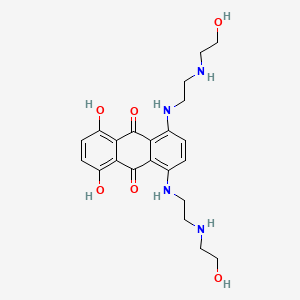
Mitoxantrone
"An anthracenedione-derived antineoplastic agent." (MeSH 2013)
Found this page useful?
 Web Resources: Mitoxantrone
Web Resources: Mitoxantrone Latest Research Publications
Latest Research PublicationsWeb Resources: Mitoxantrone (6 links)
Cancer Research UK
Irish Cancer Society
Macmillan Cancer Support
NHS Evidence
 Mitoxantrone - Substance Summary
Mitoxantrone - Substance Summary
PubChem
MedlinePlus
Latest Research Publications
This list of publications is regularly updated (Source: PubMed).
Pawlik A, Szczepanski MA, Klimaszewska-Wisniewska A, et al.
Cytoskeletal reorganization and cell death in mitoxantrone-treated lung cancer cells.
Acta Histochem. 2016; 118(8):784-796 [PubMed] Related Publications
Cytoskeletal reorganization and cell death in mitoxantrone-treated lung cancer cells.
Acta Histochem. 2016; 118(8):784-796 [PubMed] Related Publications
The aim of this study was to investigate the cytotoxic effect of mitoxantrone on two human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines, A549 (p53+) and H1299 (p53-). To our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the impact of MXT on the organization of cytoskeletal proteins. Analyses were performed using fluorescence and transmission electron microscopy, spectrophotometric techniques, flow cytometry and Western blotting. It was shown that H1299 cells are significantly more sensitive to mitoxantrone than the A549 cell line, and that the growth-inhibitory effect of the drug is dose-dependent only after longer incubation. The observed presence of ring-like microtubule structures and mitochondria surrounding the nuclei of H1299 cells could be a manifestation of increased tubulin polymerization requiring large amounts of energy, whereas the loss of actin stress fibers was presumably not the cause but rather the consequence of cell death induction. Treatment with mitoxantrone also led to the appearance of structures resembling agresomes in H1299 cells and to nucleolar segregation in both cell lines. It was demonstrated that cells arrested in the S phase were most susceptible to cell death induction, and that triggered intracellular changes led mainly to apoptosis. High concentrations induced necrosis and some H1299 cells exhibited morphological features of mitotic catastrophe.
Arami S, Mahdavi M, Rashidi MR, et al.
Novel polyacrylate-based cationic nanoparticles for survivin siRNA delivery combined with mitoxantrone for treatment of breast cancer.
Biologicals. 2016; 44(6):487-496 [PubMed] Related Publications
Novel polyacrylate-based cationic nanoparticles for survivin siRNA delivery combined with mitoxantrone for treatment of breast cancer.
Biologicals. 2016; 44(6):487-496 [PubMed] Related Publications
As a gene delivery method in breast cancer therapy, knocking down the undesired genes in the cancerous cells would be promising. Inhibitors of Apoptosis Protein (IAP) family genes are some of the genes whose responsibility is inhibition of apoptosis in cells. Silencing these genes seems to be helpful directing the tumor cells to death. siRNA sequence designed against survivin anti-apoptotic gene can play this role if carried to the cytoplasm. Here we prepared a positive charged biocompatible nano-sized particle made up of a Fe3O4 core covered respectively by polyacrylate (PA) and polyethyleneimine (PEI) layer, which could successfully deliver the siRNA into the MCF-7 cells. The particle structure was checked and having less than 50 nm diameter in size, positive charge and, safety towards MCF-7 cells besides being able to form nanoplexes with the siRNA strand helps it entering into the biologic assays part. The siRNA delivery evaluated via flowcytometry. Apoptosis induction was determined by DAPI staining. The efficiency of survivin gene knockdown was evaluated in mRNA and protein levels using Real time PCR and western blotting methods. Overall, the Fe3O4-PA-PEI nanoparticles can deliver siRNA effectively into the cytoplasm of the MCF-7 breast cancer cells and induce apoptosis.
Ling G, Zhang T, Zhang P, et al.
Synergistic and complete reversal of the multidrug resistance of mitoxantrone hydrochloride by three-in-one multifunctional lipid-sodium glycocholate nanocarriers based on simultaneous BCRP and Bcl-2 inhibition.
Int J Nanomedicine. 2016; 11:4077-91 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Synergistic and complete reversal of the multidrug resistance of mitoxantrone hydrochloride by three-in-one multifunctional lipid-sodium glycocholate nanocarriers based on simultaneous BCRP and Bcl-2 inhibition.
Int J Nanomedicine. 2016; 11:4077-91 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Multidrug resistance (MDR) is a severe obstacle to successful chemotherapy due to its complicated nature that involves multiple mechanisms, such as drug efflux by transporters (P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein, BCRP) and anti-apoptotic defense (B-cell lymphoma, Bcl-2). To synergistically and completely reverse MDR by simultaneous inhibition of pump and non-pump cellular resistance, three-in-one multifunctional lipid-sodium glycocholate (GcNa) nanocarriers (TMLGNs) have been designed for controlled co-delivery of water-soluble cationic mitoxantrone hydrochloride (MTO), cyclosporine A (CsA - BCRP inhibitor), and GcNa (Bcl-2 inhibitor). GcNa and dextran sulfate were incorporated as anionic compounds to enhance the encapsulation efficiency of MTO (up to 97.8%±1.9%) and sustain the release of cationic MTO by electrostatic interaction. The results of a series of in vitro and in vivo investigations indicated that the TMLGNs were taken up by the resistant cancer cells by an endocytosis pathway that escaped the efflux induced by BCRP, and the simultaneous release of CsA with MTO further efficiently inhibited the efflux of the released MTO by BCRP; meanwhile GcNa induced the apoptosis process, and an associated synergistic antitumor activity and reversion of MDR were achieved because the reversal index was almost 1.0.
Aurer I, Nemet D, Mitrović Z, et al.
High-dose ifosfamide and mitoxantrone (HDIM) in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Ann Hematol. 2016; 95(7):1129-36 [PubMed] Related Publications
High-dose ifosfamide and mitoxantrone (HDIM) in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Ann Hematol. 2016; 95(7):1129-36 [PubMed] Related Publications
Relapsed/refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL) is treated with salvage chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). Optimal chemotherapy is unknown. We retrospectively analyzed outcomes of 58 patients treated with 2 cycles of high-dose ifosfamide and mitoxantrone (HDIM). HDIM consisted of ifosfamide 5 g/m(2)/day and MESNA 5 g/m(2)/day in continuous 24-h infusion (days 1 and 2), MESNA 2.5 g/m(2) over 12 h (day 3), and mitoxantrone 20 mg/m(2) (day 1) administered every 2 weeks. Stem cells were collected after the first cycle. Responding patients proceeded to ASCT. Toxicity was acceptable. Stem cell mobilization was successful in 96 % of patients. Overall response rate was 74 % (89 % in relapsing and 45 % in refractory patients) with 31 % complete remissions. After a median follow-up of 54 months, 5-year event-free survival was 56 % (69 % for relapsing and 35 % for refractory patients), and 5-year overall survival was 67 % (73 % for relapsing and 55 % for refractory patients). Significant adverse prognostic factors were refractoriness to previous therapy and HDIM failure. No differences in outcomes were noted between patients with early and late relapses or between complete and partial responders. HDIM is a well-tolerated and effective regimen for relapsed and refractory HL with excellent stem cell mobilizing properties. Patients failing HDIM may still benefit from other salvage options.
Abu Saleh M, Solayman M, Hoque MM, et al.
Inhibition of DNA Topoisomerase Type IIα (TOP2A) by Mitoxantrone and Its Halogenated Derivatives: A Combined Density Functional and Molecular Docking Study.
Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:6817502 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Inhibition of DNA Topoisomerase Type IIα (TOP2A) by Mitoxantrone and Its Halogenated Derivatives: A Combined Density Functional and Molecular Docking Study.
Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:6817502 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
In this study, mitoxantrone and its halogenated derivatives have been designed by density functional theory (DFT) to explore their structural and thermodynamical properties. The performance of these drugs was also evaluated to inhibit DNA topoisomerase type IIα (TOP2A) by molecular docking calculation. Noncovalent interactions play significant role in improving the performance of halogenated drugs. The combined quantum and molecular mechanics calculations revealed that CF3 containing drug shows better preference in inhibiting the TOP2A compared to other modified drugs.
Hu T, Cao H, Yang C, et al.
LHD-Modified Mechanism-Based Liposome Coencapsulation of Mitoxantrone and Prednisolone Using Novel Lipid Bilayer Fusion for Tissue-Specific Colocalization and Synergistic Antitumor Effects.
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016; 8(10):6586-601 [PubMed] Related Publications
LHD-Modified Mechanism-Based Liposome Coencapsulation of Mitoxantrone and Prednisolone Using Novel Lipid Bilayer Fusion for Tissue-Specific Colocalization and Synergistic Antitumor Effects.
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016; 8(10):6586-601 [PubMed] Related Publications
Coencapsulation liposomes are of interest to researchers because they maximize the synergistic effect of loaded drugs. A combination regimen of mitoxantrone (MTO) and prednisolone (PLP) has been ideal for tumor therapy. MTO and PLP offer synergistic antitumor effects confirmed by several experiments in this research. The deduced synergistic mechanism is regulation of Akt signaling pathway including the targets of p-Akt, p-GSK-3β, p-s6 ribosomal protein, and p-AMPK by MTO reactivating PLP-induced apoptosis. The liposome fusion method is adopted to create coencapsulation liposomes (PLP-MTO-YM). Low molecular weight heparin-sodium deoxycholate conjugate (LHD) then is used as a targeting ligand to prove target binding and inhibition of angiogenesis. LHD-modified liposomes (PLP-MTO-HM) have a high entrapment efficiency around 95% for both MTO and PLP. DSC results indicate that both drugs interacted with liposomes to prevent drug leak during liposome fusion. DiD-C6-HM dyes colocalize well to tumor tissue, and coadministration of DiD-HM and C6-CM did not achieve dye colocalization until 24 h after administration. In both CT26 and B16F10 mouse model, PLP-MTO-HM shows a significantly higher tumor inhibition rate relative to the coadministration of MTO-HM and PLP-CM (p < 0.05 or p < 0.01). Thus, the coencapsulation system (PLP-MTO-HM) offers ideal antitumor effects relative to coadministration therapy due to enhanced synergistic effect, and this suggests a promising future for the tumor targeting vectors.
Carter KA, Wang S, Geng J, et al.
Metal Chelation Modulates Phototherapeutic Properties of Mitoxantrone-Loaded Porphyrin-Phospholipid Liposomes.
Mol Pharm. 2016; 13(2):420-7 [PubMed] Related Publications
Metal Chelation Modulates Phototherapeutic Properties of Mitoxantrone-Loaded Porphyrin-Phospholipid Liposomes.
Mol Pharm. 2016; 13(2):420-7 [PubMed] Related Publications
Liposomes incorporating porphyrin-phospholipid (PoP) can be formulated to release entrapped contents in response to near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation. Here, we examine effects of chelating copper or zinc into the PoP. Cu(II) and Zn(II) PoP liposomes, containing 10 molar % HPPH-lipid, exhibited unique photophysical properties and released entrapped cargo in response to NIR light. Cu-PoP liposomes exhibited minimal fluorescence and reduced production of reactive oxygen species upon irradiation. Zn-PoP liposomes retained fluorescence and singlet oxygen generation properties; however, they rapidly self-bleached under laser irradiation. Compared to the free base form, both Cu- and Zn-PoP liposomes exhibited reduced phototoxicity in mice. When loaded with mitoxantrone and administered intravenously at 5 mg/kg to mice bearing human pancreatic cancer xenografts, synergistic effects between the drug and the light treatment (for this particular dose and formulation) were realized with metallo-PoP liposomes. The drug-light-interval affected chemophototherapy efficacy and safety.
Hou L, Feng Q, Wang Y, et al.
Multifunctional hyaluronic acid modified graphene oxide loaded with mitoxantrone for overcoming drug resistance in cancer.
Nanotechnology. 2016; 27(1):015701 [PubMed] Related Publications
Multifunctional hyaluronic acid modified graphene oxide loaded with mitoxantrone for overcoming drug resistance in cancer.
Nanotechnology. 2016; 27(1):015701 [PubMed] Related Publications
Multifunctional nanosheets (HA-GO/Pluronic) with targeted chemo-photothermal properties were successfully developed for controlled delivery of mitoxantrone (MIT) to overcome multidrug resistance (MDR). In vitro release profiles displayed that both an acidic environment and a NIR laser could trigger and accelerate the release of a drug, which ensured nanosheets were stable in blood circulation and released MIT within tumor cells under laser irradiation. HA-GO/Pluronic nanosheets were taken up into MCF-7/ADR cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis, which further facilitated escapement of P-gp efflux. Compared with MIT solution, MIT/HA-GO/Pluronic showed greater cytotoxicity and increase in cellular MIT accumulation in MCF-7/ADR cells. Cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest studies also revealed that MIT/HA-GO/Pluronic was more potent than MIT/GO/Pluronic and MIT solution. The anticancer efficacy in vivo was evaluated in MCF-7 and MCF-7/ADR-bearing mice, and inhibition of tumors by MIT/HA-GO/Pluronic with NIR laser irradiation was the most effective among all MIT formulations. In summary, the MIT/HA-GO/Pluronic system had striking functions such as P-gp reversible inhibitor and anticancer efficacy, and could present a promising platform for drug-resistant cancer treatment.
Bagan JV, Bagan L, Poveda R, Scully C
Mitoxantrone as a contributing factor in medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016; 45(3):377-9 [PubMed] Related Publications
Mitoxantrone as a contributing factor in medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016; 45(3):377-9 [PubMed] Related Publications
Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (BRONJ) is usually initiated by dental surgery, but is occasionally exacerbated by other antiresorptive (denosumab) and anti-angiogenic therapies, and in such cases is currently termed medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws (MRONJ). The case of a 58-year-old female with breast cancer who developed multiple and ultimately fatal metastases despite 3 years of treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs and intravenous bisphosphonates, is presented herein. Her malignant disease worsened and she was started on mitoxantrone. She developed a severe adverse reaction to this drug soon after starting treatment. As well as diarrhoea and vomiting, she had a very aggressive gingival inflammation with multiple ulcerations in both jaws and wide areas of necrotic bone, affecting the attached gingiva, and seemingly unrelated to dental plaque. These ulcerations and the exposed necrotic bone persisted for more that 6 months, until her death. This report describes a case in which severe gingival ulcerations that occurred after mitoxantrone treatment for metastatic breast cancer were a local factor that initiated MRONJ.
Ćmielová J, Lesná M, Řezáčová M
Subcellular Localization of Proteins Responding to Mitoxantrone-Induced DNA Damage in Leukaemic Cells.
Folia Biol (Praha). 2015; 61(2):60-5 [PubMed] Related Publications
Subcellular Localization of Proteins Responding to Mitoxantrone-Induced DNA Damage in Leukaemic Cells.
Folia Biol (Praha). 2015; 61(2):60-5 [PubMed] Related Publications
The aim of the present study was to investigate the subcellular localization of proteins participating in the double-strand break response pathway - p53, Mdm2, p21 and Chk2. MOLT-4 cells were pre-treated with mitoxantrone in concentrations 1 nmol/l and 5 nmol/l. The trypan blue technique was used to determine cell viability and proliferation. Western blotting was used to evaluate changes in p53, Mdm2 and Chk2 protein expression and sandwich ELISA was used to evaluate changes in the p21 protein amount. After 1 nmol/l mitoxantrone cells did not die, but their ability to proliferate was decreased. The p53 protein was activated and phosphorylated at serines 15 and 392 and accumulated in the nucleus after 24 and 48 h. The Mdm2 protein was present in the cytoplasm with its maximal level after 8 and 16 h. The p21 protein was detected in the nucleus after 24 and 48 h. Increased levels of phosphorylated Chk2 at threonine 68 were observed in the cytoplasmic fraction after 24 and 48 h of mitoxantrone treatment. We used mitoxantrone as an inducer of double-strand breaks to bring new data about the subcellular distribution of proteins responding to DNA damage. In MOLT-4 cells, the p53 protein was activated. p53 was phosphorylated at serines 15 and 392 and accumulated in the nucleus. The Mdm2 protein was activated in advance to p53 and occurred in the cytoplasm. The p21 protein was present in the nucleus. Chk2 kinase was activated by the phosphorylation at threonine 68 and we observed increased levels of this protein in the cytoplasmic fraction.
Sakai T, Masaki Y, Otsuki N, et al.
Prospective clinical study of R-CMD therapy for indolent B cell lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma from the Hokuriku Hematology Oncology Study Group.
Med Oncol. 2015; 32(9):232 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Prospective clinical study of R-CMD therapy for indolent B cell lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma from the Hokuriku Hematology Oncology Study Group.
Med Oncol. 2015; 32(9):232 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Standardized treatments for indolent B cell lymphoma primarily consisting of follicular lymphoma (FL) and for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) have yet to be established. Here the Hokuriku Hematology Oncology Study Group conducted a multicenter prospective study to investigate the efficacy and safety of a combination regimen of rituximab, cladribine, mitoxantrone, and dexamethasone (R-CMD) in indolent B cell lymphoma and MCL. A total of 33 CD20-positive patients who received care between January 2008 and August 2011 were investigated. These patients' illnesses were FL (n = 21), nodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma (NMZB, n = 3), MCL (n = 3), splenic marginal zone B cell lymphoma (n = 2), hairy cell leukemia (n = 1), Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia (WM, n = 1), and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL, n = 2). Patients received four 21-day cycles of rituximab 375 mg/m(2) (day 1), cladribine 0.10 mg/kg (days 1-3), mitoxantrone 8 mg/m(2) (day 1), and dexamethasone 8 mg/body (days 1-3), with four additional rituximab doses at 4-week intervals. Of the 33 patients, 26 achieved complete response/unconfirmed complete response, and six achieved a partial response (4 with FL, 1 with NMZB, 1 with WM). One had progressive disease (FL), and four relapsed after remission (1 with FL, 2 with MCL, 1 with LPL). R-CMD therapy was relatively convenient and effective in indolent B cell lymphoma and MCL. Nonetheless, to suppress the number and function of both B cells and T cells, comprehensive infection prevention and follow-up are necessary in the future.
Hiľovská L, Jendželovský R, Jendželovská Z, et al.
Downregulation of BCRP and anti-apoptotic proteins by proadifen (SKF-525A) is responsible for the enhanced mitoxantrone accumulation and toxicity in mitoxantrone-resistant human promyelocytic leukemia cells.
Int J Oncol. 2015; 47(4):1572-84 [PubMed] Related Publications
Downregulation of BCRP and anti-apoptotic proteins by proadifen (SKF-525A) is responsible for the enhanced mitoxantrone accumulation and toxicity in mitoxantrone-resistant human promyelocytic leukemia cells.
Int J Oncol. 2015; 47(4):1572-84 [PubMed] Related Publications
Multidrug resistance caused by the overexpression of ABC transporter proteins in cancer cells remains a major obstacle limiting chemotherapy efficacy. Drugs inhibiting these transporters have been shown to increase the anti-proliferative properties of chemotherapeutics. As we previously described, proadifen, a P450 monooxygenase inhibitor, might also be able to inhibit some ABC transporters, including breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). Because mitoxantrone (MTX) is a strong BCRP substrate and is often used in the treatment of leukemia, we investigated the effect of 24 h proadifen pre-treatment on the cytotoxicity of MTX in leukemic cell lines that are sensitive to MTX (HL-60) and MTX-resistant ABCG2-overexpressing subclone (cBCRP). We show for the first time that proadifen is able to enhance the cytotoxic properties of MTX in cBCRP cells, particularly through the inhibition of BCRP expression and activity. This proadifen-MTX synergism was also mediated by the inhibition of various cellular proteins engaged in apoptosis, including Mc-1, Bcl-xL, survivin and activation of procaspase-3. Proadifen also decreased the expression of γH2AX, which is involved in the recruitment of reparation proteins. Moreover, the inhibition of DNA damage repair proteins Ku86 and B23 after proadifen treatment indicate a possible role of proadifen in DNA repair blockage, thus suppressing the reparation rate of MTX-induced DSBs.
Shaul P, Steinbuch KB, Blacher E, et al.
Exploring the Effects of Glycosylation and Etherification of the Side Chains of the Anticancer Drug Mitoxantrone.
ChemMedChem. 2015; 10(9):1528-38 [PubMed] Related Publications
Exploring the Effects of Glycosylation and Etherification of the Side Chains of the Anticancer Drug Mitoxantrone.
ChemMedChem. 2015; 10(9):1528-38 [PubMed] Related Publications
Herein we report the synthesis and biological evaluation of symmetric and asymmetric analogues of the DNA intercalating drug mitoxantrone (MTX) in which the side chains of the parent drug were modified through glycosylation or methyl etherification. Several analogues with glycosylated side chains exhibited higher DNA affinity than the parent MTX. The most potent in vitro cytotoxicity was observed for MTX analogue 8 (1,4-dimethoxy-5,8-bis[2-(2-methoxyethylamino)ethylamino]anthracene-9,10-dione) with methoxy ether containing side chains. Treatment of melanoma-bearing mice with MTX or analogue 8 decreased the intraperitoneal tumor burden relative to untreated mice; the effect of 8 was less pronounced than that of MTX. In vitro metabolism assays of MTX with rabbit liver S9 fraction gave rise to several metabolites; almost no metabolites were detected for MTX analogue 8. The results presented indicate that derivatization of the MTX side chain primary hydroxy groups may result in a significant improvement in DNA affinity and lower susceptibility to the formation of potentially toxic metabolites.
Cordeiro Pedrosa LR, van Tellingen O, Soullié T, et al.
Plasma membrane targeting by short chain sphingolipids inserted in liposomes improves anti-tumor activity of mitoxantrone in an orthotopic breast carcinoma xenograft model.
Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015; 94:207-19 [PubMed] Related Publications
Plasma membrane targeting by short chain sphingolipids inserted in liposomes improves anti-tumor activity of mitoxantrone in an orthotopic breast carcinoma xenograft model.
Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015; 94:207-19 [PubMed] Related Publications
Mitoxantrone (MTO) is clinically used for treatment of various types of cancers providing an alternative for similarly active, but more toxic chemotherapeutic drugs such as anthracyclines. To further decrease its toxicity MTO was encapsulated into liposomes. Although liposomal drugs can accumulate in target tumor tissue, they still face the plasma membrane barrier for effective intracellular delivery. Aiming to improve MTO tumor cell availability, we used short chain lipids to target and modulate the tumor cell membrane, promoting MTO plasma membrane traversal. MTO was encapsulated in liposomes containing the short chain sphingolipid (SCS), C8-Glucosylceramide (C8-GluCer) or C8-Galactosylceramide (C8-GalCer) in their bilayer. These new SCS-liposomes containing MTO (SCS-MTOL) were tested in vivo for tolerability, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, tumor drug delivery by intravital microscopy and efficacy, and compared to standard MTO liposomes (MTOL) and free MTO. Liposomal encapsulation decreased MTO toxicity and allowed administration of higher drug doses. SCS-MTOL displayed increased clearance and lower skin accumulation compared to standard MTOL. Intratumoral liposomal drug delivery was heterogeneous and rather limited in hypoxic tumor areas, yet SCS-MTOL improved intracellular drug uptake in comparison with MTOL. The increased MTO availability correlated well with the improved antitumor activity of SCS-MTOL in a MDAMB-231 breast carcinoma model. Multiple dosing of liposomal MTO strongly delayed tumor growth compared to free MTO and prolonged mouse survival, whereas among the liposomal MTO treatments, C8-GluCer-MTOL was most effective. Targeting plasma membranes with SCS improved MTO tumor availability and thereby therapeutic activity and represents a promising approach to improve MTO-based chemotherapy.
Long X, Yu Y, Perlaky L, et al.
Stromal CYR61 Confers Resistance to Mitoxantrone via Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Activation in Human Acute Myeloid Leukaemia.
Br J Haematol. 2015; 170(5):704-18 [PubMed] Related Publications
Stromal CYR61 Confers Resistance to Mitoxantrone via Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Activation in Human Acute Myeloid Leukaemia.
Br J Haematol. 2015; 170(5):704-18 [PubMed] Related Publications
Approximately 50% of children with acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) relapse, despite aggressive chemotherapy. The bone marrow stromal environment protects leukaemia cells from chemotherapy (i.e., stroma-induced chemoresistance), eventually leading to recurrence. Our goal is to delineate the mechanisms underlying stroma-mediated chemoresistance in AML. We used two human bone marrow stromal cell lines, HS-5 and HS-27A, which are equally effective in protecting AML cells from chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in AML-stromal co-cultures. We found that CYR61 was highly expressed by stromal cells, and was upregulated in AML cells by both stromal cell lines. CYR61 is a secreted matricellular protein and is associated with cell-intrinsic chemoresistance in other malignancies. Here, we show that blocking stromal CYR61 activity, by neutralization or RNAi, increased mitoxantrone-induced apoptosis in AML cells in AML-stromal co-cultures, providing functional evidence for its role in stroma-mediated chemoresistance. Further, we found that spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) mediates CYR61 signalling. Exposure to stroma increased SYK expression and activation in AML cells, and this increase required CYR61. SYK inhibition reduced stroma-dependent mitoxantrone resistance in the presence of CYR61, but not in its absence. Therefore, SYK is downstream of CYR61 and contributes to CYR61-mediated mitoxantrone resistance. The CYR61-SYK pathway represents a potential target for reducing stroma-induced chemoresistance.
Green AK, Corty RW, Wood WA, et al.
Comparative effectiveness of mitoxantrone plus prednisone versus prednisone alone in metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer after docetaxel failure.
Oncologist. 2015; 20(5):516-22 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Comparative effectiveness of mitoxantrone plus prednisone versus prednisone alone in metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer after docetaxel failure.
Oncologist. 2015; 20(5):516-22 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
BACKGROUND: Mitoxantrone was approved for use in metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) based on pain palliation without observed survival benefit in a small phase III trial in 1996. To re-evaluate for possible survival benefits in a larger contemporary sample and to demonstrate analytic uses of the newly available Project Data Sphere online resource, we used data from control arms of completed clinical trials to compare survival and toxicity among patients with postdocetaxel mCRPC treated with mitoxantrone and prednisone.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Control arm data from two phase III randomized control trials, SUN 1120 and TROPIC, were used to examine the efficacy of mitoxantrone plus prednisone (n = 305) versus prednisone alone (n = 257) among patients with postdocetaxel mCRPC. Propensity score matching was used to balance patient characteristics between the separate trials, conditioned on age and key prognostic variables of survival. The primary outcome was overall survival. Secondary endpoints evaluated safety.
RESULTS: Median survival was similar among patients receiving mitoxantrone plus prednisone versus prednisone alone (385 days vs. 336 days; deceleration factor = 0.04; 95% confidence interval: -0.12 to 0.22). Prevalence of several any-grade toxicity, including fatigue, back pain, and peripheral neuropathy, was increased among patients who received mitoxantrone.
CONCLUSION: There was no significant survival benefit for mitoxantrone plus prednisone over prednisone alone among men with mCRPC after docetaxel therapy. This finding is consistent with prior studies showing no survival advantage with mitoxantrone in the predocetaxel setting. Furthermore, our data suggest that mitoxantrone may be associated with increased toxicity compared with prednisone alone.
PATIENTS AND METHODS: Control arm data from two phase III randomized control trials, SUN 1120 and TROPIC, were used to examine the efficacy of mitoxantrone plus prednisone (n = 305) versus prednisone alone (n = 257) among patients with postdocetaxel mCRPC. Propensity score matching was used to balance patient characteristics between the separate trials, conditioned on age and key prognostic variables of survival. The primary outcome was overall survival. Secondary endpoints evaluated safety.
RESULTS: Median survival was similar among patients receiving mitoxantrone plus prednisone versus prednisone alone (385 days vs. 336 days; deceleration factor = 0.04; 95% confidence interval: -0.12 to 0.22). Prevalence of several any-grade toxicity, including fatigue, back pain, and peripheral neuropathy, was increased among patients who received mitoxantrone.
CONCLUSION: There was no significant survival benefit for mitoxantrone plus prednisone over prednisone alone among men with mCRPC after docetaxel therapy. This finding is consistent with prior studies showing no survival advantage with mitoxantrone in the predocetaxel setting. Furthermore, our data suggest that mitoxantrone may be associated with increased toxicity compared with prednisone alone.
Jaime-Perez JC, Colunga-Pedraza PR, Gutiérrez-Aguirre CH, et al.
Efficacy of mitoxantrone as frontline anthracycline during induction therapy in adults with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a single-center experience.
Leuk Lymphoma. 2015; 56(9):2524-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Efficacy of mitoxantrone as frontline anthracycline during induction therapy in adults with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a single-center experience.
Leuk Lymphoma. 2015; 56(9):2524-8 [PubMed] Related Publications
Remission induction regimens for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in adults induce complete remission (CR) in 60-90% and cure in 20-40%. A cohort study of newly diagnosed patients with ALL treated with mitoxantrone versus doxorubicin was conducted from 2005 to 2013. The primary endpoint was the proportion of CR. Eighty-five patients were included. Fifty-three received induction with doxorubicin and 32 with mitoxantrone. Median follow-up in the cohort was 40.2 months (range 2-95). Twenty-nine patients (90.6%) achieved CR in the mitoxantrone arm compared with 37 (69.8%) in the doxorubicin group (p = 0.032). There was no difference in death or relapse rate (p = 0.095 and 0.075), hematological recovery (p = 0.654), incidence of adverse events (p = 0.6), in-hospital days during induction (p = 0.456) or overall survival (p = 0.105). Induction toxicities were comparable. Mitoxantrone can be safely and effectively used as a frontline anthracycline in adults newly diagnosed with ALL.
Guerriero E, Sorice A, Capone F, et al.
Vitamin C effect on mitoxantrone-induced cytotoxicity in human breast cancer cell lines.
PLoS One. 2014; 9(12):e115287 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Vitamin C effect on mitoxantrone-induced cytotoxicity in human breast cancer cell lines.
PLoS One. 2014; 9(12):e115287 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
In recent years the use of natural dietary antioxidants to minimize the cytotoxicity and the damage induced in normal tissues by antitumor agents is gaining consideration. In literature, it is reported that vitamin C exhibits some degree of antineoplastic activity whereas Mitoxantrone (MTZ) is a synthetic anti-cancer drug with significant clinical effectiveness in the treatment of human malignancies but with severe side effects. Therefore, we have investigated the effect of vitamin C alone or combined with MTZ on MDA-MB231 and MCF7 human breast cancer cell lines to analyze their dose-effect on the tumor cellular growth, cellular death, cell cycle and cell signaling. Our results have evidenced that there is a dose-dependence on the inhibition of the breast carcinoma cell lines, MCF7 and MDA-MB231, treated with vitamin C and MTZ. Moreover, their combination induces: i) a cytotoxic effect by apoptotic death, ii) a mild G2/M elongation and iii) H2AX and mild PI3K activation. Hence, the formulation of vitamin C with MTZ induces a higher cytotoxicity level on tumor cells compared to a disjointed treatment. We have also found that the vitamin C enhances the MTZ effect allowing the utilization of lower chemotherapic concentrations in comparison to the single treatments.
Alpay K, Farshchian M, Tuomela J, et al.
Inhibition of c-Abl kinase activity renders cancer cells highly sensitive to mitoxantrone.
PLoS One. 2014; 9(8):e105526 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Inhibition of c-Abl kinase activity renders cancer cells highly sensitive to mitoxantrone.
PLoS One. 2014; 9(8):e105526 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Although c-Abl has increasingly emerged as a key player in the DNA damage response, its role in this context is far from clear. We studied the effect of inhibition of c-Abl kinase activity by imatinib with chemotherapy drugs and found a striking difference in cell survival after combined mitoxantrone (MX) and imatinib treatment compared to a panel of other chemotherapy drugs. The combinatory treatment induced apoptosis in HeLa cells and other cancer cell lines but not in primary fibroblasts. The difference in MX and doxorubicin was related to significant augmentation of DNA damage. Transcriptionally active p53 accumulated in cells in which human papillomavirus E6 normally degrades p53. The combination treatment resulted in caspase activation and apoptosis, but this effect did not depend on either p53 or p73 activity. Despite increased p53 activity, the cells arrested in G2 phase became defective in this checkpoint, allowing cell cycle progression. The effect after MX treatment depended partially on c-Abl: Short interfering RNA knockdown of c-Abl rendered HeLa cells less sensitive to MX. The effect of imatinib was decreased by c-Abl siRNA suggesting a role for catalytically inactive c-Abl in the death cascade. These findings indicate that MX has a unique cytotoxic effect when the kinase activity of c-Abl is inhibited. The treatment results in increased DNA damage and c-Abl-dependent apoptosis, which may offer new possibilities for potentiation of cancer chemotherapy.
Zagotto G, Gianoncelli A, Sissi C, et al.
Novel ametantrone-amsacrine related hybrids as topoisomerase IIβ poisons and cytotoxic agents.
Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2014; 347(10):728-37 [PubMed] Related Publications
Novel ametantrone-amsacrine related hybrids as topoisomerase IIβ poisons and cytotoxic agents.
Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2014; 347(10):728-37 [PubMed] Related Publications
The precise definition of the structural requirements for effective topoisomerase II poisoning by drug molecules is still an elusive issue. In the attempt to better define a pharmacophoric pattern, we prepared several conjugates combining the chemical features of two well-known topoisomerase II poisons, amsacrine and ametantrone. Indeed, an appropriate fusion geometry, which entails the anthracenedione moiety of ametantrone appropriately connected to the methanesulfonamidoaniline side chain of amsacrine, elicits DNA-intercalating properties, the capacity to inhibit the human topoisomerase IIβ isoform, and cytotoxic activity resembling that of the parent compounds. In addition, the properties of the lateral groups linked to the anthracenedione group play an important role in modulating DNA binding and cell cytotoxicity. Among the compounds tested, 10, 11, and 19 appear to be promising for further development.
Yang J, Shi Y, Li C, et al.
Phase I clinical trial of pegylated liposomal mitoxantrone plm60-s: pharmacokinetics, toxicity and preliminary efficacy.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014; 74(3):637-46 [PubMed] Related Publications
Phase I clinical trial of pegylated liposomal mitoxantrone plm60-s: pharmacokinetics, toxicity and preliminary efficacy.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014; 74(3):637-46 [PubMed] Related Publications
PURPOSE: Plm60-s is a pegylated liposomal mitoxantrone formulation, in which mitoxantrone was loaded into small unilamellar vesicles (~60 nm) made from solid lipid membrane. This two-arm, dose-escalating phase I study was designed to determine safety and pharmacokinetics of plm60-s, and to compare with those of conventional mitoxantrone injection (c-MI).
METHODS: Patients received an intravenous infusion of plm60-s at 6, 10, 12, 14, 16 and 18 mg/m(2) every 4 weeks. Three or 6 patients were in each group of dose level. If more than one third patients of a group experienced dose-limiting toxicity, dose climbing will stop. The control group of 3 patients received c-MI at 10 mg/m(2) every 28 days. Samples for pharmacokinetic studies were collected. The analysis of the safety and tolerability was done according to the record and laboratory examination, etc.
RESULTS: Twenty patients were enrolled. One grade 3 leukocytopenia occurred in plm60-s groups. Plm60-s was safer than c-MI at the same dose of 10 mg/m(2). Two complete responses and one partial response occurred in plm60-s group. In plasma, plm60-s exhibited sustained release of the content, resulting in the reduced peak concentrations and enhanced AUC of released MIT. Total mitoxantrone was linearly cleared, and mitoxantrone was predominantly in the liposomal encapsulation form. Repeated administration of plm60-s did not affect the clearance kinetics.
CONCLUSIONS: At a dose of up to 18 mg/m(2), plm60-s could be well tolerated and potential efficacy could be observed. The pharmacokinetic profile of plm60-s was remarkably altered. Further investigations are in progression.
METHODS: Patients received an intravenous infusion of plm60-s at 6, 10, 12, 14, 16 and 18 mg/m(2) every 4 weeks. Three or 6 patients were in each group of dose level. If more than one third patients of a group experienced dose-limiting toxicity, dose climbing will stop. The control group of 3 patients received c-MI at 10 mg/m(2) every 28 days. Samples for pharmacokinetic studies were collected. The analysis of the safety and tolerability was done according to the record and laboratory examination, etc.
RESULTS: Twenty patients were enrolled. One grade 3 leukocytopenia occurred in plm60-s groups. Plm60-s was safer than c-MI at the same dose of 10 mg/m(2). Two complete responses and one partial response occurred in plm60-s group. In plasma, plm60-s exhibited sustained release of the content, resulting in the reduced peak concentrations and enhanced AUC of released MIT. Total mitoxantrone was linearly cleared, and mitoxantrone was predominantly in the liposomal encapsulation form. Repeated administration of plm60-s did not affect the clearance kinetics.
CONCLUSIONS: At a dose of up to 18 mg/m(2), plm60-s could be well tolerated and potential efficacy could be observed. The pharmacokinetic profile of plm60-s was remarkably altered. Further investigations are in progression.
Pavese JM, Bergan RC
Circulating tumor cells exhibit a biologically aggressive cancer phenotype accompanied by selective resistance to chemotherapy.
Cancer Lett. 2014; 352(2):179-86 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Circulating tumor cells exhibit a biologically aggressive cancer phenotype accompanied by selective resistance to chemotherapy.
Cancer Lett. 2014; 352(2):179-86 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
With prostate cancer (PCa), circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) portend a poor clinical prognosis. Their unknown biology precludes rational therapeutic design. We demonstrate that CTC and DTC cell lines, established from mice bearing human PCa orthotopic implants, exhibit increased cellular invasion in vitro, increased metastasis in mice, and express increased epithelial to mesenchymal transition biomarkers. Further, they are selectively resistant to growth inhibition by mitoxantrone-like agents. These findings demonstrate that CTC formation is accompanied by phenotypic progression without obligate reversion. Their increased metastatic potential, selective therapeutic resistance, and differential expression of potential therapeutic targets provide a rational basis to test further interventions.
Ellis R, Brown S, Boggild M
Therapy-related acute leukaemia with mitoxantrone: four years on, what is the risk and can it be limited?
Mult Scler. 2015; 21(5):642-5 [PubMed] Related Publications
Therapy-related acute leukaemia with mitoxantrone: four years on, what is the risk and can it be limited?
Mult Scler. 2015; 21(5):642-5 [PubMed] Related Publications
Therapy-related acute leukaemia (TRAL) is a significant concern, when considering treatment with mitoxantrone for multiple sclerosis (MS). We re-evaluated the literature, identifying all case reports and series of > 50 patients reporting TRAL cases in MS. TRAL was diagnosed in 0.73% of the 12,896 patients identified. Median onset was 22 months following treatment. We calculated a number needed to harm of 137.5 exposed patients, significantly higher than our 2008 analysis. We found that 82.8% of patients were exposed to > 60 mg/m(2) with a relative risk of 1.85 (p = 0.018) compared to < 60 mg/m(2), strongly suggesting a relationship to dose. MS treatment regimens which limit the mitoxantrone dose to < 60 mg/m(2) reduce the risk of TRAL.
Zinzani PL, Pellegrini C, Broccoli A, et al.
Fludarabine-Mitoxantrone-Rituximab regimen in untreated indolent non-follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: experience on 143 patients.
Hematol Oncol. 2015; 33(3):141-6 [PubMed] Related Publications
Fludarabine-Mitoxantrone-Rituximab regimen in untreated indolent non-follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: experience on 143 patients.
Hematol Oncol. 2015; 33(3):141-6 [PubMed] Related Publications
Indolent non-follicular lymphomas (inFLs) are generally regarded as incurable, apart from extranodal mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue lymphomas, which can be partially cured by surgery, local radiotherapy, or antibiotic treatment. The aim of the present study was to test the degree of effectiveness and the safety of the regimen containing fludarabine, mitoxantrone, and rituximab (FMR) in inFL patients considering all the different entities belonging to this group. An observational retrospective study was conducted on 143 inFL patients providing that their first chemoimmunotherapy performed was FMR regimen and diagnosis from September 2000 to March 2011. There were 32 small lymphocytic lymphomas and 111 marginal zone lymphomas. At the end of treatment, overall response rate was 96.5% with 88% of complete responses (CR) and 8.5% of partial responses. With a median follow-up of 48 months, 10 out of 125 (8%) CR patients had disease relapse, yielding an estimated 9-year disease-free survival (DFS) of 74.9% and an estimated 10-year overall survival of 92.8%. The estimated 9-year progression free survival was 70.5%. The 10 relapsed patients showed lymphoma recurrence within 52 months: after this time, the DFS curve presented a plateau configuration. Only two (1.4%) patients developed a secondary hematological neoplasia. This study showed promising findings for the use of a fludarabine-based regimen in combination with rituximab in the front-line treatment of symptomatic inFL with a noteworthy high percentage of CR associated to an interesting long-term DFS and favorable acute and long-term safety profile.
Toh TB, Lee DK, Hou W, et al.
Nanodiamond-mitoxantrone complexes enhance drug retention in chemoresistant breast cancer cells.
Mol Pharm. 2014; 11(8):2683-91 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Nanodiamond-mitoxantrone complexes enhance drug retention in chemoresistant breast cancer cells.
Mol Pharm. 2014; 11(8):2683-91 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Chemoresistance is a prevalent issue that accounts for the vast majority of treatment failure outcomes in metastatic cancer. Among the mechanisms of resistance that markedly decrease treatment efficacy, the efflux of drug compounds by ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter proteins can impair adequate drug retention by cancer cells required for therapeutic cytotoxic activity. Of note, ABC transporters are capable of effluxing several classes of drugs that are clinical standards, including the anthracyclines such as doxorubicin, as well as anthracenediones such as mitoxantrone. To address this challenge, a spectrum of nanomaterials has been evaluated for improved drug retention and enhanced efficacy. Nanodiamonds (NDs) are emerging as a promising nanomaterial platform because they integrate several important properties into a single agent. These include a uniquely faceted truncated octahedral architecture that enables potent drug binding and dispersibility in water, scalably processed ND particles with uniform diameters of approximately 5 nm, and a demonstrated ability to improve drug tolerance while delaying tumor growth in multiple preclinical models, among others. This work describes a ND-mitoxantrone complex that can be rapidly synthesized and mediates marked improvements in drug efficacy. Comprehensive complex characterization reveals a complex with favorable drug delivery properties that is capable of improving drug retention and efficacy in an MDA-MB-231-luc-D3H2LN (MDA-MB-231) triple negative breast cancer cell line that was lentivirally transduced for resistance against mitoxantrone. Findings from this study support the further evaluation of ND-MTX in preclinical dose escalation and safety studies toward potentially clinical validation.
Workenhe ST, Pol JG, Lichty BD, et al.
Combining oncolytic HSV-1 with immunogenic cell death-inducing drug mitoxantrone breaks cancer immune tolerance and improves therapeutic efficacy.
Cancer Immunol Res. 2013; 1(5):309-19 [PubMed] Related Publications
Combining oncolytic HSV-1 with immunogenic cell death-inducing drug mitoxantrone breaks cancer immune tolerance and improves therapeutic efficacy.
Cancer Immunol Res. 2013; 1(5):309-19 [PubMed] Related Publications
Although antitumor activity of herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) ICP0 null oncolytic vectors has been validated in murine breast cancer models, oncolytic virus treatment alone is insufficient to break immune tolerance. Thus, we investigated enhancing efficacy through combination therapy with the immunogenic cell death-inducing chemotherapeutic drug, mitoxantrone. Despite a lack of enhanced cytotoxicity in vitro, HSV-1 ICP0 null oncolytic virus KM100 with 5 μmol/L mitoxantrone provided significant survival benefit to BALB/c mice bearing Her2/neu TUBO-derived tumors. This protection was mediated by increased intratumoral infiltration of neutrophils and tumor antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells. Depletion studies verified that CD8-, CD4-, and Ly6G-expressing cells are essential for enhanced efficacy of the combination therapy. Moreover, the addition of mitoxantrone to KM100 oncolytic virus treatment broke immune tolerance in BALB-neuT mice bearing TUBO-derived tumors. This study suggests that oncolytic viruses in combination with immunogenic cell death-inducing chemotherapeutics enhance the immunogenicity of the tumor-associated antigens, breaking immunologic tolerance established toward these antigens.
Horgan AM, Seruga B, Pond GR, et al.
Tolerability and efficacy of docetaxel in older men with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) in the TAX 327 trial.
J Geriatr Oncol. 2014; 5(2):119-26 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Tolerability and efficacy of docetaxel in older men with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) in the TAX 327 trial.
J Geriatr Oncol. 2014; 5(2):119-26 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
OBJECTIVE: Prostate cancer is a disease of older men. Weekly docetaxel (DPq1w) is often favored over the standard three-weekly regimen (DPq3w) due to concerns about safety and tolerability in this population.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Two subgroup analyses of TAX 327 were conducted. Among patients receiving DPq3w, tolerability and efficacy were compared between three age groups: <65, 65-74 and ≥75 years. For men ≥75 years, these outcomes were compared between DPq3w, DPq1w, and mitoxantrone (MP) arms. Tolerability outcomes included dose delivery, grade 3/4 adverse events and quality of life. Efficacy outcomes included overall survival and tumor response.
RESULTS: Of 1006 men with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) in the trial, 335 received DPq3w. Among these, 20% were age ≥75 years. For DPq3w, there were non-significant associations of worse tolerability and efficacy with advancing age. Twenty-eight percent of men age ≥75 years had an objective pain response, compared to 38% and 34% of patients 65-74 and <65 years, respectively. There were no significant differences in prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response (43-48%, p = 0.74) or measurable tumor response (7-17%, p = 0.30) according to age. Among men ≥75 years, DPq3w resulted in more dose reductions than DPq1w (22% versus 8%, p = 0.007), but tolerability was otherwise comparable. Both were associated with more favorable efficacy than mitoxantrone.
CONCLUSIONS: Tolerability and efficacy of DPq3w appear less favorable with advancing age. Compared to DPq1w, DPq3w is associated with better survival outcomes, but similar tolerability, and remains the standard first-line chemotherapy option in mCRPC. Toxicity is substantial, therefore careful patient selection, close monitoring and early management of toxicities is advised.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Two subgroup analyses of TAX 327 were conducted. Among patients receiving DPq3w, tolerability and efficacy were compared between three age groups: <65, 65-74 and ≥75 years. For men ≥75 years, these outcomes were compared between DPq3w, DPq1w, and mitoxantrone (MP) arms. Tolerability outcomes included dose delivery, grade 3/4 adverse events and quality of life. Efficacy outcomes included overall survival and tumor response.
RESULTS: Of 1006 men with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) in the trial, 335 received DPq3w. Among these, 20% were age ≥75 years. For DPq3w, there were non-significant associations of worse tolerability and efficacy with advancing age. Twenty-eight percent of men age ≥75 years had an objective pain response, compared to 38% and 34% of patients 65-74 and <65 years, respectively. There were no significant differences in prostate-specific antigen (PSA) response (43-48%, p = 0.74) or measurable tumor response (7-17%, p = 0.30) according to age. Among men ≥75 years, DPq3w resulted in more dose reductions than DPq1w (22% versus 8%, p = 0.007), but tolerability was otherwise comparable. Both were associated with more favorable efficacy than mitoxantrone.
CONCLUSIONS: Tolerability and efficacy of DPq3w appear less favorable with advancing age. Compared to DPq1w, DPq3w is associated with better survival outcomes, but similar tolerability, and remains the standard first-line chemotherapy option in mCRPC. Toxicity is substantial, therefore careful patient selection, close monitoring and early management of toxicities is advised.
Jaglal MV, Duong VH, Bello CM, et al.
Cladribine, cytarabine, filgrastim, and mitoxantrone (CLAG-M) compared to standard induction in acute myeloid leukemia from myelodysplastic syndrome after azanucleoside failure.
Leuk Res. 2014; 38(4):443-6 [PubMed] Related Publications
Cladribine, cytarabine, filgrastim, and mitoxantrone (CLAG-M) compared to standard induction in acute myeloid leukemia from myelodysplastic syndrome after azanucleoside failure.
Leuk Res. 2014; 38(4):443-6 [PubMed] Related Publications
For patients with acute myeloid leukemia from antecedent myelodysplastic syndrome particularly after azanucleoside treatment failure, outcome is poor. Here, we conducted a case-control study in these patients to compare the efficacy of CLAG-M induction (28 patients) versus standard 3+7 induction chemotherapy (24 patients). Response rates (P=0.014) and median overall survival (P=0.025) were 64% and 202 days (95% CI 37-367 days) versus 29% and 86 days (95% CI 36-136) in the CLAG-M and 3+7 cohorts, respectively. Median overall survival was 202 (95% CI 37-367 days) versus 86 days (95% CI 36-136) (P=0.025), respectively. CLAG-M has encouraging activity in this patient group.
Patel SA, Coulter DW, Grovas AC, et al.
Cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone followed by second allogeneic transplant for the treatment of children with refractory juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia.
J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014; 36(6):491-4 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Cytosine arabinoside and mitoxantrone followed by second allogeneic transplant for the treatment of children with refractory juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia.
J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014; 36(6):491-4 [PubMed] Free Access to Full Article Related Publications
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) remains the only curative option for most patients with juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML). However, persistent disease and relapse rates after transplant range from 26% to 58%. We report the successful use of second HSCT after preparation with mitoxantrone and cytosine arabinoside (Ara-C) for patients with refractory or recurrent disease. Between 1993 and 2006, 5 children who underwent HSCT at our institution as initial therapy for JMML had persistent disease or relapsed. Pre-HSCT conditioning varied and donors were either HLA-matched siblings (n=2) or matched unrelated donors (n=3). After initial HSCT, they subsequently received high-dose Ara-C (3 g/m IV) every 12 hours on days -8 through -3 and mitoxantrone (10 mg/m/d IV) on days -8, -7, -6 followed by second HSCT from their original donors. All 5 patients are alive at 88, 179, 199, 234, and 246 months with no evidence of JMML, no significant toxicity, and 100% donor chimera as determined by PCR short-tandem repeat analysis. Our experience supports second transplant utilizing high-dose Ara-C and mitoxantrone in children with JMML who do not respond or relapse after first transplant.
Grandhi TS, Potta T, Taylor DJ, et al.
Sensitizing cancer cells to TRAIL-induced death by micellar delivery of mitoxantrone.
Nanomedicine (Lond). 2014; 9(12):1775-88 [PubMed] Related Publications
Sensitizing cancer cells to TRAIL-induced death by micellar delivery of mitoxantrone.
Nanomedicine (Lond). 2014; 9(12):1775-88 [PubMed] Related Publications
TNFα-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces death selectively in cancer cells. However, subpopulations of cancer cells are either resistant to or can develop resistance to TRAIL-induced death. As a result, strategies that overcome this resistance are currently under investigation. We have recently identified several US FDA-approved drugs with TRAIL-sensitization activity against prostate, breast and pancreatic cancer cells. Mitoxantrone, a previously unknown TRAIL sensitizer identified in the screen, was successfully encapsulated in methoxy-, amine- and carboxyl-terminated PEG-DSPE micelles in order to facilitate delivery of the drug to cancer cells. All three micelle types were extensively characterized for their physicochemical properties and evaluated for their ability to sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL-induced death. Our results indicate that micelle-encapsulated mitoxantrone can be advantageously employed in synergistic treatments with TRAIL, leading to a biocompatible delivery system and amplified cell killing activity for combination chemotherapeutic cancer treatments.


 Apoptosis
Apoptosis