dose of 75 mg/m2. A total of 43 patients were entered in the study. There were 4 dose escalations, reaching a maximum tolerated BCNU dose of 175 mg/m2. At this dose, thrombocytopenia was the dose-limiting toxicity (one patient, 25-49 x 10(9)/liter; 2 patients, less than 25 x 10(9)/liter); neutropenia was less severe (2 patients, 2.0-3.9 x 10(9)/liter, 1 patient, 1.0-1.9 x 10(9)/liter). Two other commonly seen toxicities were elevations in the serum alkaline phosphatase and mild elevations in the serum creatinine. Peripheral blood lymphocyte O6-AGAT levels decreased from a mean of 212 fmol/mg protein pretherapy to 8.2 fmol/mg protein on day 3 prior to BCNU (P = 0.03). Three partial responses were seen. There were no therapy-related fatalities, and toxicity was easily managed. This study established that 150 mg of BCNU can be administered safely together with STZ, 500 mg/m2/day for 4 days. Additional studies are required to determine whether O6-AGAT-mediated BCNU resistance is suppressed.
Srivenugopal KS
Formation and disappearance of DNA interstrand cross-links in human colon tumor cell lines with different levels of resistance to chlorozotocin.
Biochem Pharmacol. 1992; 43(5):1159-63 [PubMed] Related Publications
Formation and disappearance of DNA interstrand cross-links in human colon tumor cell lines with different levels of resistance to chlorozotocin.
Biochem Pharmacol. 1992; 43(5):1159-63 [PubMed] Related Publications
Three human colon tumor (HCT) cell lines, designated C, Moser and 116, exhibiting a gradation of resistance to chlorozotocin, a glucose-linked chloroethylnitrosourea (1-, 2.9-, and 5.8-fold respectively) were examined to assess the determinants of drug sensitivity. Although the O6-alkylguanine-DNA transferase content was relatively higher in the most resistant 116 cells than in the sensitive cell line C, its level in Moser cells did not correlate with the intermediate chlorozotocin sensitivity. Glutathione content in these tumor cell lines did not show a parallelism with drug resistance. The ethidium bromide fluorescence assay was used to quantitate the kinetics of DNA interstrand cross-link formation and its removal after drug exposure. The peak levels of DNA interstrand cross-links induced in HCT cells correlated with their resistance to chlorozotocin with cross-link indices of 0.03, 0.10 and 0.20, respectively, for 116, Moser and C cell lines. All three cell lines demonstrated DNA cross-link repair to different extents. While the smaller number of cross-links formed in resistant 116 and Moser cells were eliminated in a rapid phase of repair, the lesions formed at a much greater frequency in C cells remained largely unrepaired. These results draw attention to the role of increased DNA cross-link repair as a mechanism of nitrosourea resistance in the HCT cells studied.
Moertel CG, Lefkopoulo M, Lipsitz S, et al.
Streptozocin-doxorubicin, streptozocin-fluorouracil or chlorozotocin in the treatment of advanced islet-cell carcinoma.
N Engl J Med. 1992; 326(8):519-23 [PubMed] Related Publications
Streptozocin-doxorubicin, streptozocin-fluorouracil or chlorozotocin in the treatment of advanced islet-cell carcinoma.
N Engl J Med. 1992; 326(8):519-23 [PubMed] Related Publications
BACKGROUND: The combination of streptozocin and fluorouracil has become the standard therapy for advanced islet-cell carcinoma. However, doxorubicin has also been shown to be active against this type of tumor, as has chlorozotocin, a drug that is structurally similar to streptozocin but less frequently causes vomiting.
METHODS: In this multicenter trial, we randomly assigned 105 patients with advanced islet-cell carcinoma to receive one of three treatment regimens: streptozocin plus fluorouracil, streptozocin plus doxorubicin, or chlorozotocin alone. The 31 patients in whom the disease did not respond to treatment were crossed over to chlorozotocin alone or to one of the combination regimens.
RESULTS: Streptozocin plus doxorubicin was superior to streptozocin plus fluorouracil in terms of the rate of tumor regression, measured objectively (69 percent vs. 45 percent, P = 0.05), and the length of time to tumor progression (median, 20 vs. 6.9 months; P = 0.001). Streptozocin plus doxorubicin also had a significant advantage in terms of survival (median, 2.2 vs. 1.4 years; P = 0.004) that was accentuated when we considered long-term survival (greater than 2 years). Chlorozotocin alone produced a 30 percent regression rate, with the length of time to tumor progression and the survival time equivalent to those observed with streptozocin plus fluorouracil. Crossover therapy after the failure of either chlorozotocin alone or one of the combination regimens produced an overall response rate of only 17 percent, and the responses were transient. Toxic reactions to all regimens included vomiting, which was least severe with chlorozotocin; hematologic depression; and, with long-term therapy, renal insufficiency.
CONCLUSIONS: The combination of streptozocin and doxorubicin is superior to the current standard regimen of streptozocin plus fluorouracil in the treatment of advanced islet-cell carcinoma. Chlorozotocin alone is similar in efficacy to streptozocin plus fluorouracil, but it produces fewer gastrointestinal side effects than the regimens containing streptozocin. It therefore merits study as a constituent of combination drug regimens.
METHODS: In this multicenter trial, we randomly assigned 105 patients with advanced islet-cell carcinoma to receive one of three treatment regimens: streptozocin plus fluorouracil, streptozocin plus doxorubicin, or chlorozotocin alone. The 31 patients in whom the disease did not respond to treatment were crossed over to chlorozotocin alone or to one of the combination regimens.
RESULTS: Streptozocin plus doxorubicin was superior to streptozocin plus fluorouracil in terms of the rate of tumor regression, measured objectively (69 percent vs. 45 percent, P = 0.05), and the length of time to tumor progression (median, 20 vs. 6.9 months; P = 0.001). Streptozocin plus doxorubicin also had a significant advantage in terms of survival (median, 2.2 vs. 1.4 years; P = 0.004) that was accentuated when we considered long-term survival (greater than 2 years). Chlorozotocin alone produced a 30 percent regression rate, with the length of time to tumor progression and the survival time equivalent to those observed with streptozocin plus fluorouracil. Crossover therapy after the failure of either chlorozotocin alone or one of the combination regimens produced an overall response rate of only 17 percent, and the responses were transient. Toxic reactions to all regimens included vomiting, which was least severe with chlorozotocin; hematologic depression; and, with long-term therapy, renal insufficiency.
CONCLUSIONS: The combination of streptozocin and doxorubicin is superior to the current standard regimen of streptozocin plus fluorouracil in the treatment of advanced islet-cell carcinoma. Chlorozotocin alone is similar in efficacy to streptozocin plus fluorouracil, but it produces fewer gastrointestinal side effects than the regimens containing streptozocin. It therefore merits study as a constituent of combination drug regimens.
Ridolfi R, Amaducci L, Derni S, et al.
Chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and streptozotocin in carcinoid tumors of gastrointestinal origin: experiences with 13 patients.
J Chemother. 1991; 3(5):328-31 [PubMed] Related Publications
Chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil and streptozotocin in carcinoid tumors of gastrointestinal origin: experiences with 13 patients.
J Chemother. 1991; 3(5):328-31 [PubMed] Related Publications
The Authors report their experiences on the treatment of 13 consecutive cases of gastro-intestinal carcinoid tumors observed over the last 11 years. The primary sites were as follows: intestine (5 cases), appendix (3 cases), colon (1 case) and peritoneum (4 cases); only 3 patients presented systemic signs. Ten patients in advanced phase were treated with a chemotherapeutic regimen containing 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu) and streptozotocin (STZ). One case was excluded from the study because of a concomitant gastric carcinoma. Of the 9 evaluable patients, two achieved partial remission (22%) with a duration of 18+ and 66 months respectively; 4 (44.5%) had stable disease for periods ranging from 7 to 40 months and 3 cases progressed. Severe toxicity (thrombocytopenia and diarrhea) occurred in 2 cases and disappeared with the suspension of therapy. The systemic signs disappeared with treatment and did not appear in 2 cases out of 3. The prospective of the employment of new drugs such as alpha-interferon and, above all, somatostatin provides hope that this uncommon disease may have an improved response rate to treatment in the future.
Bar M, Burke M, Isakov A, Almog C
Insulinoma after streptozotocin therapy for metastatic gastrinoma: natural history or iatrogenic complication?
J Clin Gastroenterol. 1990; 12(5):579-80 [PubMed] Related Publications
Insulinoma after streptozotocin therapy for metastatic gastrinoma: natural history or iatrogenic complication?
J Clin Gastroenterol. 1990; 12(5):579-80 [PubMed] Related Publications
Islet cell carcinoma frequently produces more than one chemical product, although its clinical expression is usually restricted to a single hormone. We describe an unusual patient who presented with full-blown metastasizing gastrinoma. He was treated with cimetidine for five years and then streptozotocin therapy, which resulted in a regression in hepatomegaly and a fall in serum gastrin levels. Following one year's therapy with streptozotocin, he was admitted in hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemic stupor. This appears to be the first reported case of a "shift" from clinical gastrinoma to insulinoma possibly related to prolonged streptozotocin therapy.
Cunningham RT, Johnston CF, Irvine GB, et al.
Development of a radioimmunoassay for neurone specific enolase (NSE) and its application in the study of patients receiving intra hepatic arterial streptozotocin and floxuridine.
Clin Chim Acta. 1990; 189(3):275-86 [PubMed] Related Publications
Development of a radioimmunoassay for neurone specific enolase (NSE) and its application in the study of patients receiving intra hepatic arterial streptozotocin and floxuridine.
Clin Chim Acta. 1990; 189(3):275-86 [PubMed] Related Publications
A radioimmunoassay has been developed for neurone specific enolase (NSE) and used to measure serum NSE levels in patients with neuroendocrine and non-neuroendocrine tumours following intra hepatic arterial chemotherapy. Ten patients were studied, 7 receiving streptozotocin and floxuridine for neuroendocrine tumours and three receiving cisplatinum for non-neuroendocrine neoplasms. All ten patients had liver metastases. In patients with tumours of neuroendocrine origin, a significant increase in serum NSE was recorded within 24 h of therapy. Slight increases in serum NSE levels were also recorded in three patients with non neuroendocrine tumours. These increases may reflect lysis of neuroendocrine cells within the tumour. Raised levels in non-neuroendocrine tumour patients may reveal damage done to healthy neuronal and neuroendocrine cells during treatment. NSE may be a useful marker of the extent of cell death following chemotherapy.
Schulz B, Hehmke B, Zander E, Ziegler B
Autoimmune reactions in a patient with malignant insulinoma treated by multiple low dose streptozotocin.
Exp Clin Endocrinol. 1990; 95(1):77-82 [PubMed] Related Publications
Autoimmune reactions in a patient with malignant insulinoma treated by multiple low dose streptozotocin.
Exp Clin Endocrinol. 1990; 95(1):77-82 [PubMed] Related Publications
A 66-year-old female patient with a malignant insulinoma was treated with streptozotocin (STZ; Zanosar) in 5 cycles every 4 weeks as 5 day courses with an intravenous dosage of 850 mg per day. Under this treatment hypoglycemic episodes decreased continuously in number as well as severity and - after a delay of 12 months after the last treatment - an overt diabetes mellitus appeared. Plasma insulin concentrations dropped immediately after starting of STZ therapy. On the other hand, islet cell surface antibodies and their complement-dependent cytotoxicity increased continuously, being at their highest 6 months after termination of STZ treatment. Thus, STZ is able to induce a specific immune response against islet cells with a progressive damage of malignant insulin producing cells.
Deutsch M, Green SB, Strike TA, et al.
Results of a randomized trial comparing BCNU plus radiotherapy, streptozotocin plus radiotherapy, BCNU plus hyperfractionated radiotherapy, and BCNU following misonidazole plus radiotherapy in the postoperative treatment of malignant glioma.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989; 16(6):1389-96 [PubMed] Related Publications
Results of a randomized trial comparing BCNU plus radiotherapy, streptozotocin plus radiotherapy, BCNU plus hyperfractionated radiotherapy, and BCNU following misonidazole plus radiotherapy in the postoperative treatment of malignant glioma.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989; 16(6):1389-96 [PubMed] Related Publications
In Brain Tumor Cooperative Group Study 77-02, eleven institutions randomized 603 adult patients with supratentorial malignant glioma to one of four treatment groups following surgery: conventional radiotherapy (6000 cGy in 30-35 fractions) + BCNU, conventional radiotherapy + streptozotocin, hyperfractionated (twice daily) radiotherapy (6600 cGy in 60 fractions) + BCNU, and conventional radiotherapy with misonidazole followed by BCNU. Data were analyzed for the total randomized population and for the 557 patients (86% with glioblastoma multiforme) who met protocol eligibility specifications (including confirmed histopathology on central review). Median survival was approximately 10 months following randomization. Overall there was no statistically significant difference in survival among the four groups. Among non-glioblastoma patients, the misonidazole group appeared to have poor survival. Peripheral neuropathy was a dose-limiting toxicity with misonidazole. It is concluded that neither the addition of misonidazole nor hyperfractionated radiotherapy as given in this protocol offered any advantage over conventional radiotherapy plus either BCNU or streptozotocin for treatment of malignant glioma.
Gerson SL
Modulation of human lymphocyte O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase by streptozotocin in vivo.
Cancer Res. 1989; 49(11):3134-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Modulation of human lymphocyte O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase by streptozotocin in vivo.
Cancer Res. 1989; 49(11):3134-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
The ability to modulate DNA repair has been proposed as an effective method to overcome cytotoxic drug resistance in human tumors. However, no studies have shown that it is possible to achieve modulation of DNA repair in humans in vivo. This study analyzes modulation of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase, a DNA repair protein that protects cells from cytotoxic DNA adducts formed by nitrosoureas. Streptozotocin has been shown to inactivate the alkyltransferase in vitro and sensitize tumor cells to other nitrosoureas. Thus, we determined whether biochemical modulation of alkyltransferase activity could be documented in patients receiving therapeutic doses of streptozotocin and whether the modulation was specific to streptozotocin or occurred in patients undergoing treatment with other DNA-damaging agents as well. Normal peripheral blood lymphocytes were used to analyze modulation of the alkyltransferase. We found that lymphocyte alkyltransferase activity was significantly decreased 20 h after treatment with streptozotocin (500 mg/m2) or high dose 1,3-bis-(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea (350 mg/m2) but not after treatment with the other DNA-damaging agents or lower doses of 1,3-bis-(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea. A cumulative decline in lymphocyte alkyltransferase activity occurred with daily streptozotocin treatment, reaching 26 +/- 9% of control after the third day of treatment (P less than 0.0005). Thus, the alkyltransferase DNA repair protein can be modulated in vivo in humans given systemic drug treatment. While further studies are needed to document that biochemical modulation can be achieved in the target tumor in humans, this study supports the development of clinical trials using streptozotocin as a biochemical modulator of nitrosourea resistance in human malignancies.


 Cancer of the Pancreas
Cancer of the Pancreas